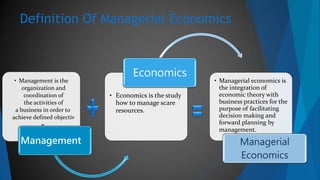
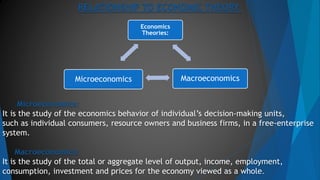
Managerial economics refers to the application of economic theory and tools of decision-making to business management. It helps integrate economics with business practices to facilitate optimal decision-making and planning. Managerial economics draws from microeconomics, macroeconomics, mathematical economics, econometrics, and other business disciplines. It is relevant for production planning, pricing decisions, capacity expansion planning, and human resource management. Managerial economics provides frameworks to analyze demand, costs, and guide profit-oriented decision-making.