Managerial_Economics.docx
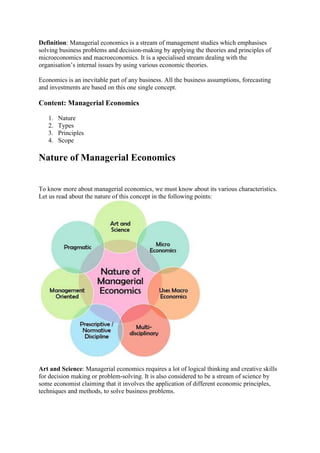
- 1. Definition: Managerial economics is a stream of management studies which emphasises solving business problems and decision-making by applying the theories and principles of microeconomics and macroeconomics. It is a specialised stream dealing with the organisation’s internal issues by using various economic theories. Economics is an inevitable part of any business. All the business assumptions, forecasting and investments are based on this one single concept. Content: Managerial Economics 1. Nature 2. Types 3. Principles 4. Scope Nature of Managerial Economics To know more about managerial economics, we must know about its various characteristics. Let us read about the nature of this concept in the following points: Art and Science: Managerial economics requires a lot of logical thinking and creative skills for decision making or problem-solving. It is also considered to be a stream of science by some economist claiming that it involves the application of different economic principles, techniques and methods, to solve business problems.
- 2. Micro Economics: In managerial economics, managers generally deal with the problems related to a particular organisation instead of the whole economy. Therefore it is considered to be a part of microeconomics. Uses Macro Economics: A business functions in an external environment, i.e. it serves the market, which is a part of the economy as a whole. Therefore, it is essential for managers to analyse the different factors of macroeconomics such as market conditions, economic reforms, government policies, etc. and their impact on the organisation. Multi-disciplinary: It uses many tools and principles belonging to various disciplines such as accounting, finance, statistics, mathematics, production, operation research, human resource, marketing, etc. Prescriptive / Normative Discipline: It aims at goal achievement and deals with practical situations or problems by implementing corrective measures. Management Oriented: It acts as a tool in the hands of managers to deal with business-related problems and uncertainties appropriately. It also provides for goal establishment, policy formulation and effective decision making. Pragmatic: It is a practical and logical approach towards the day to day business problems. Types of Managerial Economics All managers take the concept of managerial economics differently. Some may be more focused on customer’s satisfaction while others may prioritize efficient production. The various approach to managerial economics can be seen in detail below: Liberal Managerialism A market is a democratic place where people are liberal to make their choices and decisions. The organisation and the managers have to function according to the customer’s demand and market trend; else it may lead to business failures. Normative Managerialism
- 3. The normative view of managerial economics states that administrative decisions are based on real-life experiences and practices. They have a practical approach to demand analysis, forecasting, cost management, product design and promotion, recruitment, etc. Radical Managerialism Managers must have a revolutionary attitude towards business problems, i.e. they must make decisions to change the present situation or condition. They focus more on the customer’s requirement and satisfaction rather than only profit maximisation. Principles of Managerial Economics The great macroeconomist N. Gregory Mankiw has given ten principles to explain the significance of managerial economics in business operations. These principles are classified as follows: Principles of How People Make Decisions To understand how the decision making takes place in real life, let us go through the following principles: People Face Tradeoffs
- 4. To make decisions, people have to make choices where they have to select among the various options available. Opportunity Cost Every decision involves an opportunity cost which the cost of those options which we let go while selecting the most appropriate one. Rational People Think at the Margin People usually think about the margin or the profit they will earn before investing their money or resources at a particular project or person. People Respond to Incentives Decisions making highly depends upon the incentives associated with a product, service or activity. Negative incentives discourage people, whereas positive incentives motivate them. Principles of How People Interact Communication and market affect business operations. To justify the statement, let us see the following related principles: Trade Can Make Everyone Better off This principle says that trade is a medium of exchange among people. Everyone gets a chance to offer those products or services which they are good at making. And purchase those products or services too, which others are good at manufacturing. Markets Are Usually A Good Way to Organize Economic Activity Markets mostly act as a medium of interaction among the consumers and the producers. The consumers express their needs and requirement (demands) whereas the producers decide whether to produce goods or services required or not. Governments Can Sometimes Improve Market Outcomes Government intervenes business operations at the time of unfavourable market conditions or for the welfare of society. One such example is when the government decides minimum wages for labour welfare. Principles of How Economy Works As A Whole The following principle explains the role of the economy in the functioning of an organization: A Country’s Standard of Living Depends on Its Ability to Produce Goods and Services
- 5. For the growth of the economy of a country, the organisations must be efficient enough to produce goods and services. It ultimately meets the consumer’s demand and improves GDP to raise the country’s standard of living. Prices Rise When the Government Prints Too Much Money If there are surplus money available with people, their spending capacity increases, ultimately leading to a rise in demand. When the producers are unable to meet the consumer’s demand, inflation takes place. Society Faces a Short-Run Tradeoff Between Inflation and Unemployment To reduce unemployment, the government brings in various economic policies into action. These policies aim at boosting the economy in the short run. Such practices lead to inflation. Scope of Managerial Economics Managerial economics is widely applied in organizations to deal with different business issues. Both the micro and macroeconomics equally impact the business and its functioning. Following points illustrate its scope: Micro-Economics Applied to Operational Issues To resolve the organisation’s internal issues arising in business operations, the various theories or principles of microeconomics applied are as follows: Theory of Demand: The demand theory emphasises on the consumer’s behaviour towards a product or service. It takes into consideration the needs, wants, preferences and requirement of the consumers to enhance the production process.
- 6. Theory of Production and Production Decisions: This theory is majorly concerned with the volume of production, process, capital and labour required, cost involved, etc. It aims at maximising the output to meet the customer’s demand. Pricing Theory and Analysis of Market Structure: It focuses on the price determination of a product keeping in mind the competitors, market conditions, cost of production, maximising sales volume, etc. Profit Analysis and Management: The organisations work for a profit. Therefore they always aim at profit maximisation. It depends upon the market demand, cost of input, competition level, etc. Theory of Capital and Investment Decisions: Capital is the most critical factor of business. This theory prevails the proper allocation of the organisation’s capital and making investments in profitable projects or venture to improve organisational efficiency. Macro-Economics Applied to Business Environment Any organisation is much affected by the environment it operates in. The business environment can be classified as follows: Economic Environment: The economic conditions of a country, GDP, economic policies, etc. indirectly impacts the business and its operations. Social Environment: The society in which the organisation functions also affects it like employment conditions, trade unions, consumer cooperatives, etc. Political Environment: The political structure of a country, whether authoritarian or democratic; political stability; and attitude towards the private sector, influence organizational growth and development. Managerial economics provides an essential tool for determining the business goals and targets, the actual position of the organization, and what the management should do fill the gap between the two.
- 7. MEANING AND NATURE OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS Managerial Economics is economics applied in decision-making. It is that branch of economics that serves as a link between abstract theory and managerial practice. Managerial economics is concerned with the business firm and the economic problems that every management need to solve. Economics as a science is concerned with the problem of allocation of scarce resources among competing ends. These problems of allocation are on a regular basis confronted by individuals, households, firms as well as economies. Economics provide us with a number of concepts and analytical tools to help us understand and analyze such problems. Managerial Economics may be taken as economics applied to problems of choice of alternatives of economic nature and allocation of the resources by the firms. In other words, managerial economics involves analysis of allocation of the resources available to a firm or a unit of management among the activities of that unit. It is thus concerned with choice or selection among alternatives. Definition of Managerial Economics Some of the popular definitions of managerial economics are: “Managerial economics…is the integration of economics theory with business practice for the purpose of facilitating decision-making and forward planning by management.” ___Spencer and Siegelman. “Managerial economics… is the use of economics mode of thought to analyze business situation.”___McNair and Meriam. “A fundamental academic subject which seeks to understand and to analyse the problems of business decision-making.”____ Hague. As is evident, there are different projections of the subject matter on managerial economics by different authorities, but the following features seem common to these viewpoints. 1. Concerned with decision-making of economic nature.
- 8. This implies that managerial economics deals with identification of economic choices and allocation. 2. Micro-economic in character, where the unit of study is a firm. It concentrates on the study of the firm and not on the working of the economy. The chief source of concepts and analytical tools for managerial economics is micro- economic theory, also known as price theory, some of the popular micro- economic concepts are the elasticity of demand, marginal cost, the long-run economies and diseconomies of scale, opportunity cost, present value and market structures. Managerial economics also uses some of the well-accepted models in price theory, such as model for monopoly price, kinked demand model, the model of price discrimination and the behavioral and managerial models. 3. Concerned with normative micro-economics, where the economist says what he thinks should happen rather than what does happen to the firm. When applies that the decisions of the firm are made almost always within the broad framework of economic environment within which thee firm operates, known as maco-economic conditions. With regards to these conditions, we may stress these points. 4. Takes the help of macro-economics to understand and adjust to the environment in which the firm operates. We know that the decisions of the firm are made almost always within the broad framework of economic environment within which firm operates, known as micro-economic conditions. With regards to these conditions, we may stress these points. i) The economy in which the business operates is predominantly a free enterprise economy using price and market. ii) The present-day economy is the one undergoing rapid technological and economic changes. iii) The intervention of government in economic affairs has increased in recent times and there is no likelihood that this intervention will stop in future. These external conditions are beyond the control of the firm, hence the firm needs to adjust itself to the changes in these conditions to survive and grow. This
- 9. sort of a management is called a progressive management. 5. Goal-oriented and prescriptive It deals with how decisions should be mad e by managers to achieve the organizational goals. Knowledge of managerial economics helps in making wise choices—as managrs continue to face the problem of scarcity of resources and making suitable choices to allocate them appropriately in order to achieve organizational goals. 6. Pragmatic Managerial Economics concentrate on making economics theory more application- oriented. It is concerned with those analytical tools which are useful in improving decision-making. 7. Both ‘conceptual’ and ‘Metrical’ An intelligent application of quantitative techniques to business presupposes considered judgement and hard and careful thinking about the nature of the particular problem to be solved. Managerial Economics provides necessary conceptual tools to achieve this. Moreover, it helps the decision makers by providing measurement of various economic entities and their relationships. This material dimension of managerial economics is complementary to its conceptual framework. SIGNIFICANCE OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS Management is concerned with decision-making; Managerial Economics helps the decision-making process in the following ways: 1. Managerial Economics a number of tools and techniques to enable a Manager to become a more competent model builder. With the help of these models, the Manager can capture the essential relationships that represent the real situation while eliminating the relatively less important details. 2. Managerial Economics provides most of the concepts that are needed for the analysis of business problems. Concepts like elasticity of demand, fixed and
- 10. various costs, short and long-run costs, opportunity costs.net present value etc. help in understand and solving a decision problem. 3. Managerial Economics helps in making decisions such as: *What should be the product mix? *Which is the production technique and the input-mix that is least costly? *What should be the level of output and price for the product? *How to take investment decisions? *How much should a firm advertise and how to allocate the advertisement fund between different Media? SCOPE OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS Managerial Economics has a close connection with economics theory (micro as well as macro-economics), operations research, statistics, mathematics and the theory of decision-making. Managerial Economics also draw together and relates ideas from various functional areas of management like production, marketing, finance & accounting, project management etc. A professional management economist has to integrate the concept and methods from all these discipline and functional area in order to understand and analyse practical managerial problems. The following aspects thus constitute the subject-matter of managerial economics: 1. Objectives of a Business firm: The role of the top management is to decide what will be the objectives of a firm. 2. Demand Analysis and Demand Forecasting: The very first thing to find out in a new business venture is the nature and amount of demand for the product, both at present and in future, Demand analysis and forecasting therefore help in the choice of the product and in planning the output levels. 3. Production and Cost: Once the output is decided, the manager then needs to choose the best input-mix and the technology. He will maximize his profits only if
- 11. he produces th desired level of output at the minimum possible cost. 4. Competition: Competition is one of the essential a manager bears in mind while making his decision of allocation of scarce resources. 5. Pricing and output: Once the quantity of output is ready for sale, the firm has to decide its price bearing in mind the conditions in the market, In fact pricing is a very important aspect of managerial economics as firm’s revenue-earnings largely depend on its pricing policy. 6. Profit: Profit management is also a study in Managerial Economics. 7. Investment and Capital Building: For maximizing its profits, the firm needs to take care of its long-range decisions i.e.it has to evaluate its investment decisions and carry on a sensible policy of capital budgeting. 8. Product Policy, Sales Promotion and Market Strategy: An intelligent market management also helps the firm to grow. Market management includes product competition like advertising, product design etc. The managerial economics, taking the help of economics concepts and relationships, tries to find out which course is likely to be the best for the firm under a given set of conditions. *Managerial Economics and Traditional Economics: *Managerial Economics and Operation Research: *Managerial Economics and Statistics: *Managerial Economics and the Theory of Decision-Making: ROLE OF A MANAGERIAL ECONOMIST IN BUSINESS The two most important role of a managerial economist is to process information and make decisions. These decisions can be specific in nature or may be general tasks. Business is influenced not only by what decisions are taken within the firm but also by the general business environment. While the internal factors are within the firm but also by the general business environment. While the internal factors
- 12. are within its control, the external factors lie outside its sphere of control. The firm can make only timely adjustments to these external factors. The role of the managerial economist is to understand these external factors and to suggest policies which the firm should follow to make the best use of these external and internal factors. The external factors comprise of general economic condition of the economy, demand for the product, input cost of the firm, market conditions of raw material and finished product, firm’s share in the market, government’s economic policies and central bank’s monetary policies, annual budgets of the government etc. The managerial economist must obtain and process information with regard to these changes, advise the management regarding their likely effects on the operations of the firm and suggest possible ways to further the organizations goals. MODEL OF PROFIT MAXIMIZATION OR THE THEORY OF FIRM Profit maximization as the single goal of the firm has been the traditional approach to the theory of the firm. Profit maximization means the striving for the largest absolute amount of profits over a time period, both short term and long term. The short run is a period where production adjustments cannot be made quickly in matters of demand and supply. Long run however enables adjustment to changed conditions. In the short run for instance, there are production and financial constraints in expanding the firm even though it would yield maximization higher profits. But given sometime, most of the constraints can be overcome. So, short-term profit differs from long-term profit maximization. Profit maximization can be viewed from the point of view of the control wielded by a firm over price and output determination. Where the firm operates under condition of perfect competition among several firms, the price is determined in the market by supply and demand conditions. The individual firm has to maximize profits at this given price. They are price-taker firms. On the other hand, when there is imperfect competition, the number of sellers is small enough so that each firm has some control over its selling price. The firms in these markets are called price searchers because they must constantly search out the price that will maximize profits. Though profit maximization can be viewed from many angles, the marginal approach helps to formulate a rule which is applicable for both price-takers and
- 13. price-searchers .Profit can be defined as the difference between total revenue (TR) and total cost (TC). Profit = TR_TC The output which yields the maximum profits is the ideal to be achieved. TC and TR represent total cost and total revenue curves respectively. The gap between the two curves is maximum (K1K2) at OQ1 output. Here the slopes of the two curves shown by “tangents” are also equal i.e. marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost. Therefore, OQ1 is the profit maximizing output. Increase in production in a firm result in output going beyond OQ1.The firm will increase output as long as it does not add more additional cost than additional
- 14. revenue. The generalized decision-making rule for this firm can be stated as follows. As long as marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost, the firm should expand its output. The firm should produce that level of output which equates marginal revenue with marginal cost. Marginal revenue is the change in total revenue which comes from selling an additional unit of output. Marginal cost is the change in cost which results from producing and additional unit of output. The profit-maximization rule in simple terms means that the firm should continue production as long as incremental cost of production is less than the likely increase in revenue. Profit maximization rule of equating marginal cost with marginal revenue to arrive at an equilibrium output is illustrated as below;
- 15. AC and AR are the average cost and average revenue curves respectively. MC is the marginal cost and MR is the marginal revenue. As the firm expands its output in the beginning, there is fall in marginal revenue and a rise in marginal cost. So long as marginal revenue is higher than marginal cost, and additional output raises profit. When the output reaches OM, marginal revenue equals marginal cost at E and the firm gets a profit of PQRS (the shaded area).Beyond OM output, since the MC curve is higher than MR curve ,it shows that the firm suffer losses on expansion of output. The maximum profit is shown by the shaded rectangular area. Thus profits are maximum when MR=MC. There are some reasons why a firm should adopt the profit maximization goal: 1. In the case of owner managed firms it is only natural that thy should get the adequate and maximum returns .Maximizing profit, is therefore ,a rational behavior of the firm. 2. Profit maximization is a necessity in perfect competition for the survival of the firm. When there are many firms as under prefect completion, it can survive only if the firm makes profits. Under monopoly, there are no rivals but the owner would instinctively wish to purpose maximization for is efforts. There is no doubt that in a competitive world, the main measure of business efficiency is the profit made by a firm. In a dynamic society, profitability is essential for survival of the business. MANAGERIAL THEORIES OF THE FIRM The main argument of managerial theories is that in modern large firms, ownership and control are divorced. Managers, therefore, have a primary role in the effective control of the firm. The firms then seem to behave so as to maximize managerial objectives rather than shareholders’ profits. Like the traditional theory of firm it is the profit maximization, while in the managerial theories it is the function of different combinations of variable like salary, power, status, growth and job security. Managerial theories are broadly classified into three categories:
- 16. a) Sales Revenue Maximization Mode by Baumol. b) Managerial Utility Models. c) Growth Maximization Models. (a) Sales Maximization Process Baumol’s Model. The Firms Prefer Sales maximization because: i. Financial institutions evaluate the success and strength of the firm in terms of rate of growth of its sales revenue. ii. Empirical evidence shows that the stock earnings and salaries of the top management are correlated more closely with sales than with profits. iii. Increasing sales revenue over a period of time gives prestige to the top management, but profits are enjoyed only by the shareholders. iv. Growing sales means higher salaries and better perquisites. Hence sales revenue maximization results in a healthy personnel policy. v. It is difficult for managers to present spectacular profits year after year. Hence they prefer a safe and steady performance with satisfactory profits but good sales. vi. Large and increasing sales help the firm in bigger market share which also gives it a greater competitive power. Assumptions of Baumol’s Sales Maximization Model *Sales maximization goal is subject to a minimum profit constraint. However, Baumol does not give a clear definition of minimum profit except to propose it represents, “the funds to pay some satisfactory rate of dividends, to reinvest for growth and ensure financial safety.” *Advertisement costs are independent of production costs. *Advertisement is a major instrument of sales revenue maximization I,e. because
- 17. advertisement will shift the demand curve to the right. *Price of the product is assumed to be given and the firm has to decide on its output. The sales maximization model is explained with the help of the following figure: (b) Managerial Utility Models There are two main versions of the cases where managers in the modern large corporations are asked to influence the goals of the firm and not go along wholly pursuing the goals of the owners.
- 18. (c) Growth Maximization Models Growth of the firm is obviously the cornerstone of corporate strategy, Rate of growth and potential of growth are generally used as yardsticks to measure corporate success. Growth of a firm must be financed either from retained earnings or from market borrowing or both. MORE ECONOMICS TOPICS MACRO-ECONOMIC ENVIRONMENT: Consists of the level and direction of aggregate economic quantities like the aggregate markets for goods and services, national income, level of employment, government policies etc. MICRO-ECONOMIC ANALYSIS: Deals with the behavior of individual economic units which include consumers, firms, investors etc. It reveals how firms, industries, and markets take decision, why do they differ from one another, and how these economics units are affected by government policies and international economic condition. NORMATIVE APPROACH: Is prescriptive approach in that it attempts to prescribe what ought to be done. ASPIRATION LEVEL: Demands of the different groups of the organization-coalition, competing for the given resources of the firm, take the form of aspiration levels. EXPENSE PREFERENCE: Certain discretionary expenditures that provide satisfaction to managers, like discretionary power of investing in projects, which may enhance his status and esteem. FIXED COSTS: That cannot be eliminated in short run. MANAGERIAL SLACK: The company fund which the manager is allowed to spend for his own ends, like entertainment expense, staff car, Luxurious office. NON-PECUNIARY ASPECTS: Relate to physical inputs, and other variable (i.e. non-
- 19. financial variables). OPTIMAL DECISION: Enables the decision-maker (firm)to attain its desired objective most closely. OLIGOPOLISTIC MARKET STRUCTURE: Market with large number of buyers but a small number of sellers; where some of the sellers dominate the market, Further, action of each firm in oligopoly affects the other sellers in the market, which invites reaction from rivals in term of price cuts, changes in quality, advertising, new product line etc. SATISFYING BEHAVIOUR: When the goal of the firm is not to maximize but only to satisfy a goal/ goals. The owners/ shareholders, according to this concept, are satisfied with adequate return and growth since they really cannot judge when profits are maximized. PROFITS: Profits may considered a reward for making innovations ,a reward for accepting risks and uncertainties and the result of imperfections in the market structure. _____Henry Grayson Marshall, Taussig, Robertson and Bober have defined profits in a broad sense. Hansen defined profits as ‘the residual payment, what is left to the producer’s income after all other payments have been met’’. Similarly, Drucker said, “the surplus of current income over past cost is profit.” DYNAMIC STATE: The economic state where the future is likely to be different from the present, but this change is unpredictable. GROSS PROFIT: The difference between receipts and payment over a time period. INFLATION ACCOUNTING: To judge the impact of changing prices on the profitability and financial health of the firm. INNOVATION: All those measures taken by an entrepreneur which reduce cost or enhance demand (i.e., finding new products, sale-territories, technology, etc.).
- 20. NET PROFIT: Profit net of implicit cost. NORMAL PROFIT: The minimum expected return to keep an entrepreneur in his present business. MONOPOLY PROFIT: Profit that arises due to disequilibrium and imperfection in the market. The term profits is also used for monopoly profits. An entrepreneur earns monopoly profits not because he performs any entrepreneurial activity, but because he has a certain degree of monopoly power in the product market. His monopoly profits are in direct proportion to the extent of his monopoly power. Monopoly profits exist because of disequilibirum and imperfect competition. They tend to persist because the economy can rarely adjust instantaneously to changes in cost and demand conditions. And so long as the monopoly power exists with the producer he keeps on earning 'monopoly profits'. RISK: Those unpredictable changes that can be insured against. UNCERTAINTY: Those unpredictable changes that cannot be insured against. WINDFALL PROFITS: Profits due to changes in the general price level in the market. These profits arise due to changes in the general price level in the market. If the producers and traders buy their inputs and raw materail when prices are low and sell their output when, due to some unforseen external factors, the prices have abruptly gone up, then the profits resulting there from called 'windfall profits'. it must be noted that these windfall profits just happen to come in the way of these producers and traders; they never planned their business operations for earning them. These come unexpectedly and cannot therefore be treated as a reward for any specific activity of the entrepreneur. OPPORTUNITY COST: Represents the benefits or revenue forgone by pursuing one course of action rather than another. MARGINAL PRODUCTIVITY: Output that results from one additional unit of a factor of production(such as a labour hour or a machine hour),all other factors remaining constant, Whereas the marginal cost indicates the added cost incurred in producing an additional unit of output, marginal product indicates the added
- 21. output accruing to an additional input. Since marginal product is measured in physical units produced, it is also called marginal physical product. PERFECT COMPETITION: A market structure in which (a) the firms take market price as given ,since an individual firm produces only a small fraction of total industry output; (b) the product of all firms is a interferences with the activities of buyers and seller; and (e) there is perfect knowledge and mobility. DEFINITIONS OF THE MARKET: A market is a body of persons in such commercial relations that ach can easily acquaint himself with the rates at which certain kinds of exchanges of goods or services are from time to time made by the others. The word market has been generalized so as to mean anybody of persons who are in intimate business relations and carry on extensive transactions in any commodity. __Jevons Market is any area over which buyers and sellers are in close touch with one another, either directly or through dealers, that the price obtainable in one part of the market affects the prices paid in other parts.__ Benham. EQUILIBRIUM PRICE: The price at which the quantity demanded by consumers of a product is equal to the quantity supplied by sellers of a product. FREE ENTRY: The absence of barriers to entry into a market. In a market characterized by free entry, greater than normal profit serves the function of drawing new firms into the industry. MARKET STRUCTURE: The number and relative sizes of buyers and sellers in a particulars market, the nature of product and the degree of ease of entry of firms into the market determine the market structure. For example, in perfect competition, large number of buyers and sellers are competing with each other for buying and selling a homogenous good, while free entry and exit is permitted. MONOPOLY: A market structure characterized by the existence of only one firm in the industry. For a firm to retain monopoly control there must be complete barriers to entry into the industry. Monopoly is a market form, which has always
- 22. attracted the attention of economists. This word has come from Greek words, monos(single), polein (selling), which mean alone to sell. Therefore, in literary terms, it implies a market structure, where there is a single seller. In economic theory, monopoly is characterized by sole producer selling a distinct product for which there are no close substitutes and there are strong barriers to entry. This sole producer (may be known as monopolist) controls the entire supply of the market. Thus, the supply curve of the firm and the industry will be one and the same. NORMAL PROFIT: The rate of profit just sufficient under conditions of free entry, to keep firms from leaving a given industry in the run. PERFECT COMPETION: A market structure in which (a) the firms take market price as given, since an individual firm produces only a small fraction of total industry output; (b) the product of all firms is homogeneous;(c) there is freedom of entry into and exit from the industry; (d) there are no interferences with the activities of buyers and seller; and (e) there is perfect knowledge and mobility. Perfect competition has an edge over other realistic and complicated market forms, as it is relatively simple to handle. This kind of idealistic market structure provides a yardstick or a standard against which other more realistic market forms can be compared, evaluated and understood better. PRICE TAKERS: Firms that cannot influence the market price. It refers to firms in perfect competitive markets. PRICE DISTRIBUTION: Charging different prices for the same product from consumers in different markets segments (based on the price elasticity of demand in each market segment). PROFT-MAXIMIZING RULE: Produce up to the point where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost; and at higher output levels marginal revenue is less than marginal cost. SHUTDOWN POINT: The point at which the firm must consider stopping its production activity because the short run loss remains the same (that is, equal to total fixed cost) whether the firm produces or not. In a perfectly competitive
- 23. situation this point is found at the lowest point of a firm’s average variable cost curve. CARTEL: A group of firms that have joined together to make arrangements on pricing and market strategy. Cartel agreement is an agreement of companies or sections of companies having common interests to form an association or a cartel. Such agreements are designed by companies to prevent extreme or unfair competition and allocate markets, and to promote the interchange of knowledge resulting from scientific and technical research, exchange of patent rights, and standardization of products.A group of companies or countries which collectively attempt to affect market prices by controlling production and marketing. Illegal in the United States and the European Union. Very few major cartels exist; the most prominent example is OPEC, a cartel which can not be considered illegal because it is made up of sovereign states, not companies. also called trust. DUOPOLY: A market form in which there are large number of buyers but only two sellers with mutual interdependence. Two firms in the industry · Strong control over price.· Uses Non price competition to compete· Very strong Barriers to entryNote. a pure dupoly very rarly occurs in real life the more common is two dominate firms who hold majority of the market share. KINKED DEMAND CURVE: A graphical representation of a situation wherein rival firms do not follow the price increase of a firm but follow its price cuts. Such a demand curve is more elastic for prices above the going market price and less elastic for prices below the going price. MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION: A market structure characterized by the existence of many firms in the industry, where each seller attempts to differentiate its product from its rivals, so that he has some control over price. Monopolistic competition pertains to a market situation where there is a relatively large number of small producers or suppliers selling similar but not identical products. Monopolistic competition is a market structure characterized by many firms selling products that are similar but not identical, so firms compete on other factors besides price. Monopolistic competition is sometimes referred to as imperfect competition, because the market structure is between pure monopoly and pure competition.
- 24. OLIGOPOLY: A market structure characterized by the existence of a few dominant firms in an industry (each recognizing their mutual interdependence) having substantial barriers to entry. An oligopoly is a market dominated by a few large suppliers. The degree of market concentration is very high (i.e. a large % of the market is taken up by the leading firms). Firms within an oligopoly produce branded products (advertising and marketing is an important feature of competition within such markets) and there are also barriers to entry.The term oligopoly is derived from two Greek words: ‘oligi’ means few and ‘polein’ means to sell. Oligopoly is a market structure in which there are only a few sellers (but more than two) of the homogeneous or differentiated products. So, oligopoly lies in between monopolistic competition and monopoly.Oligopoly refers to a market situation in which there are a few firms selling homogeneous or differentiated products. Oligopoly is, sometimes, also known as ‘competition among the few’ as there are few sellers in the market and every seller influences and is influenced by the behaviour of other firms. important characteristic of an oligopoly is interdependence between firms. This means that each firm must take into account the likely reactions of other firms in the market when making pricing and investment decisions. This creates uncertainty in such markets - which economists seek to model through the use of game theory. PRICE LEADERSHIP: It occurs when a firm in an oligopoly sets a price that subsequently determines what other firms in the industry will charge for their products (known as followers). PRODUCT DIFFERENTIATION: A wide variety of activities, such as design changes and advertising that rival firms employ to attract customers by distinguishing their product from competitors’ products.