Embed presentation
Downloaded 244 times


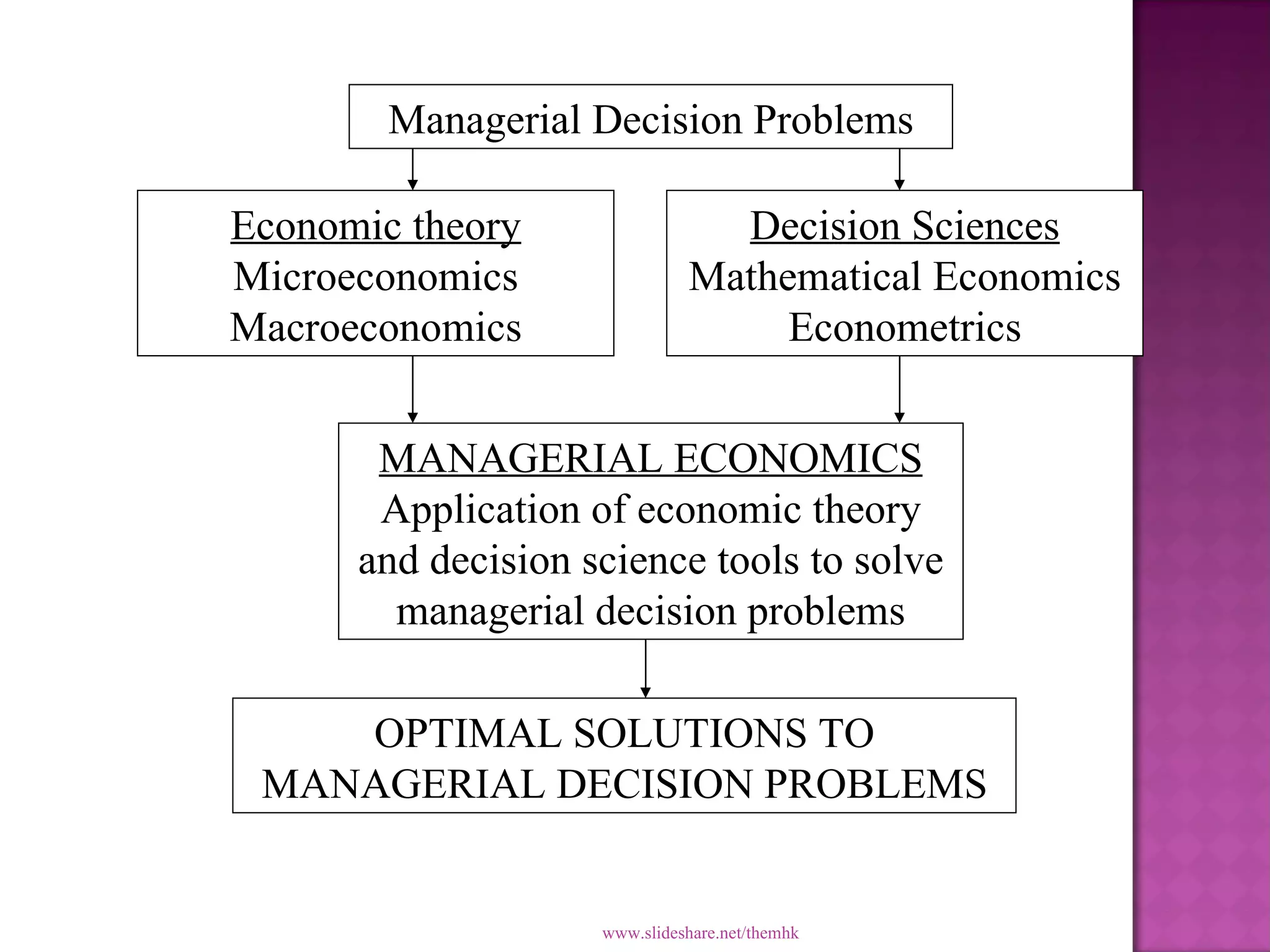

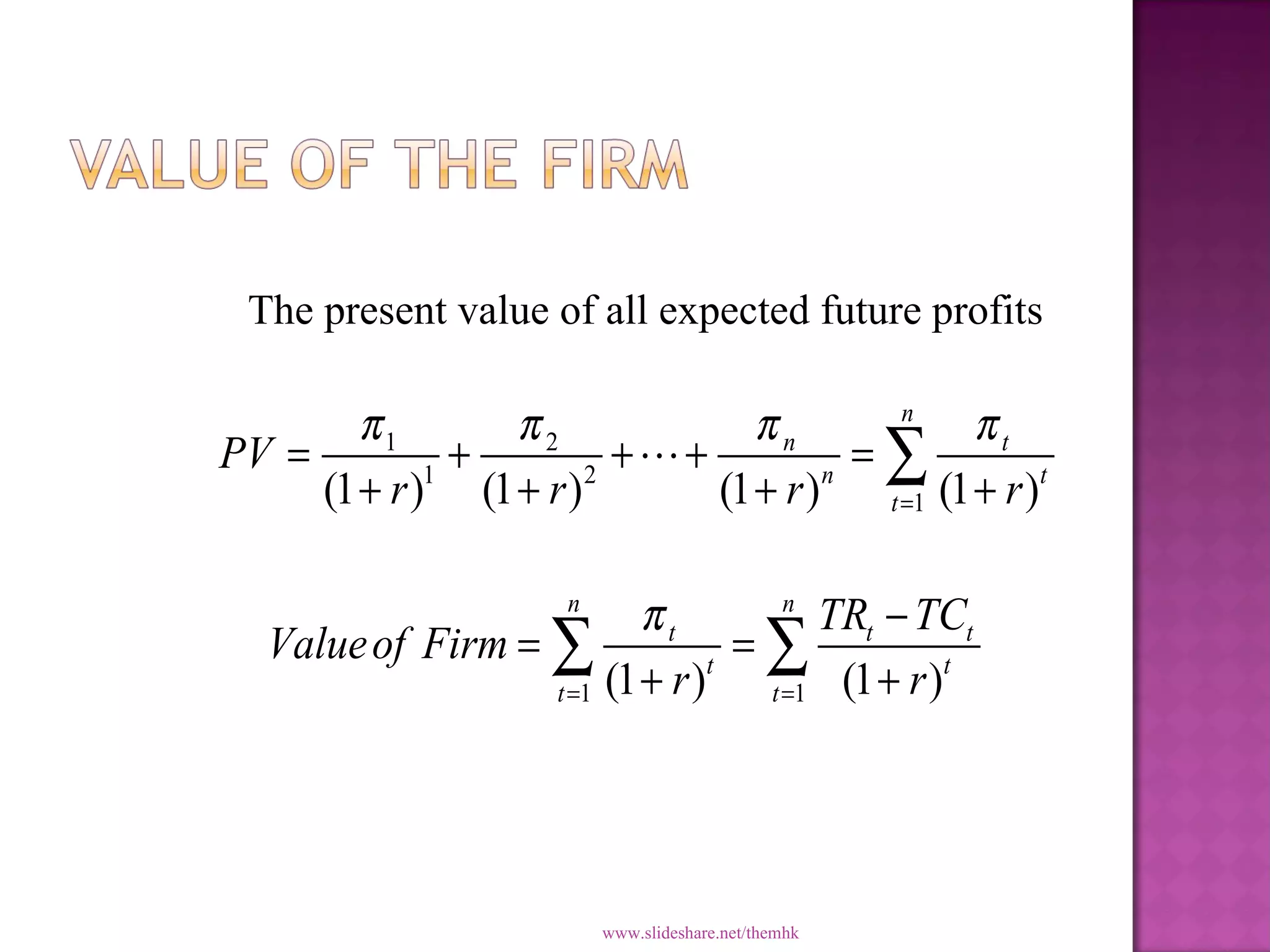
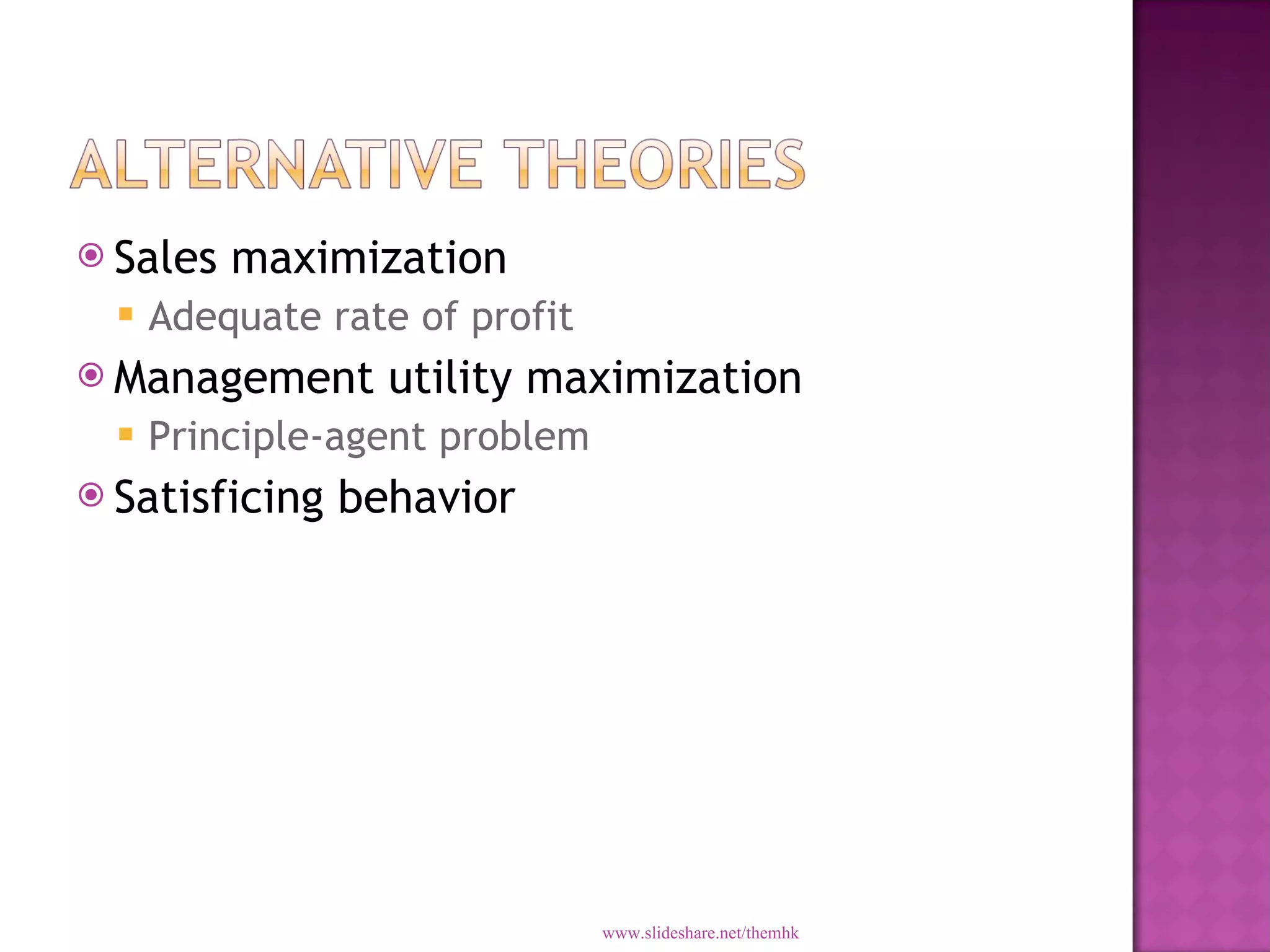






Managerial economics applies economic theory and decision-making tools to help managers solve problems and make optimal decisions. It combines resources to produce and sell goods and services while maximizing profits. Managerial economics examines how firms can achieve objectives efficiently by considering profit maximization, sales, adequate rates of return, and management utility.










