Embed presentation
Downloaded 24 times

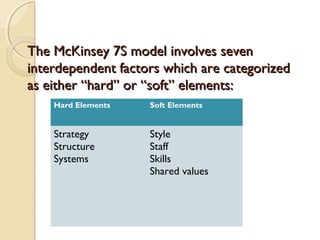


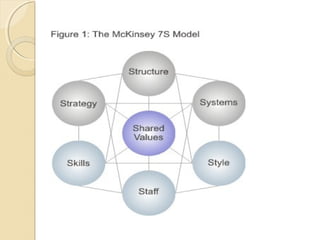
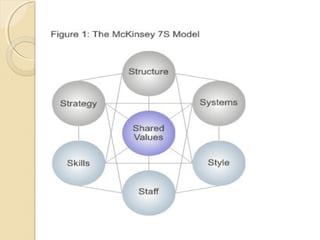

The McKinsey 7S model analyzes seven interdependent factors that influence an organization's effectiveness. The factors are categorized as either "hard" elements like strategy, structure, and systems that management can directly influence, or "soft" elements like style, staff, skills, and shared values that are more difficult to define but still important. When assessing an organization, the model depicts how a change in one element affects all the others.





