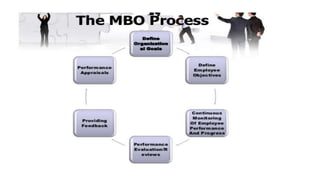
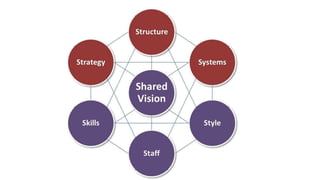
The document discusses the McKinsey 7S framework, which analyzes seven internal aspects of an organization that need to be aligned for it to be successful. The seven elements are: structure, strategy, systems, style, staff, skills, and superordinate goals. For each element, questions are provided to help assess how well an organization is currently positioned in that area and identify any needed improvements. The framework can be used to analyze performance, plan for change, and identify issues within an organization.