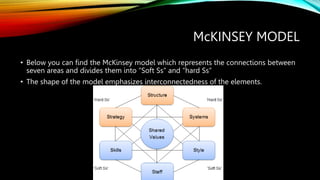
The document discusses strategic planning and management. It defines strategic planning as a process where an organization's leaders define their vision and goals for the future. This typically represents mid- to long-term goals of 3-5 years. The process of strategic planning involves determining objectives, analyzing the external environment, conducting a self-appraisal, making strategic decisions, and implementing and controlling the strategy. The McKinsey 7S framework is also summarized, which analyzes 7 internal elements that must be aligned for organizational effectiveness: strategy, structure, systems, skills, style, staff, and shared values. PEST analysis is explained as a tool to assess political, economic, social and technological factors affecting an organization.