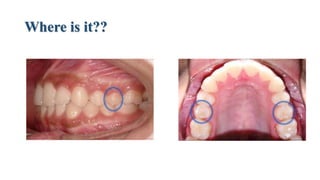
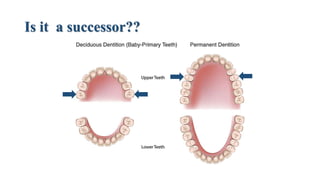
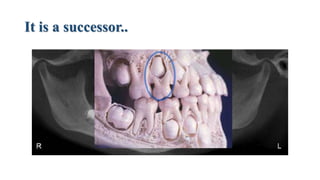
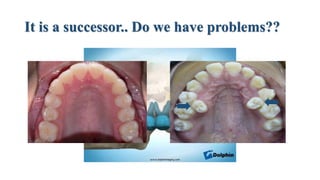
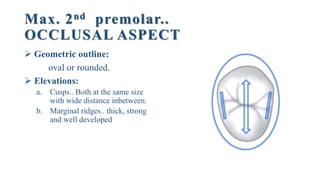
This document discusses the morphology and features of the maxillary second premolar tooth. It provides details on:
1. The maxillary second premolar's eruption timeline and root development stages.
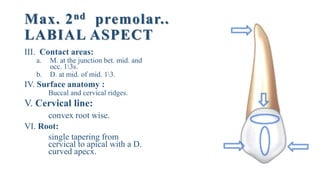
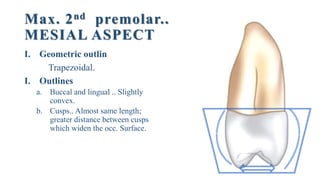
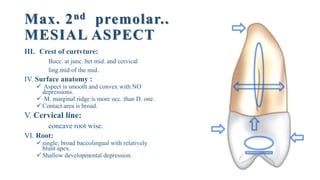
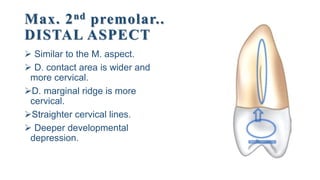
2. The geometric outlines, outlines of cusps and ridges, contact areas, surface anatomy, cervical lines, and roots for the labial, lingual, mesial, distal, and occlusal aspects of the tooth.
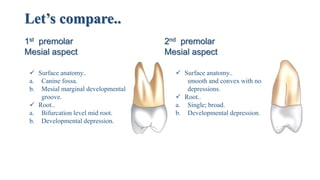
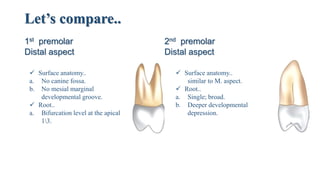
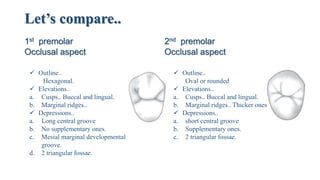
3. A comparison of the features of the maxillary first and second premolars, highlighting differences in their outlines, cusps, contact areas, surface anatomy, roots, and occlusal depressions and elevations.