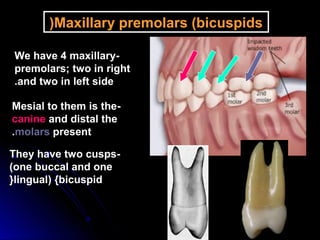
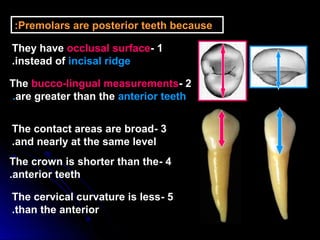
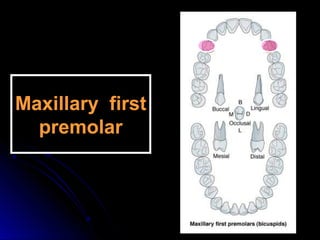
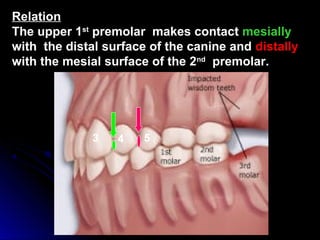
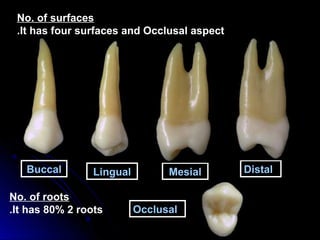
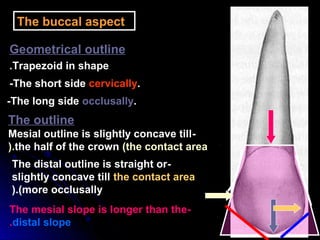
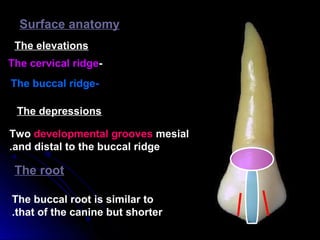
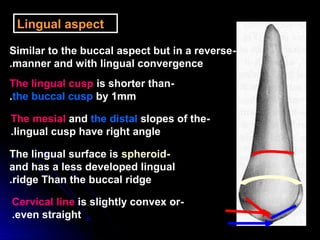
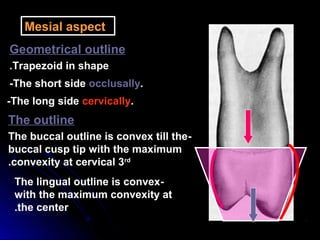
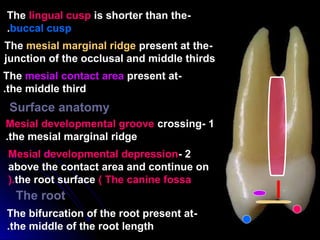
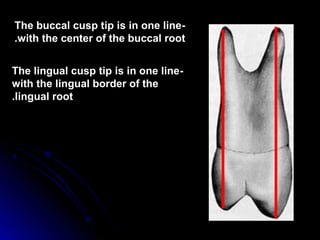
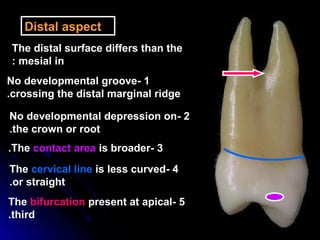
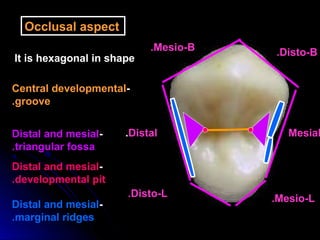
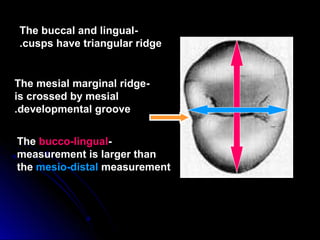
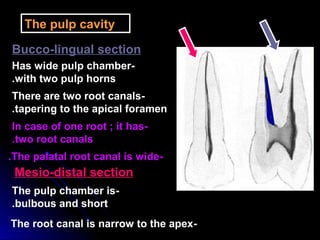
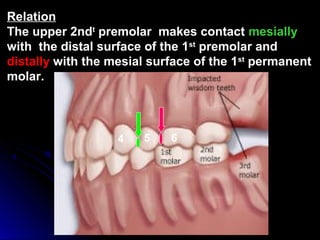
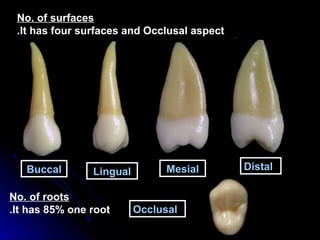
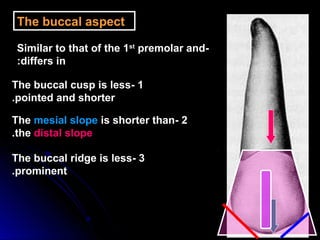
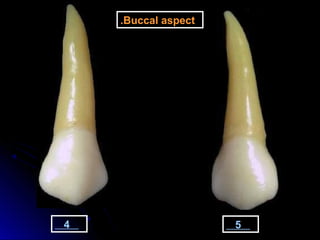
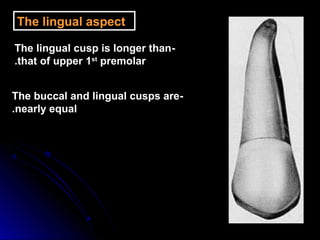
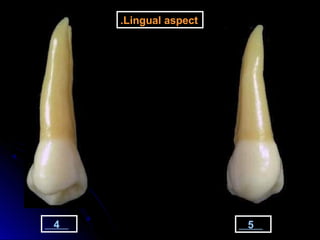
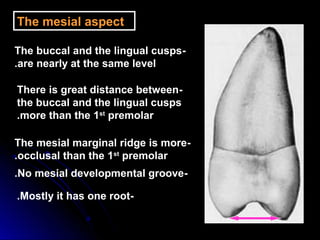
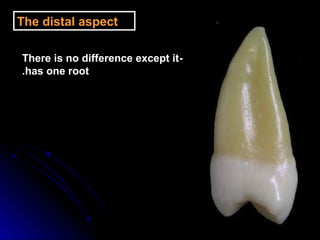
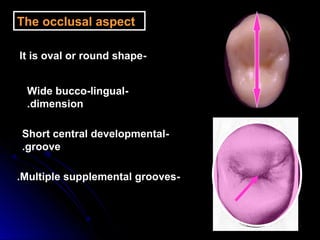
This document provides information about maxillary premolars and the first and second maxillary premolars specifically. It describes the anatomy, morphology, chronology of development, and relationships to surrounding teeth of these premolars. Key details include that maxillary premolars have two cusps, appear between ages 10-12 years, and are posterior teeth with broader contact areas than anterior teeth. The first premolar typically has two roots while the second premolar most often has one root.