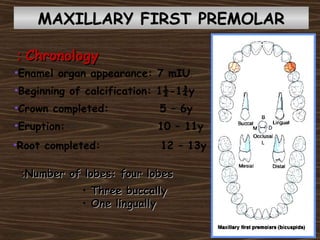
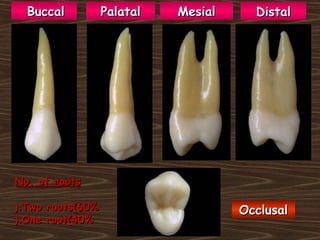
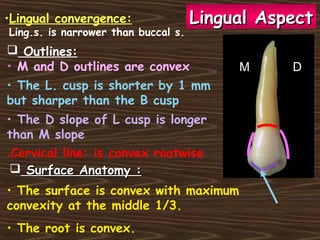
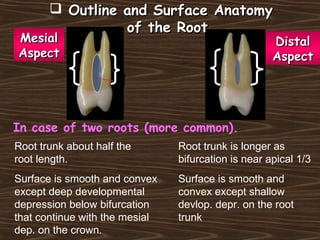
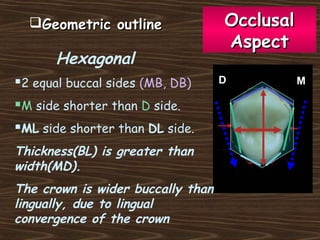
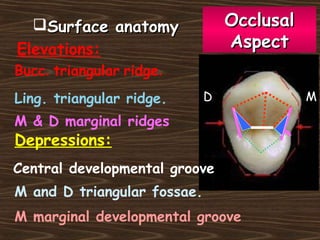
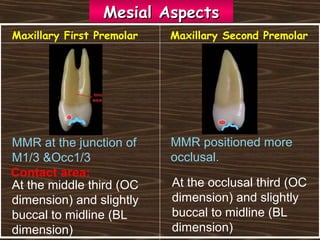
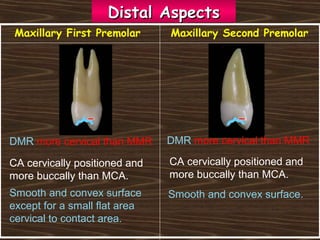
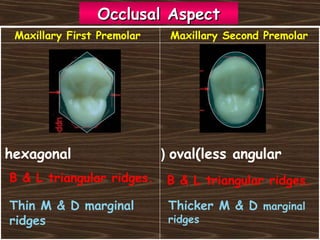
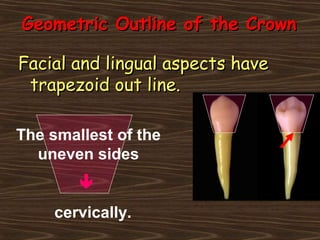
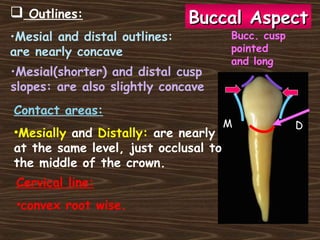
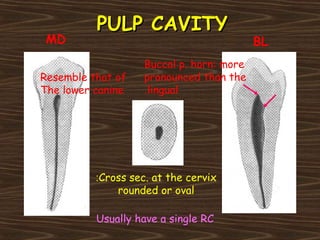
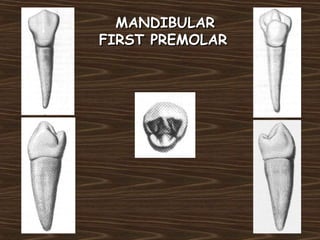
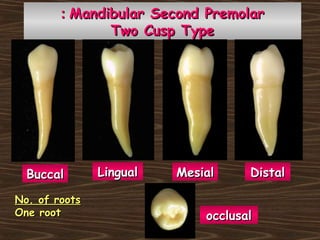
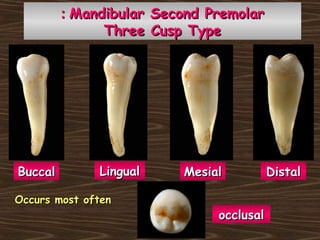
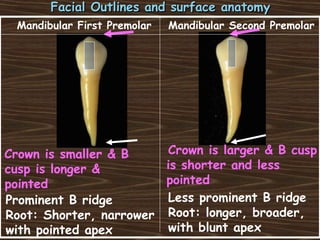
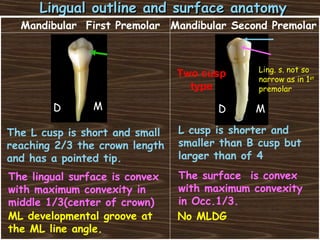
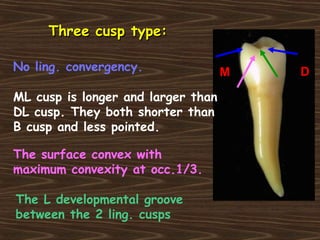
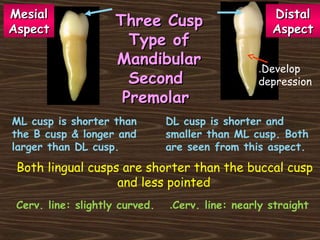
Obama and his family moved to Washington D.C. after he was elected President in 2008. The document then provides detailed anatomical descriptions of the premolars, including their number, shape, features, eruption timeline, and relations to other teeth. It describes the maxillary and mandibular first and second premolars, discussing differences between them. Diagrams illustrate aspects of the premolars like occlusal outlines, root structures, and pulp cavities.