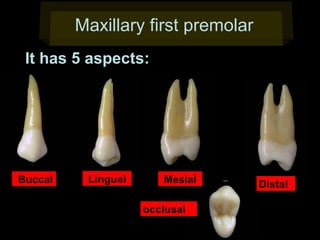
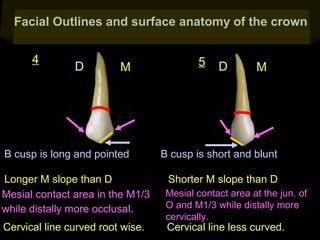
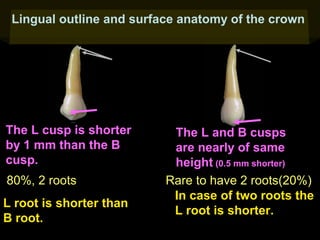
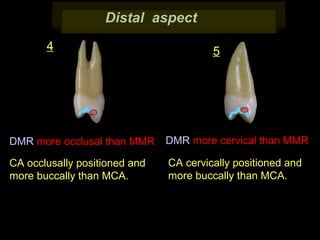
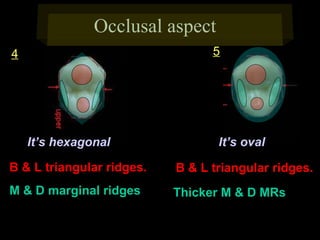
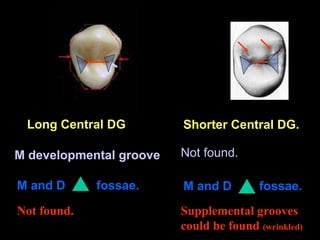
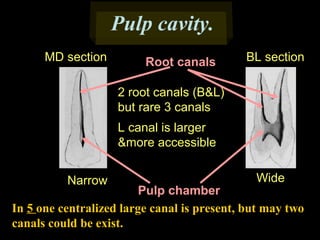
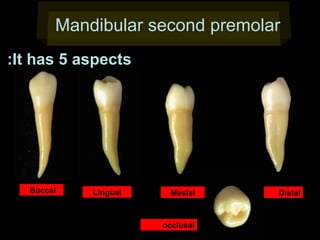
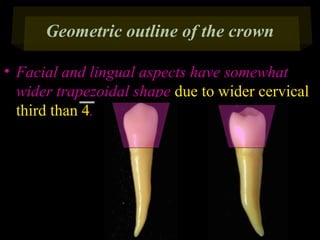
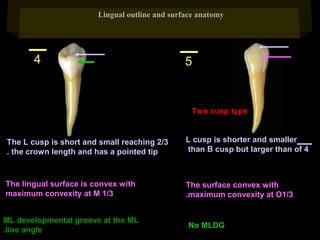
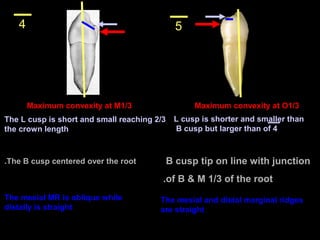
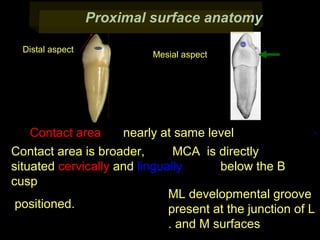
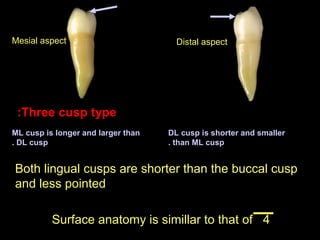
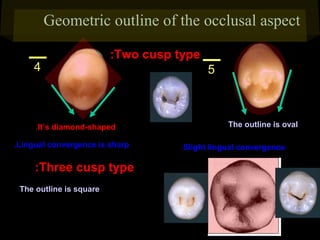
This document provides information about the maxillary and mandibular first and second premolars. It describes the anatomical features of each tooth, including the number of cusps and roots, eruption timing, outline of facial and lingual surfaces, contact areas, and occlusal morphology. Key details provided include differences in cusp shape, prominence of ridges, position of developmental grooves and fossae, and root bifurcation location between the first and second premolars. Diagrams illustrate the characteristic features and anatomical terminology.