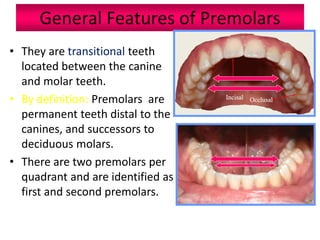
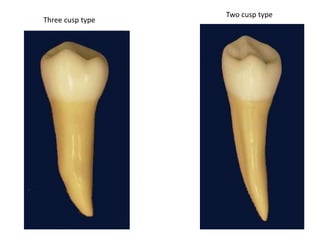
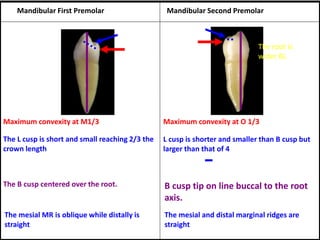
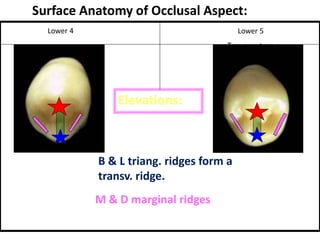
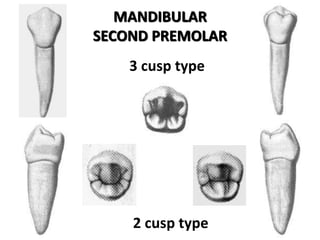
The document provides an overview of the anatomical features and characteristics of the mandibular second premolar, discussing its morphology, chronology of development, and comparisons with the first premolar. Key distinctions are made between the two cusp types and their respective shapes and root features. It also includes details about the occlusal surface anatomy, emphasizing the differences in cusps and ridges.