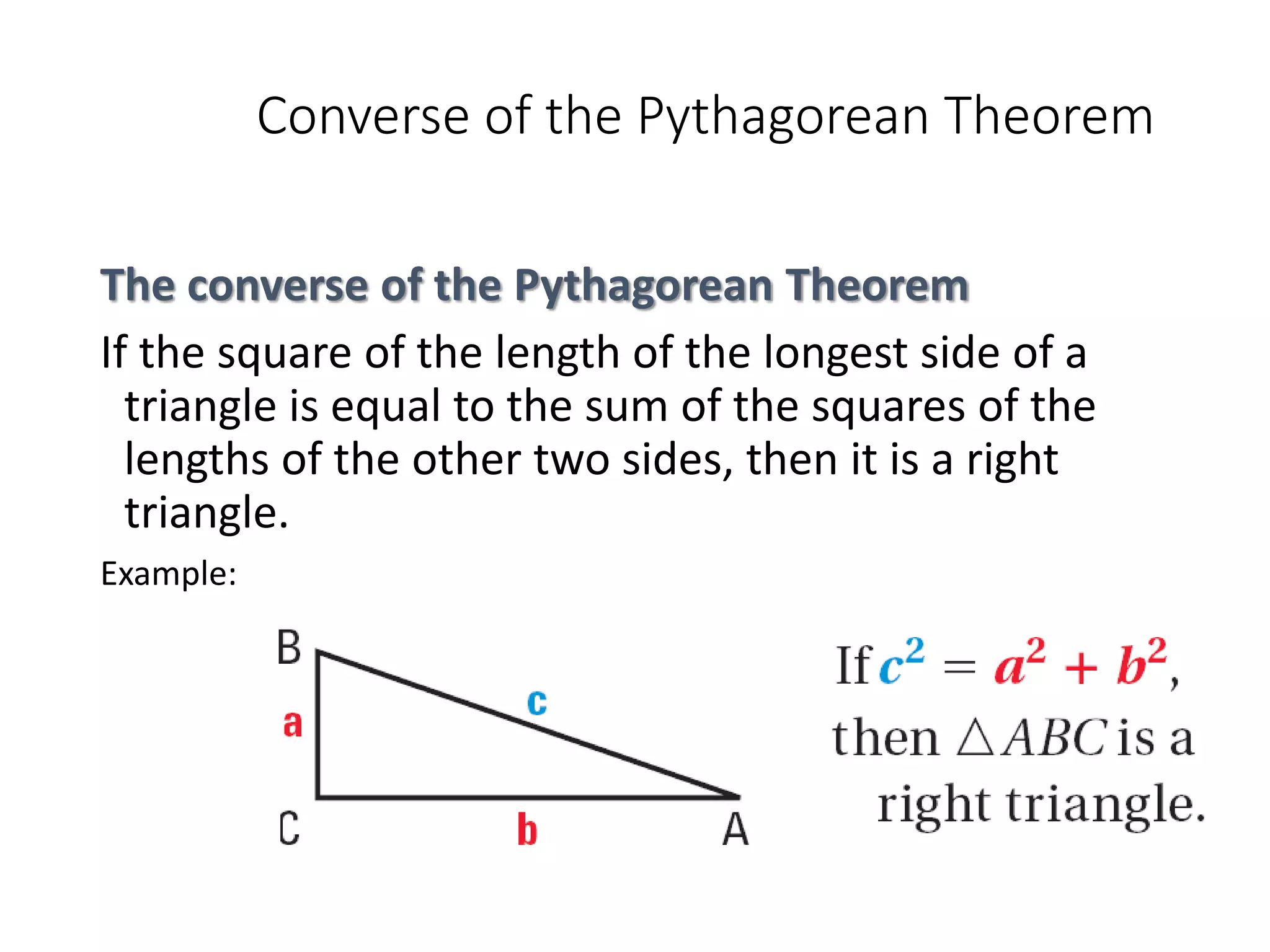
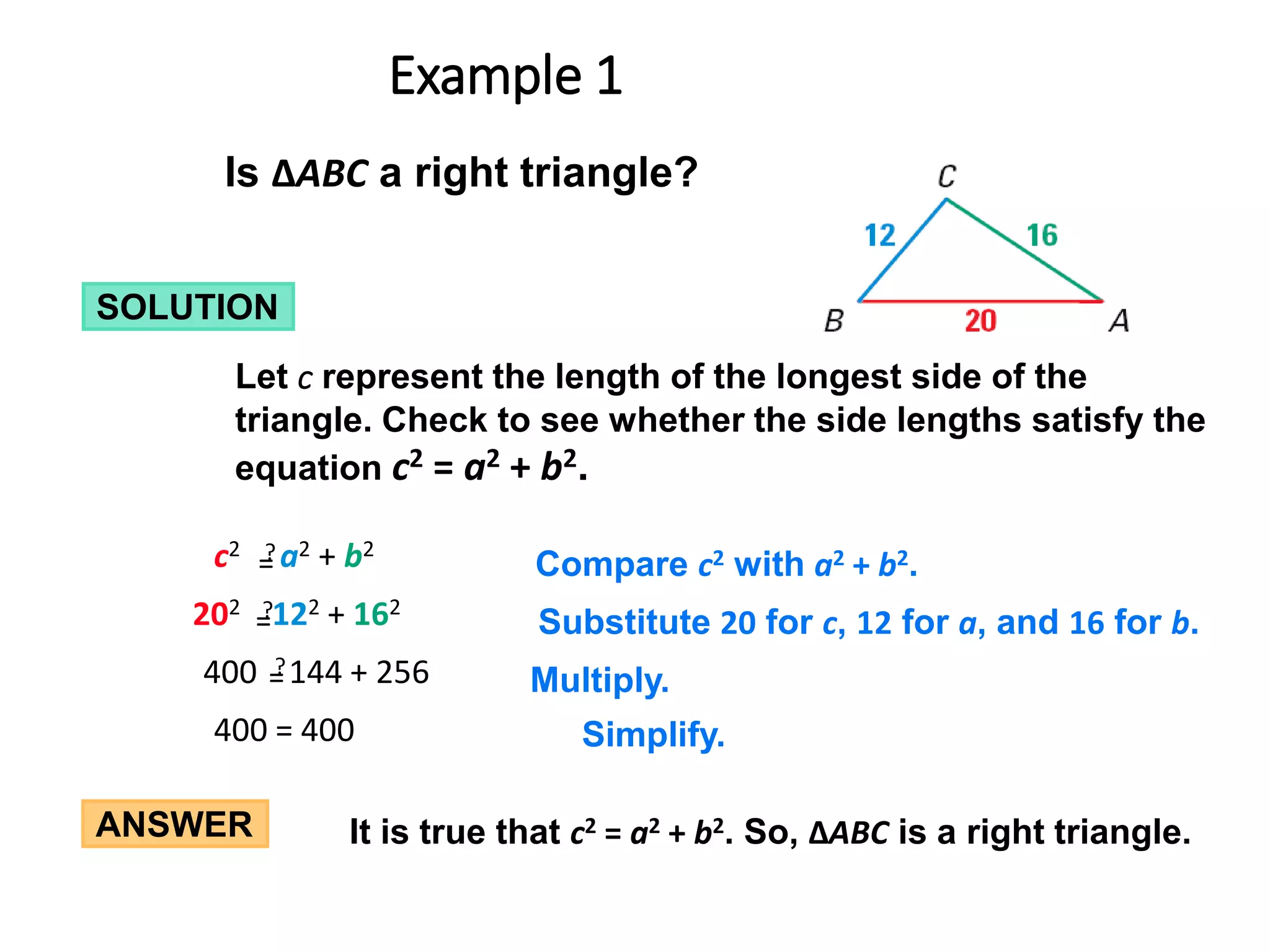
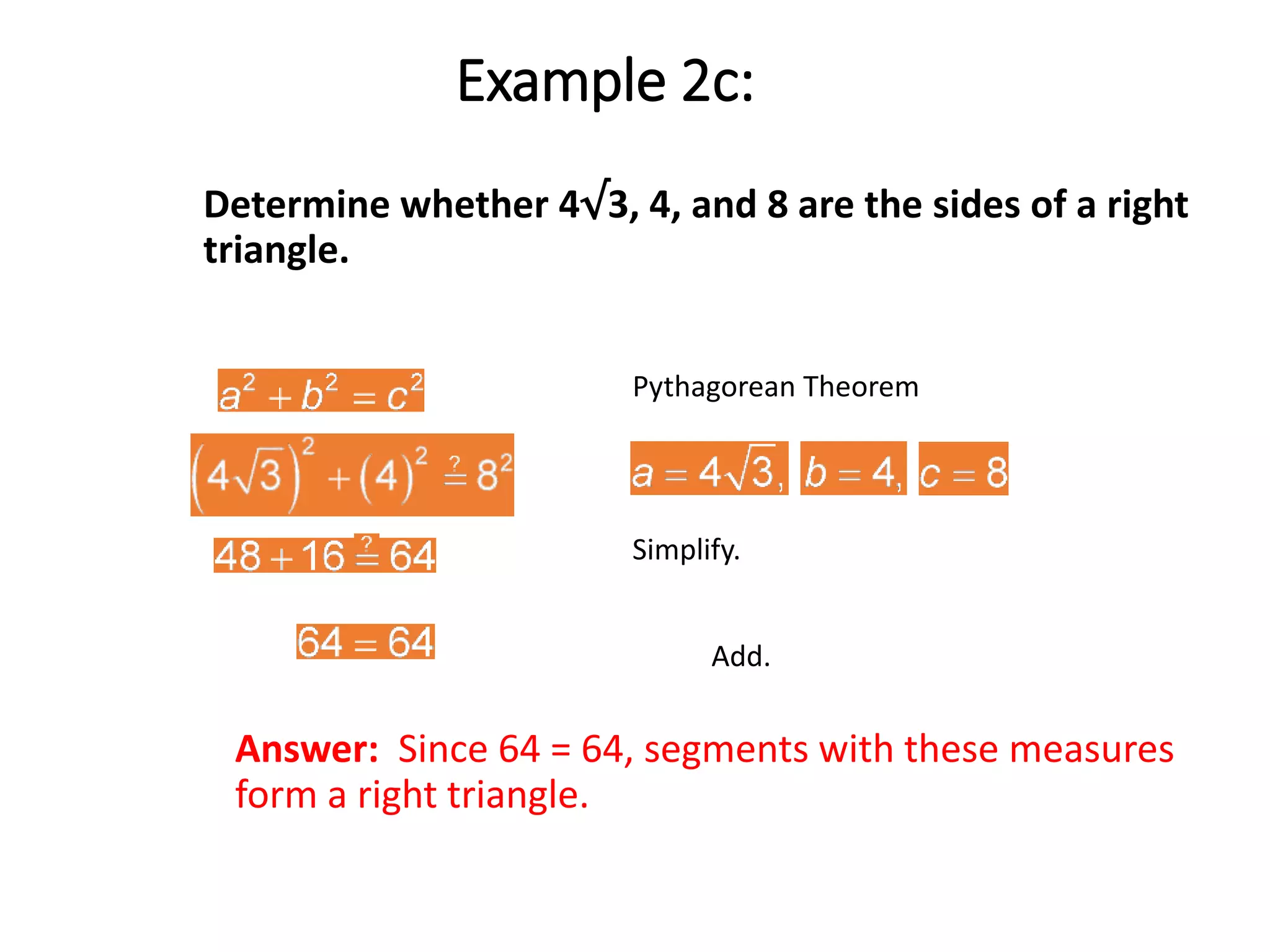
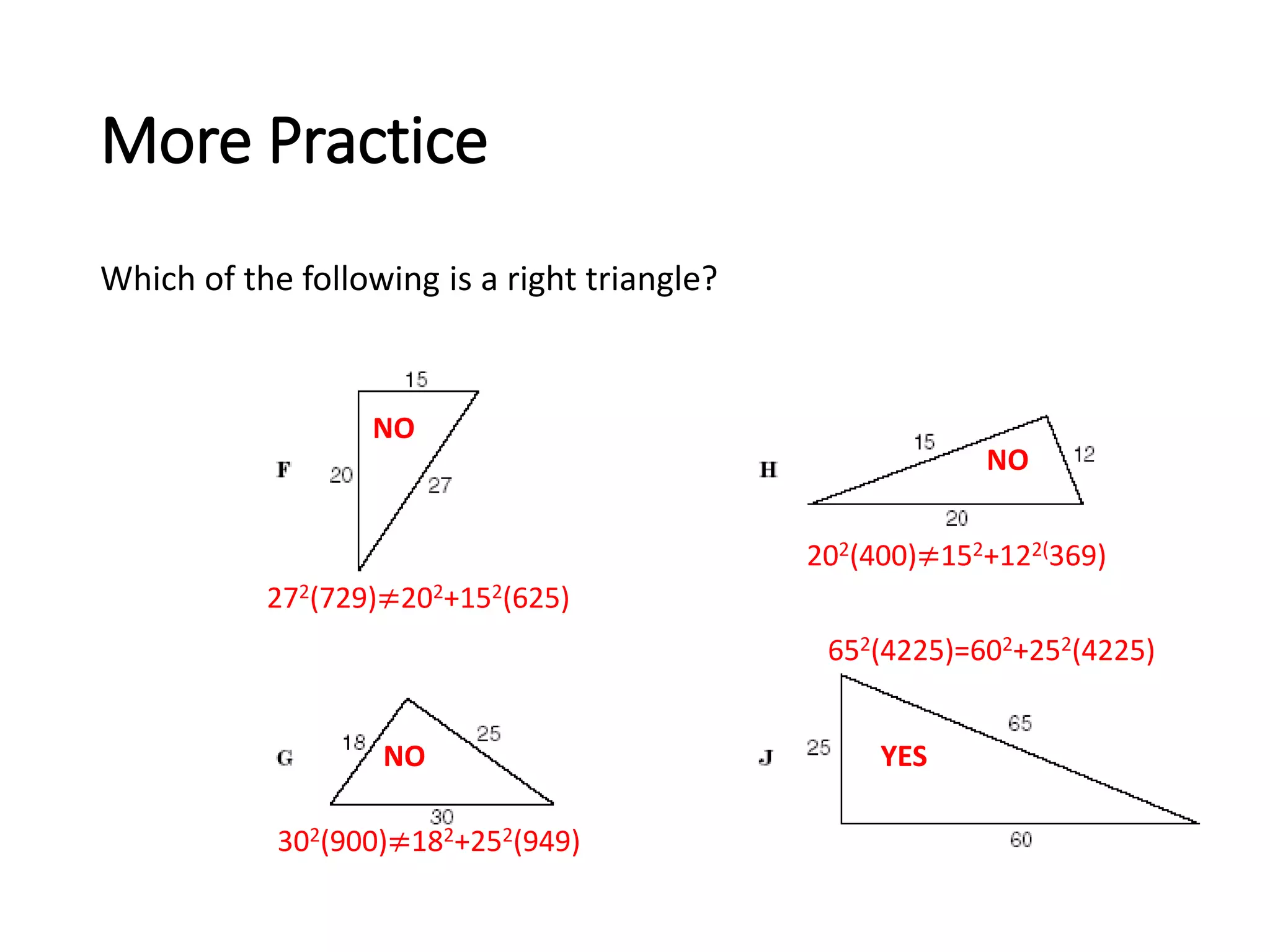
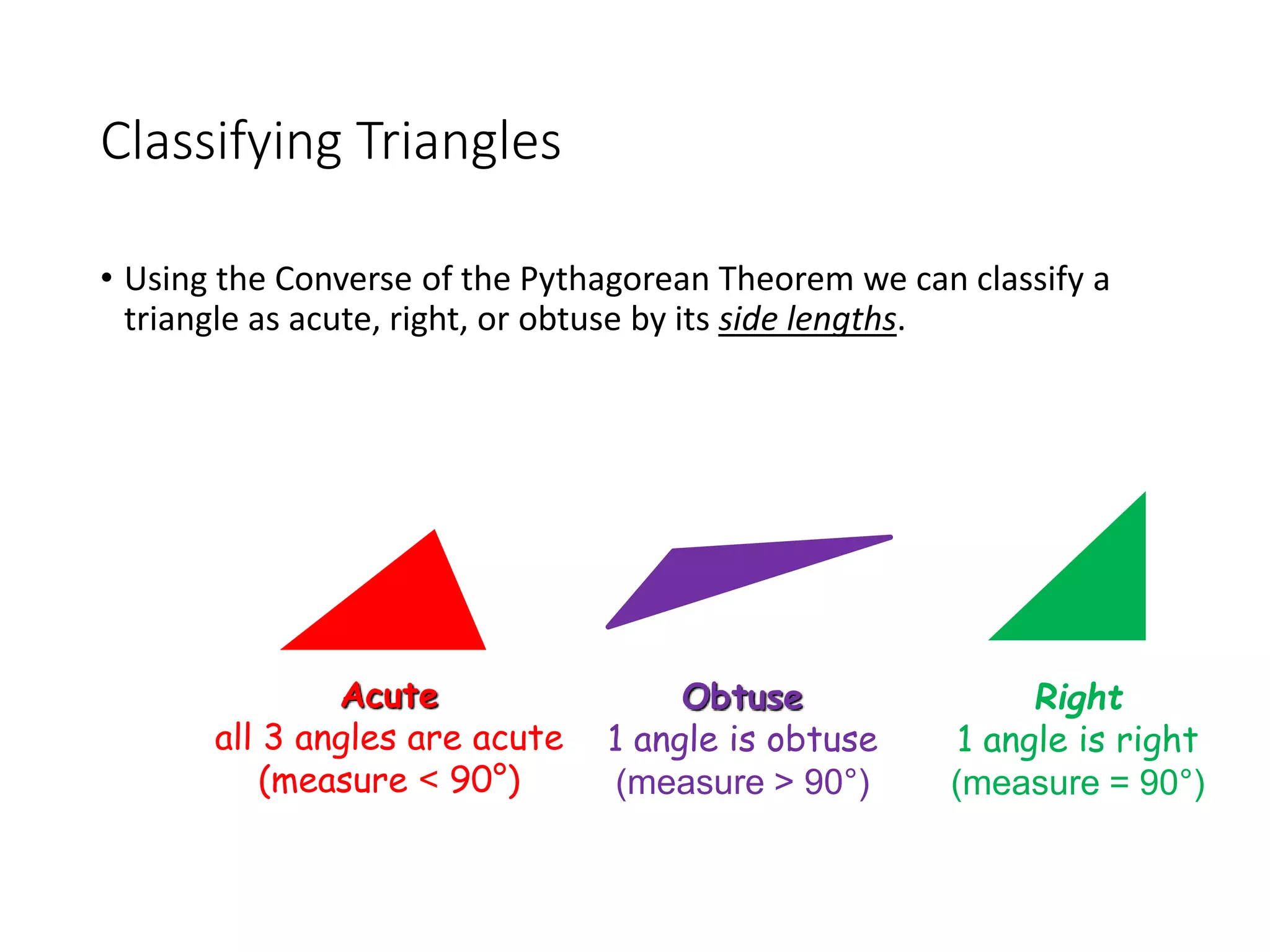
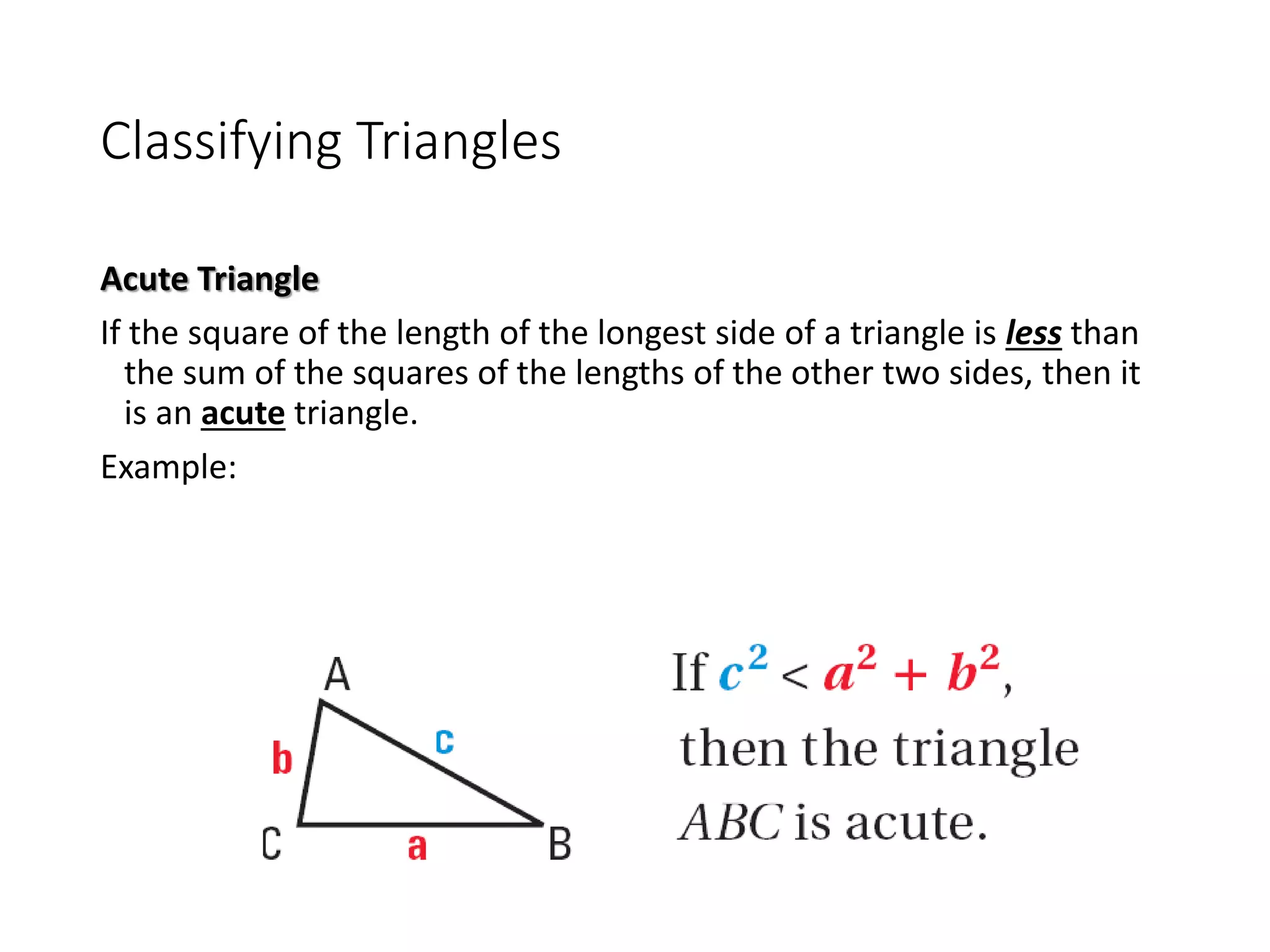
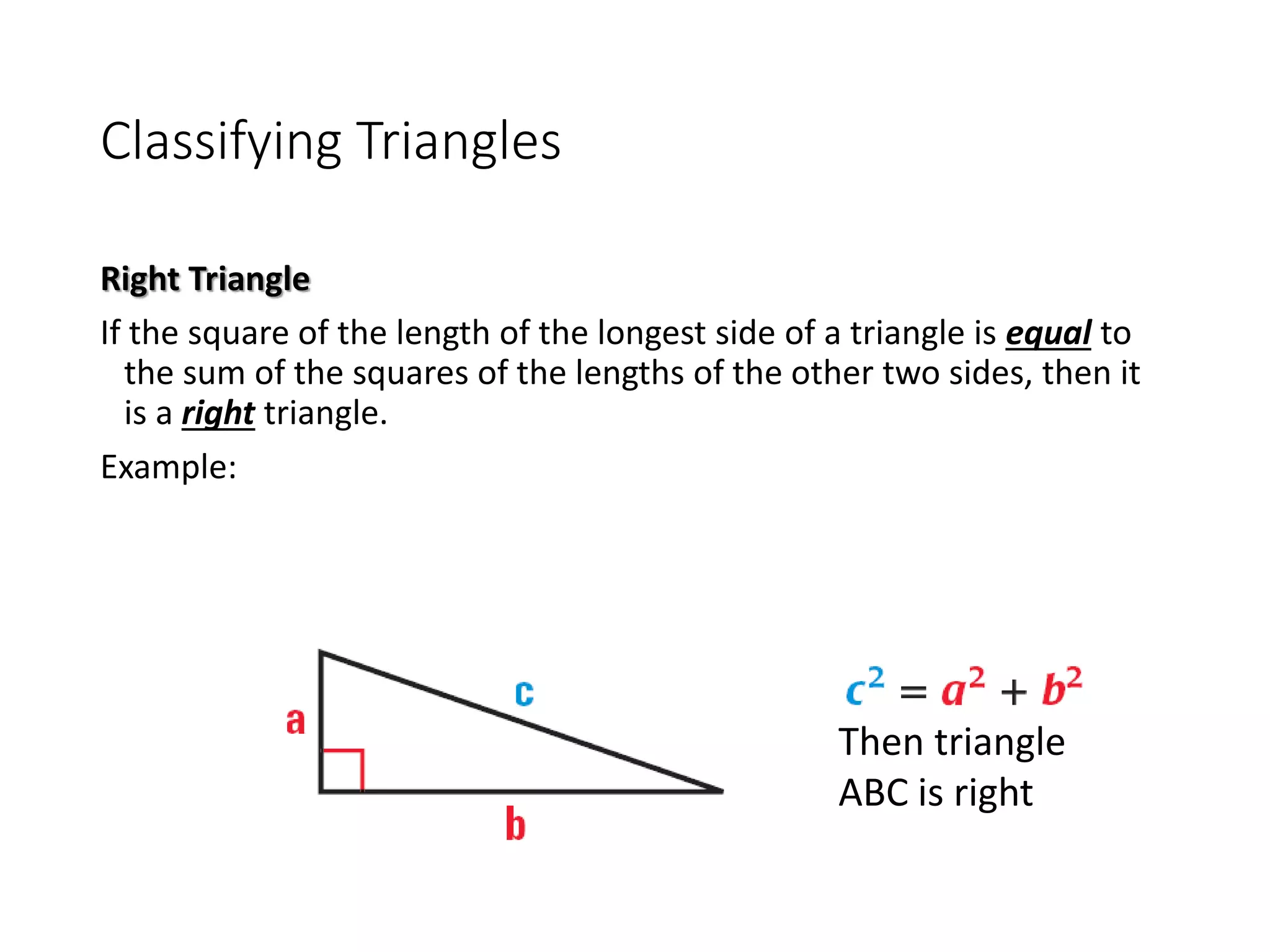
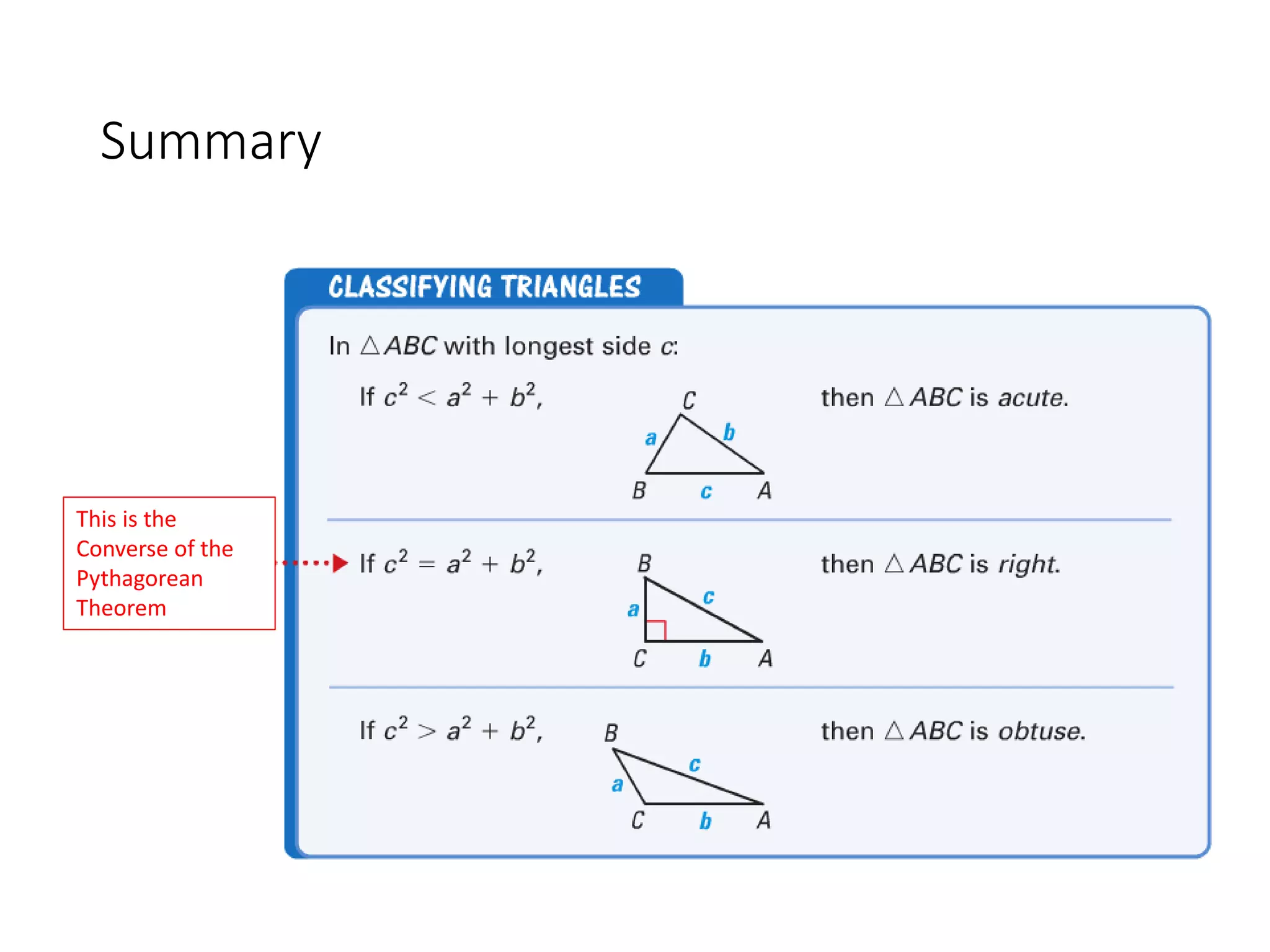
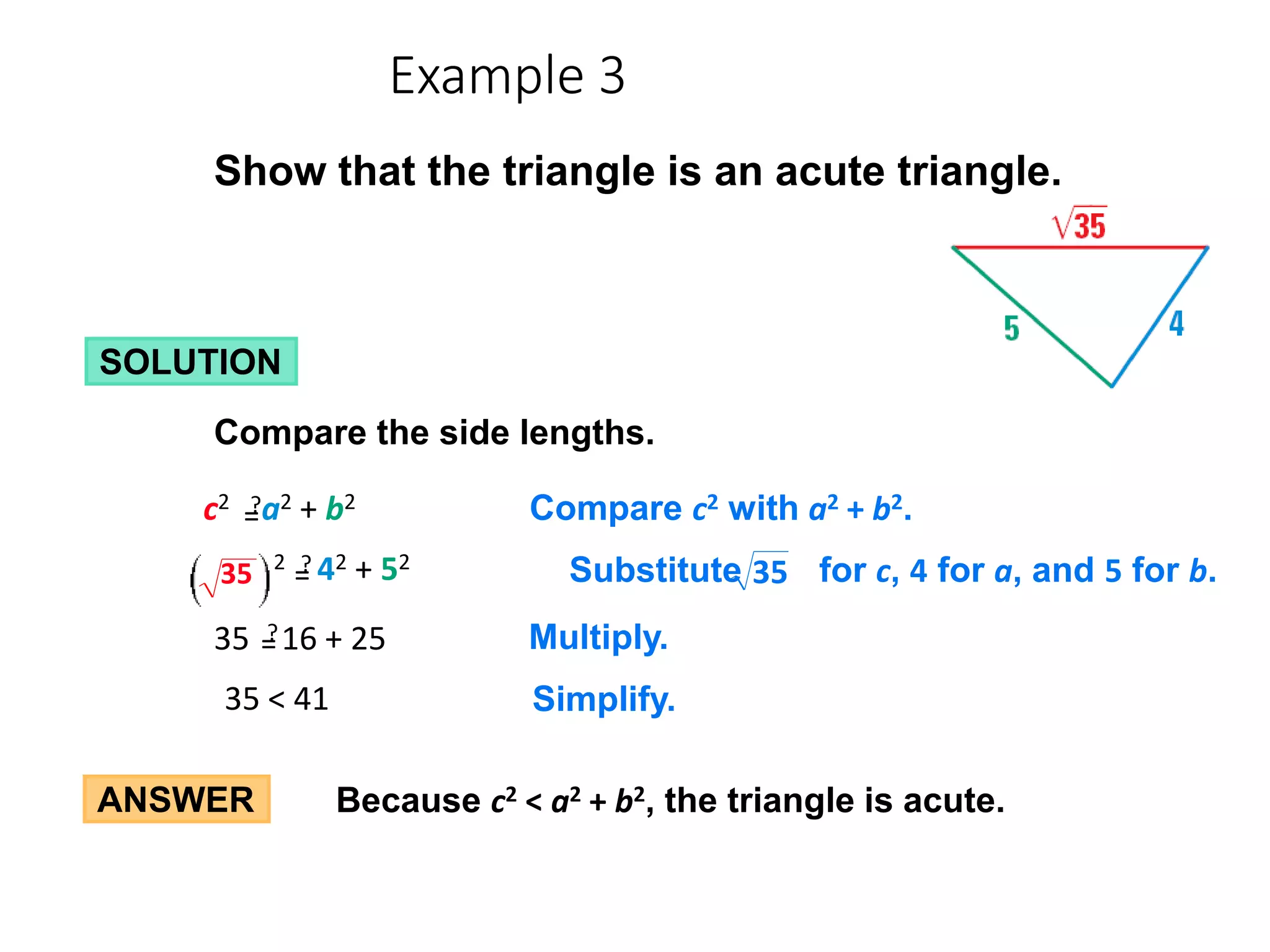
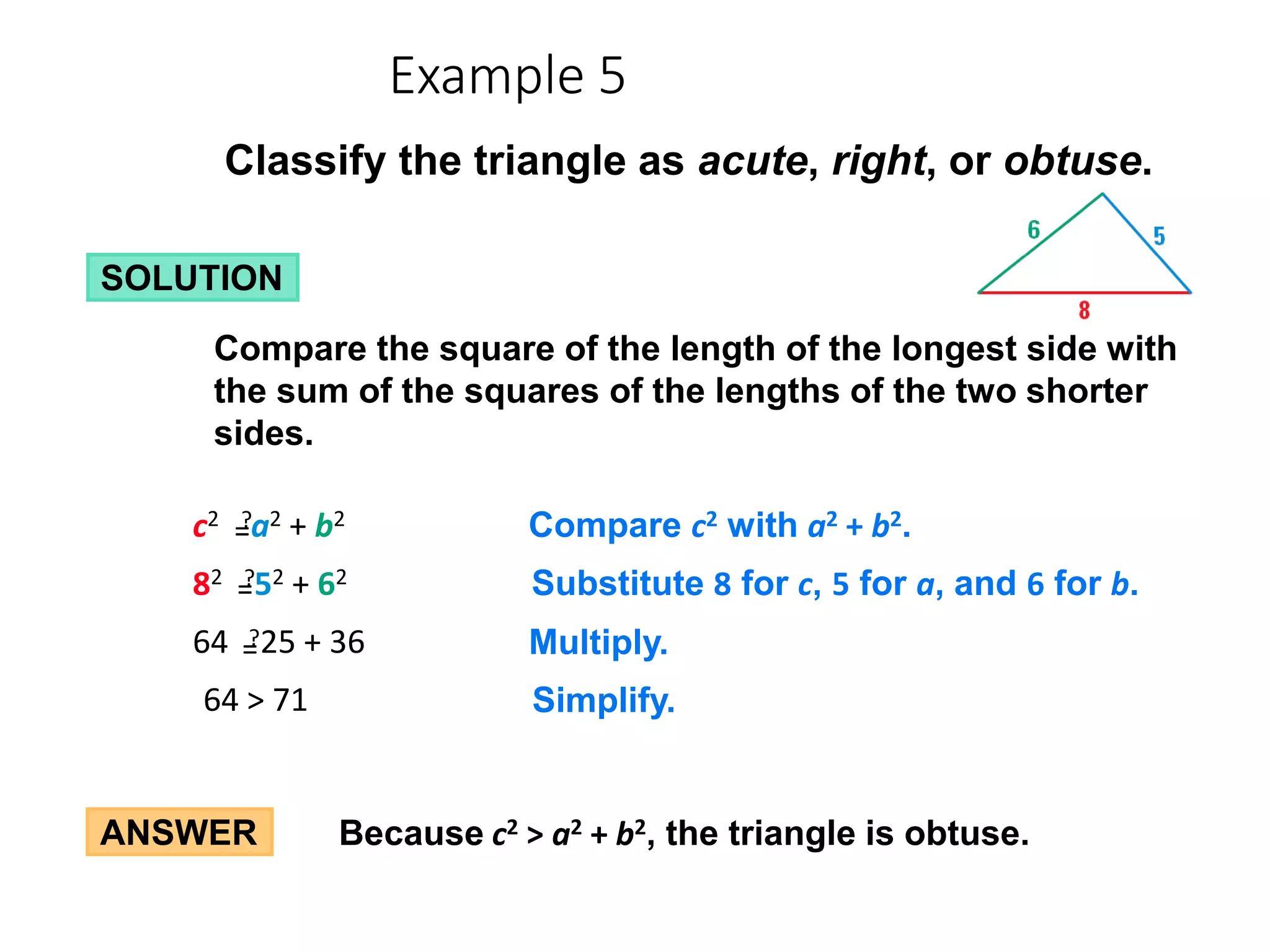
This document discusses the converse of the Pythagorean theorem and how to classify triangles as right, acute, or obtuse based on the lengths of their sides. The converse of the Pythagorean theorem states that if the square of the longest side of a triangle equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the triangle is right. If the square of the longest side is less than the sum of the squares of the other two sides, the triangle is acute. If it is greater, the triangle is obtuse. Several examples are provided to demonstrate how to use side lengths to determine the type of triangle.