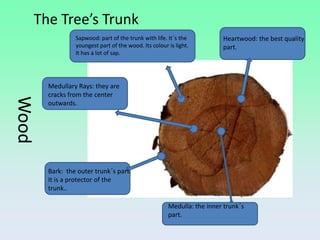
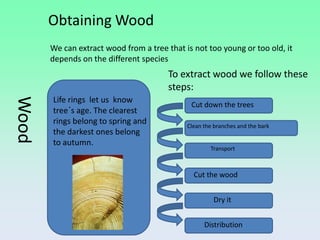
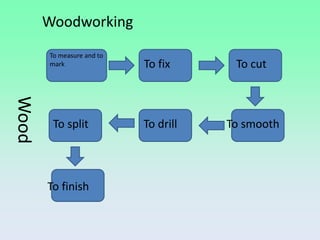
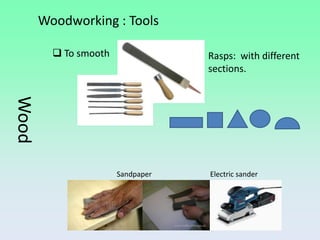
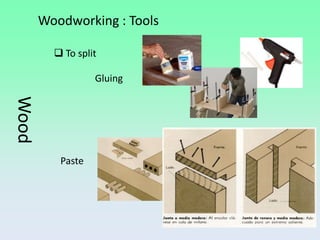
Wood is a natural material that was one of the first used by humans. Trees are cut down and processed to extract wood, which is then cut, dried, and distributed. There are different types of wood including softwoods and hardwoods. Wood can also be processed into wood derivatives like plywood, chipboard, and paper. Woodworking involves measuring, marking, cutting, drilling, smoothing, and finishing wood using both hand tools and power tools.