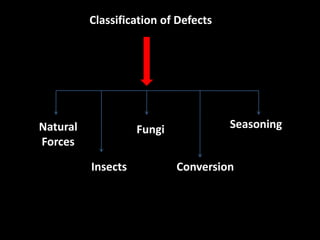
This document provides an overview of timber as a construction material. It begins with definitions of timber and discusses how trees are converted into usable wood. It then covers the various uses of timber in construction, including as forms for concrete, in scaffolding, and as a primary building material. The document discusses common timber species used in India and includes photos. It also examines the local market for timber, the workshop process, and cost comparisons. Finally, it details various defects that can occur in timber, grouping them by cause such as natural forces, fungi, insects, and the conversion process.