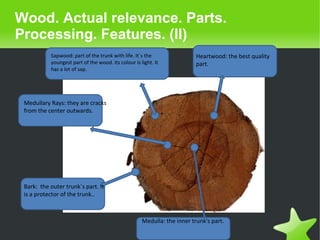
This document provides an overview of wood as a technical material. It discusses the history of materials usage from stone to modern times. Wood is described as a natural and still highly relevant material, with parts like bark, sapwood and heartwood. The document outlines wood processing techniques from cutting to drying. Different wood types like pine and oak are also covered. Derivative wood products like cardboard and types of boards are summarized. The environmental impact of deforestation and recycling is briefly mentioned at the end.