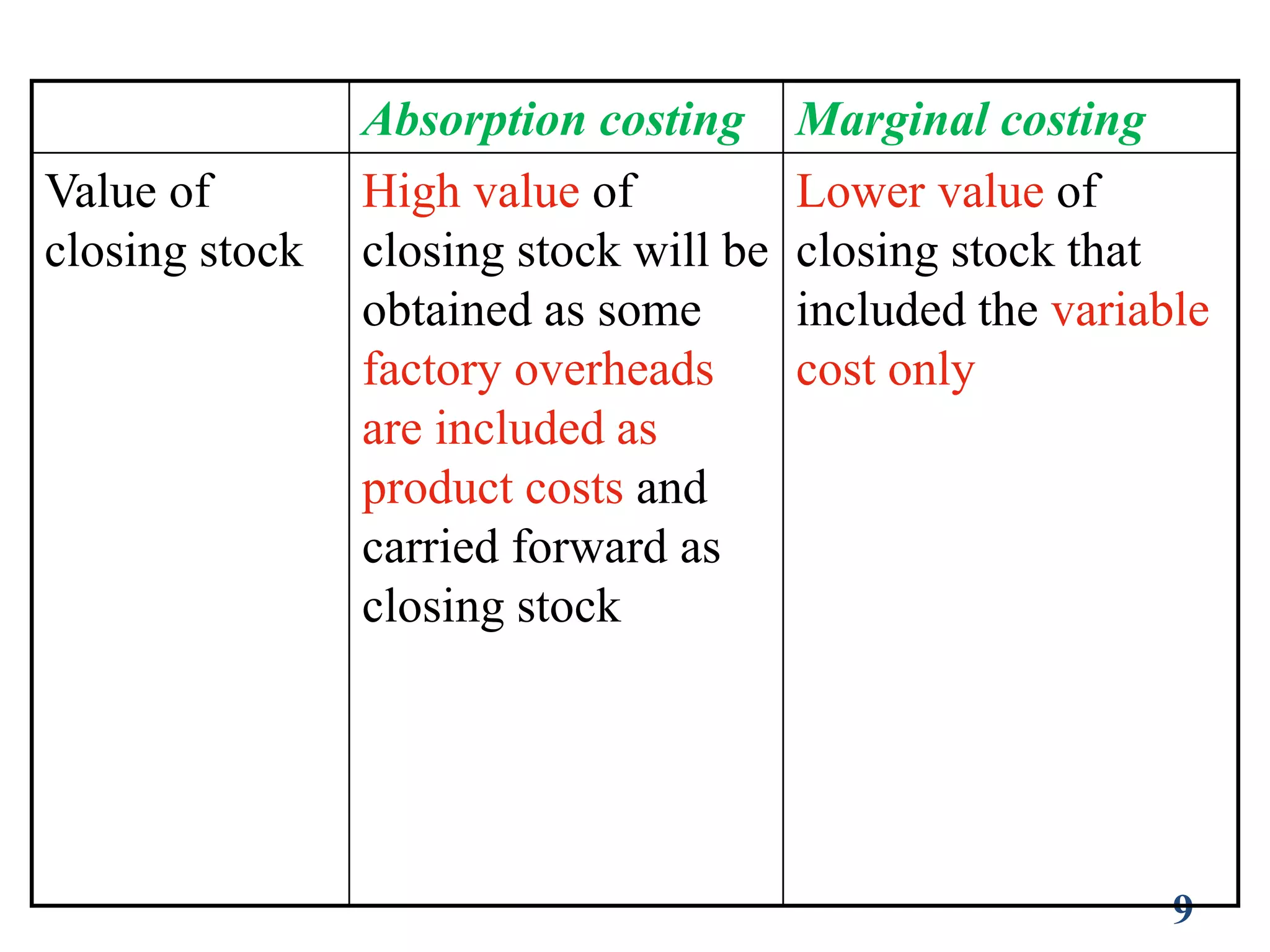
Marginal costing and absorption costing are two different costing methods. Absorption costing treats all manufacturing costs, including both fixed and variable costs, as product costs. Marginal costing only treats variable manufacturing costs as product costs and treats fixed costs as period costs. Absorption costing results in higher inventory valuations as it includes fixed overhead costs in product costs. Marginal costing is useful for decision making as it focuses only on variable costs relevant to production changes. While marginal costing is simpler, absorption costing follows accounting standards by fully allocating costs.