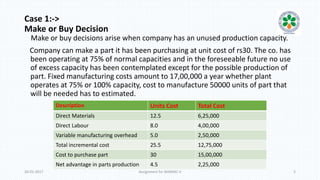
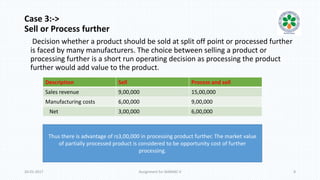
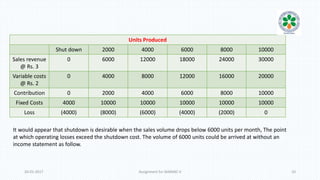
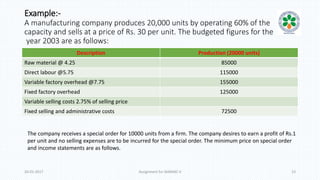
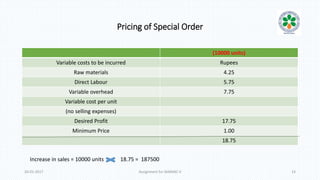
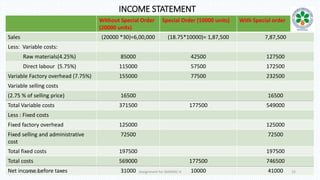
The document discusses decision-making processes in evaluating alternatives in business settings, focusing on relevant costs and revenues. It provides case studies such as make or buy decisions, product discontinuation, and special orders, illustrating the important concepts of differential costs and contributions to net income. Ultimately, it emphasizes that making informed choices requires analyzing costs and revenues associated with each alternative to optimize business outcomes.