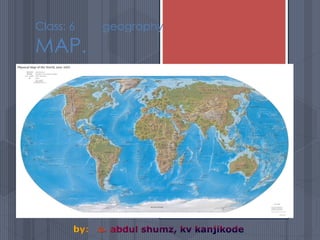
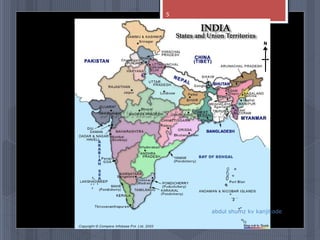
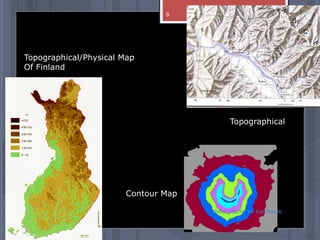
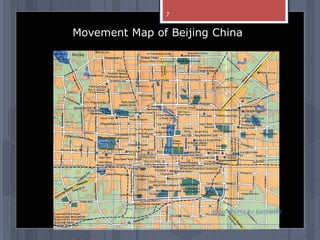
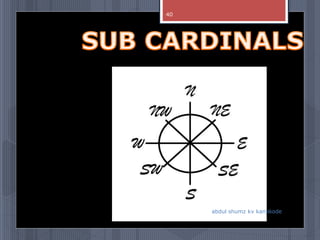
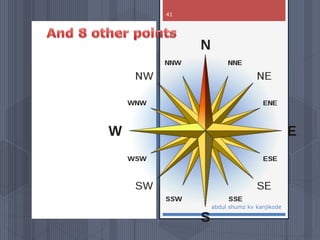
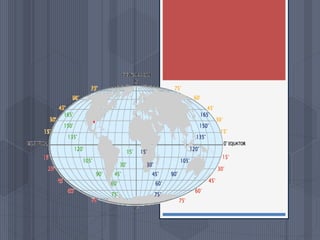
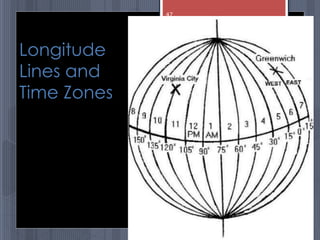
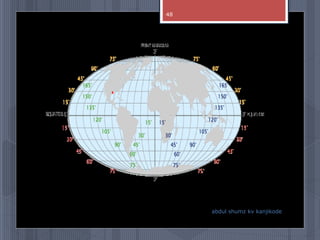
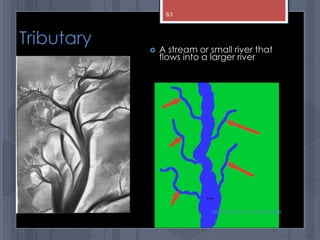
A map is a graphical representation of an area using symbols and a scale. The document outlines the key parts of a map including the legend, cardinal directions, scale, and landforms/water features. It also describes different types of maps like political, physical, and thematic maps. Finally, it discusses important map elements such as latitude and longitude lines, grids, and landforms.