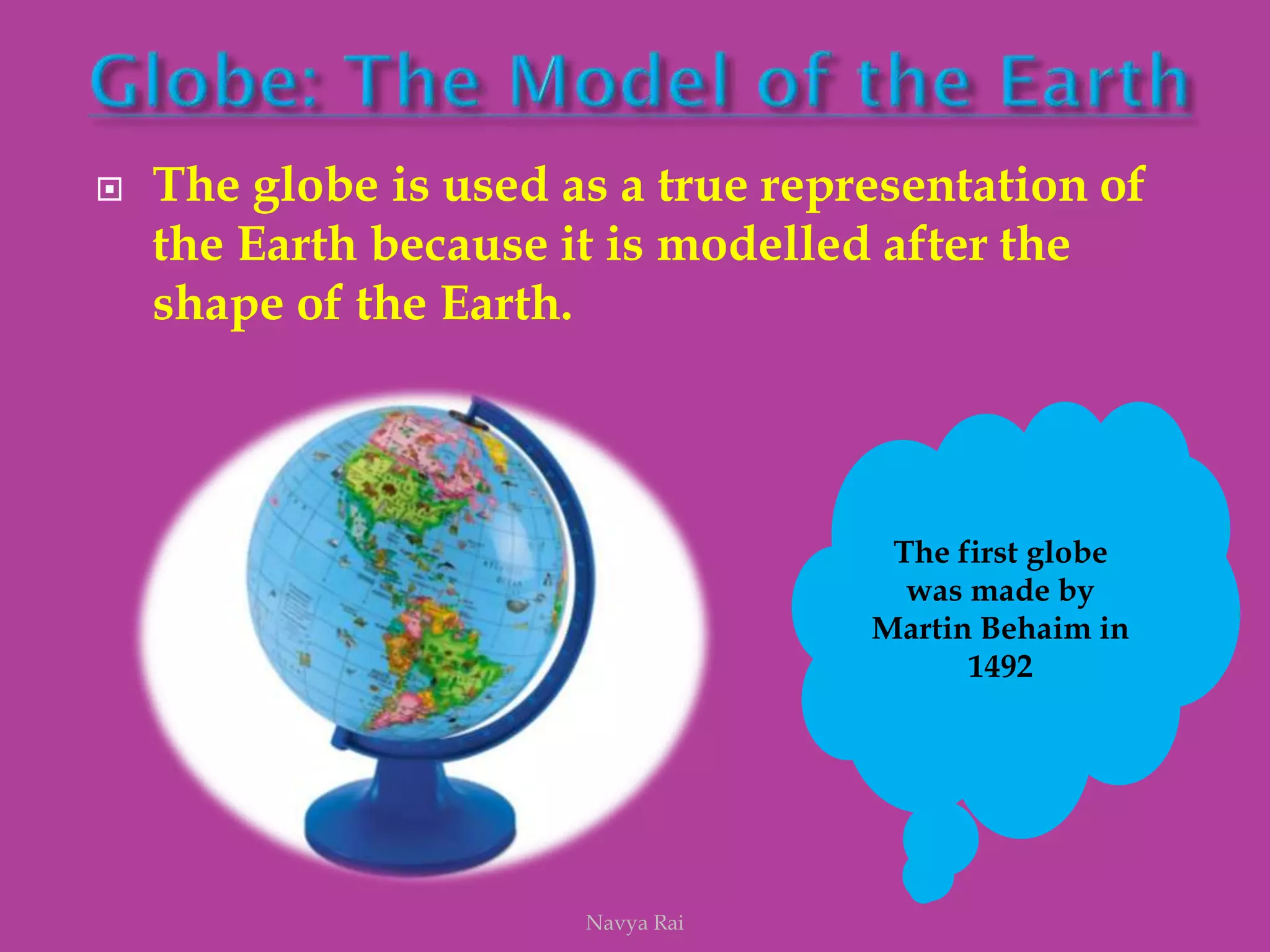
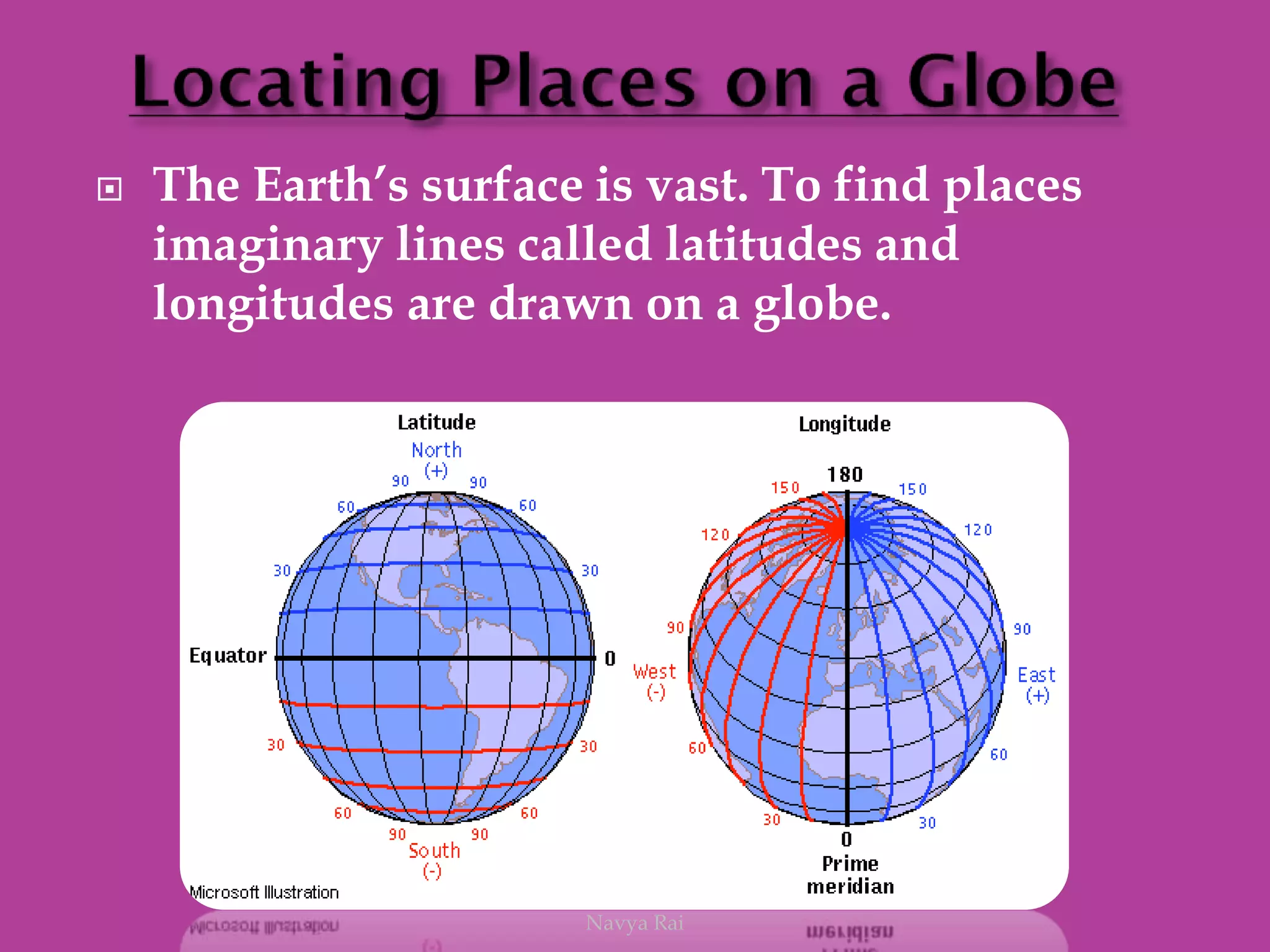
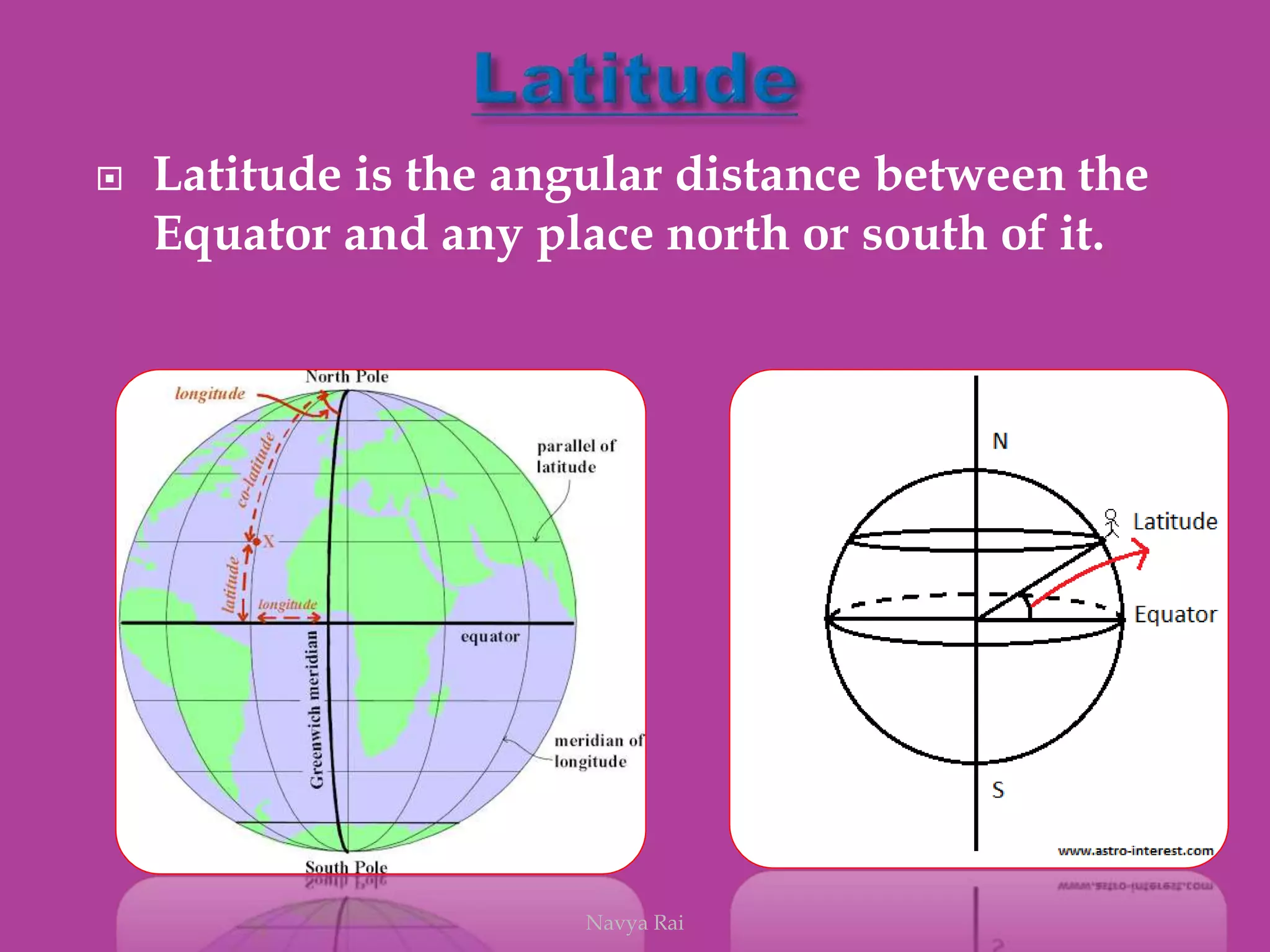
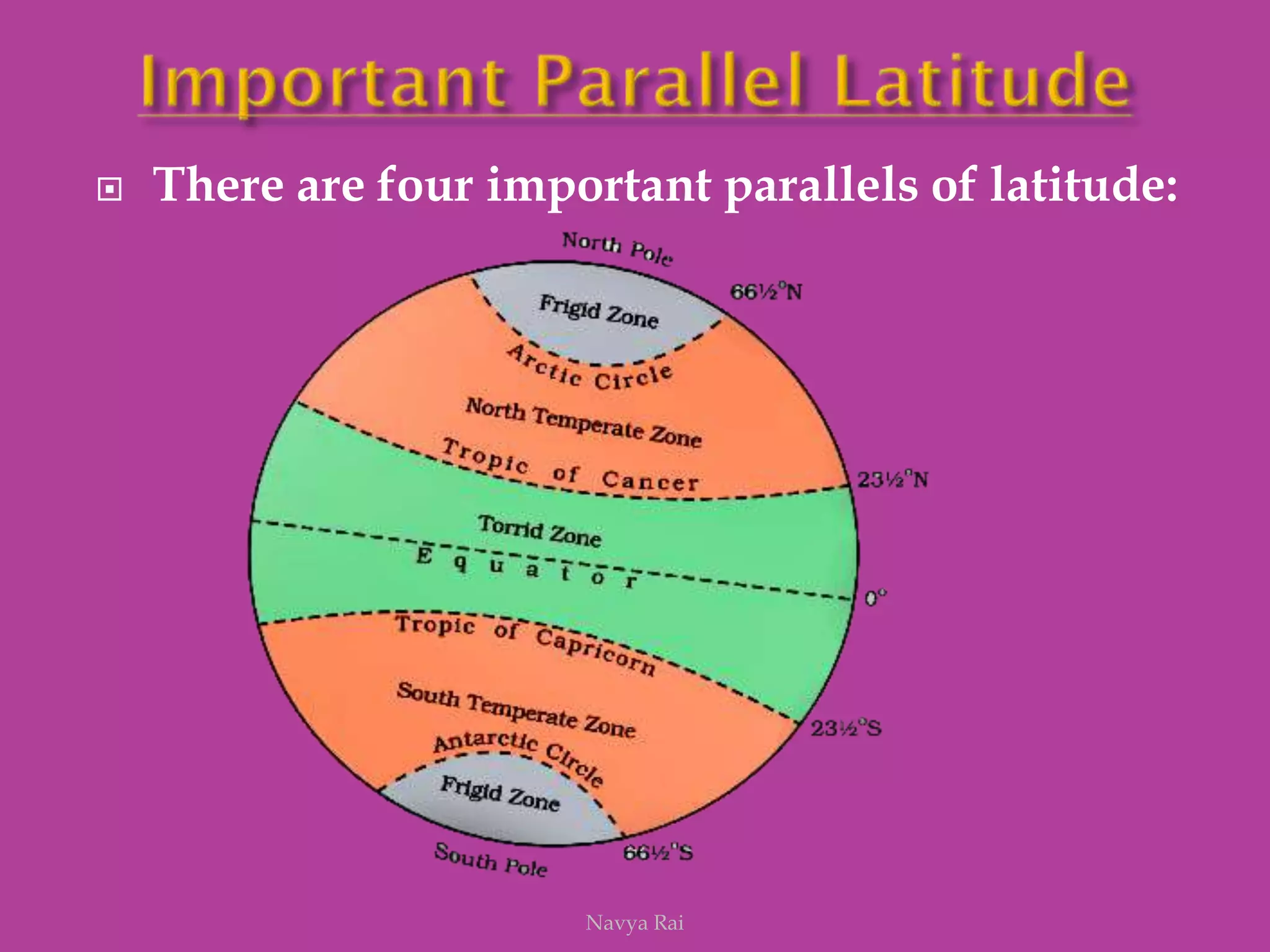
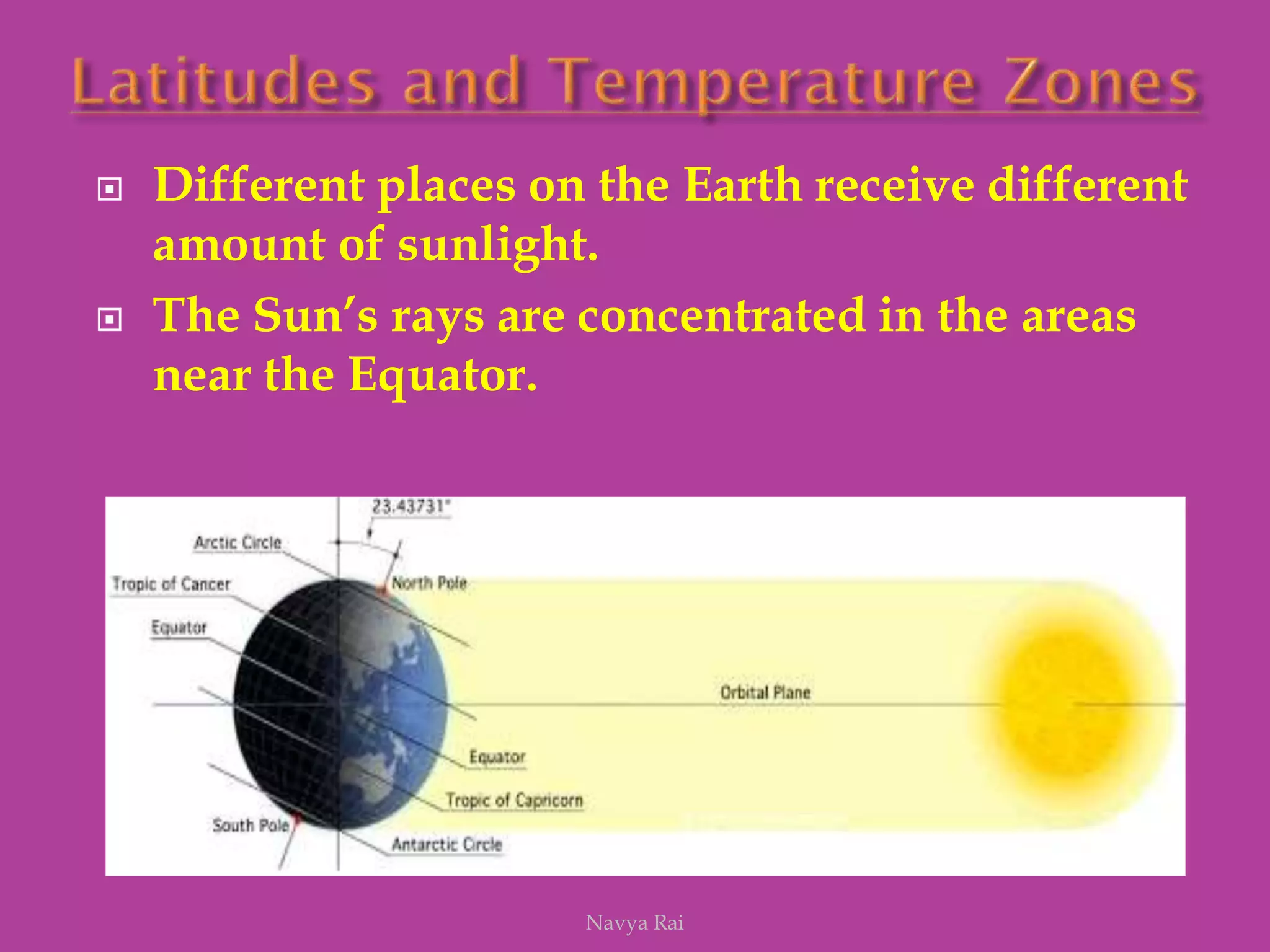
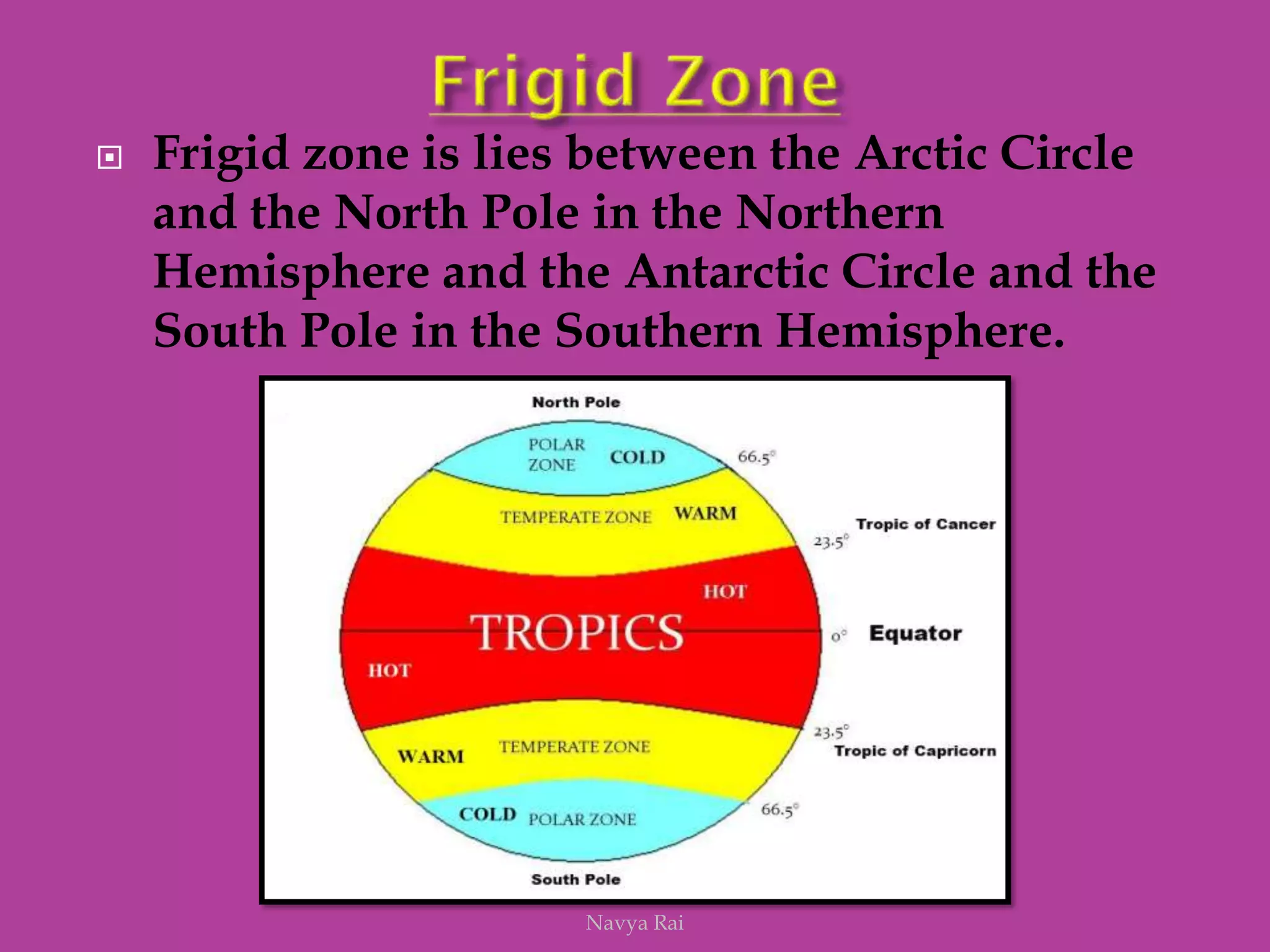
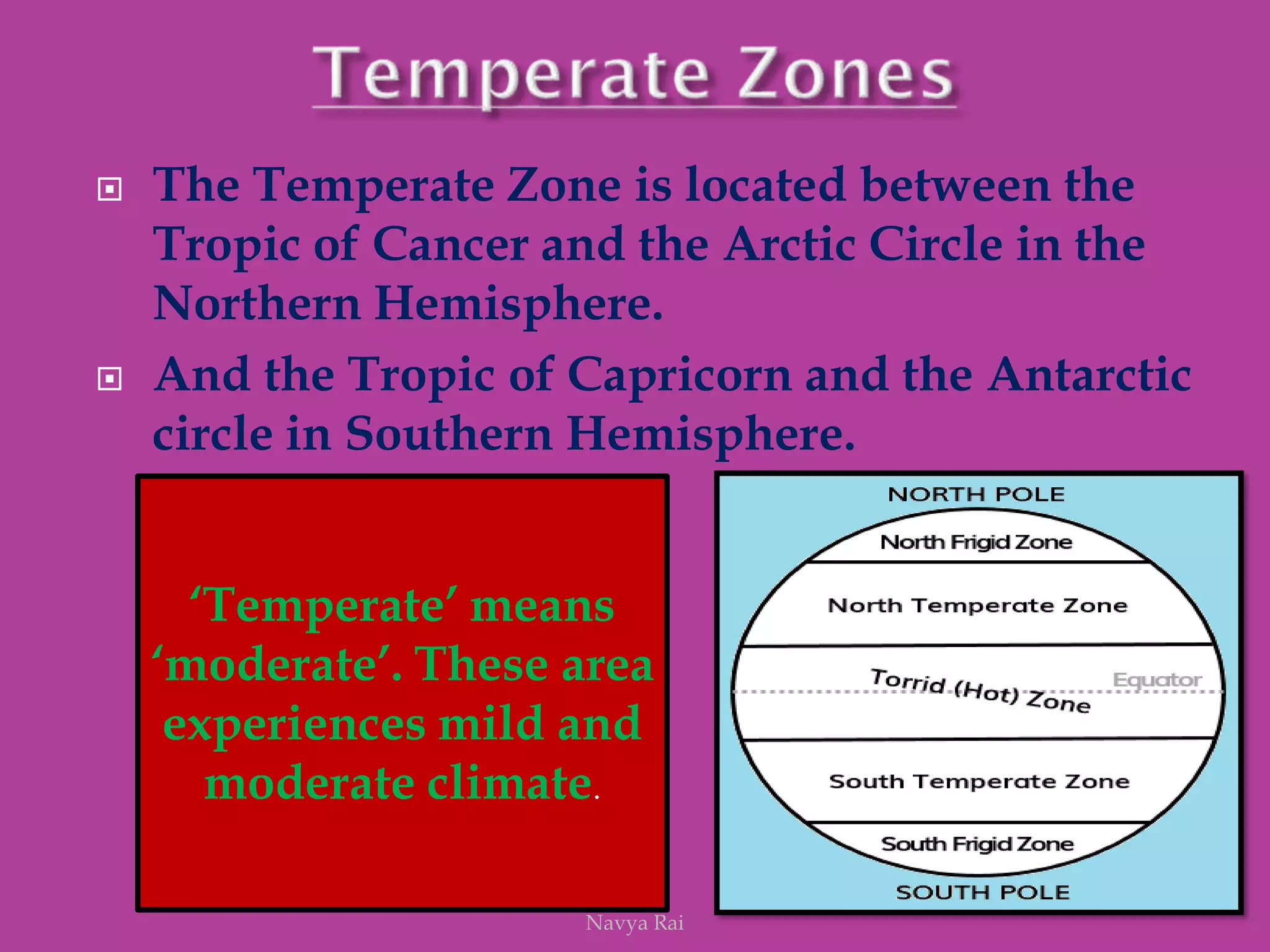
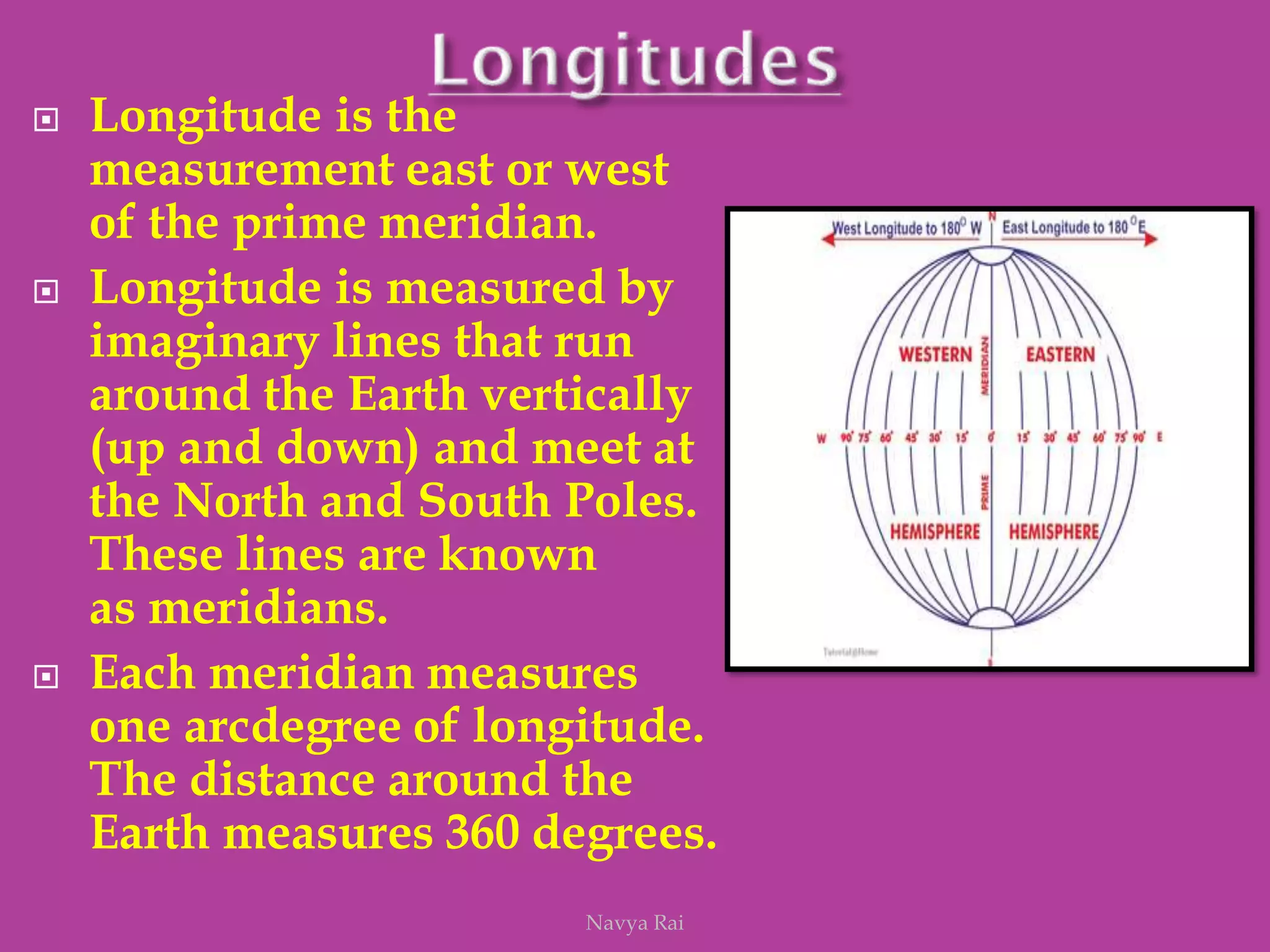
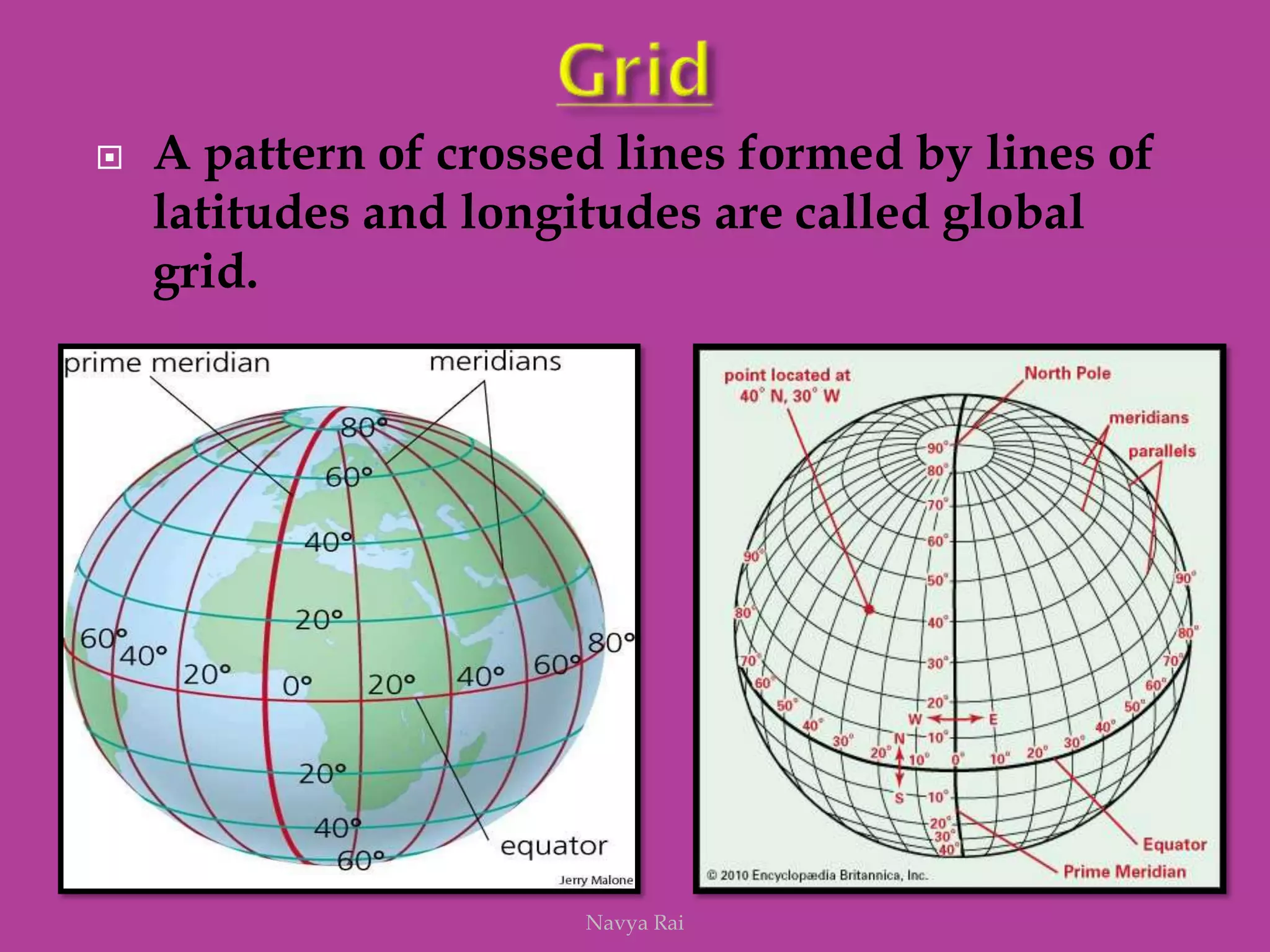
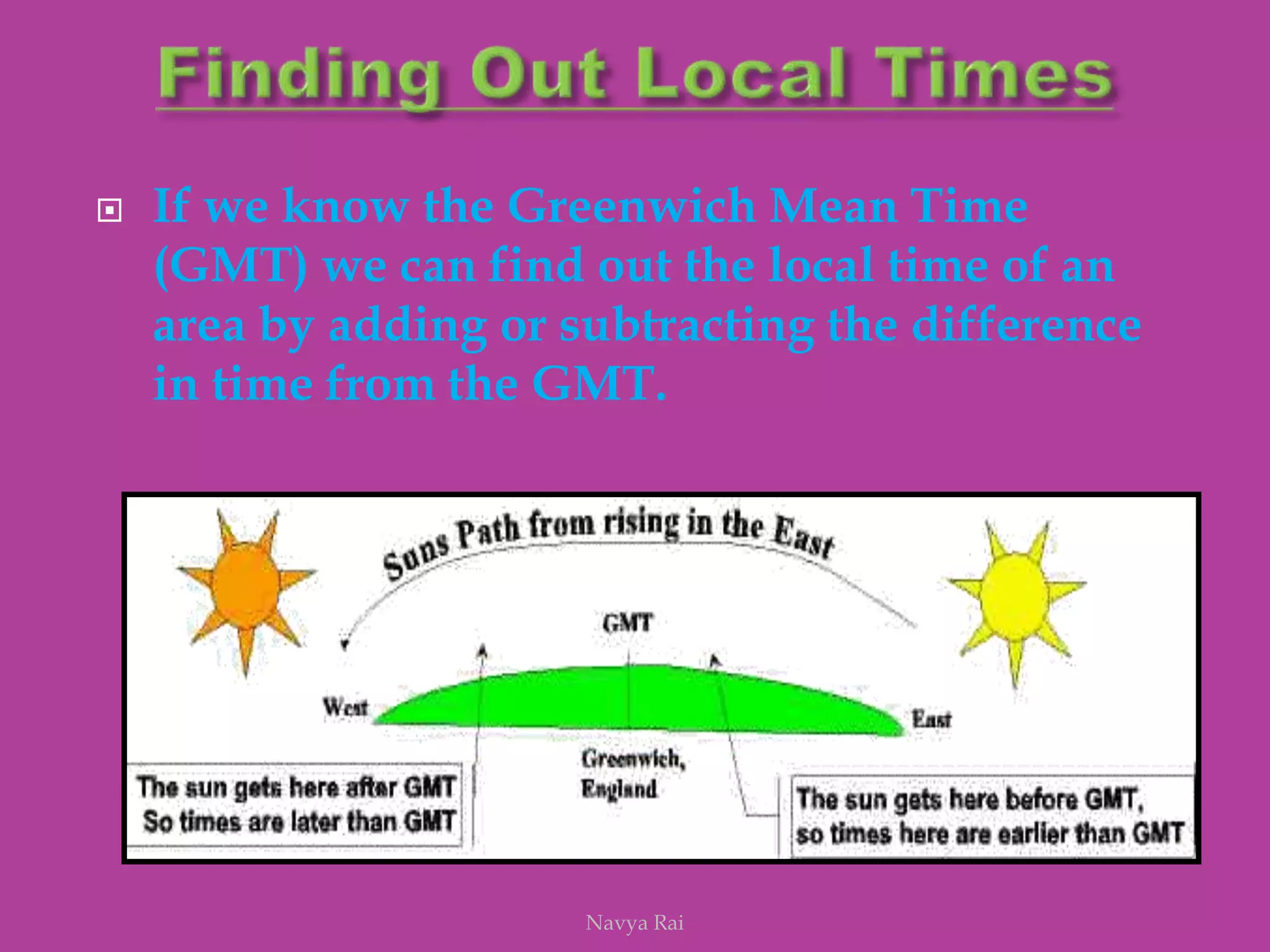
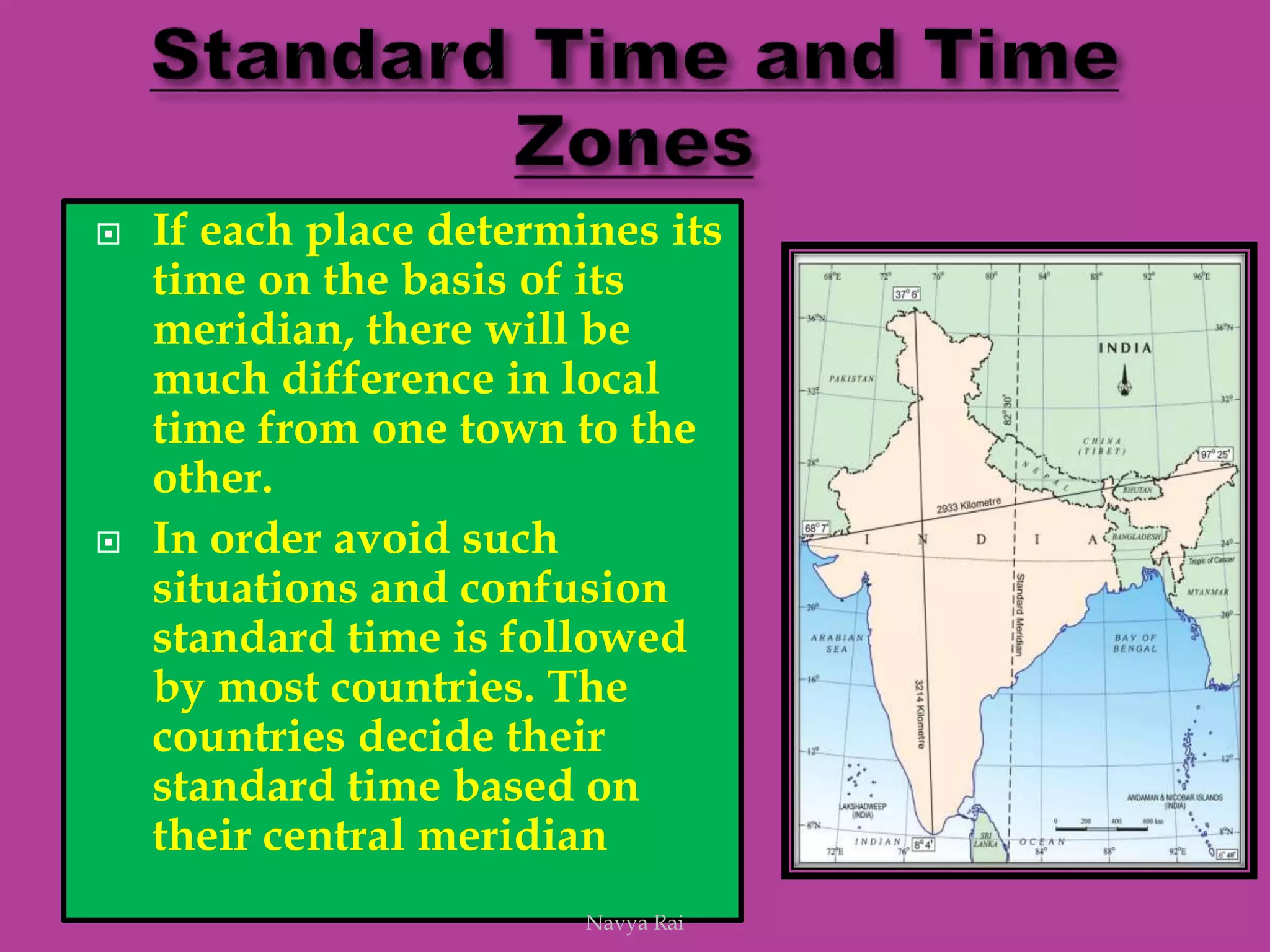
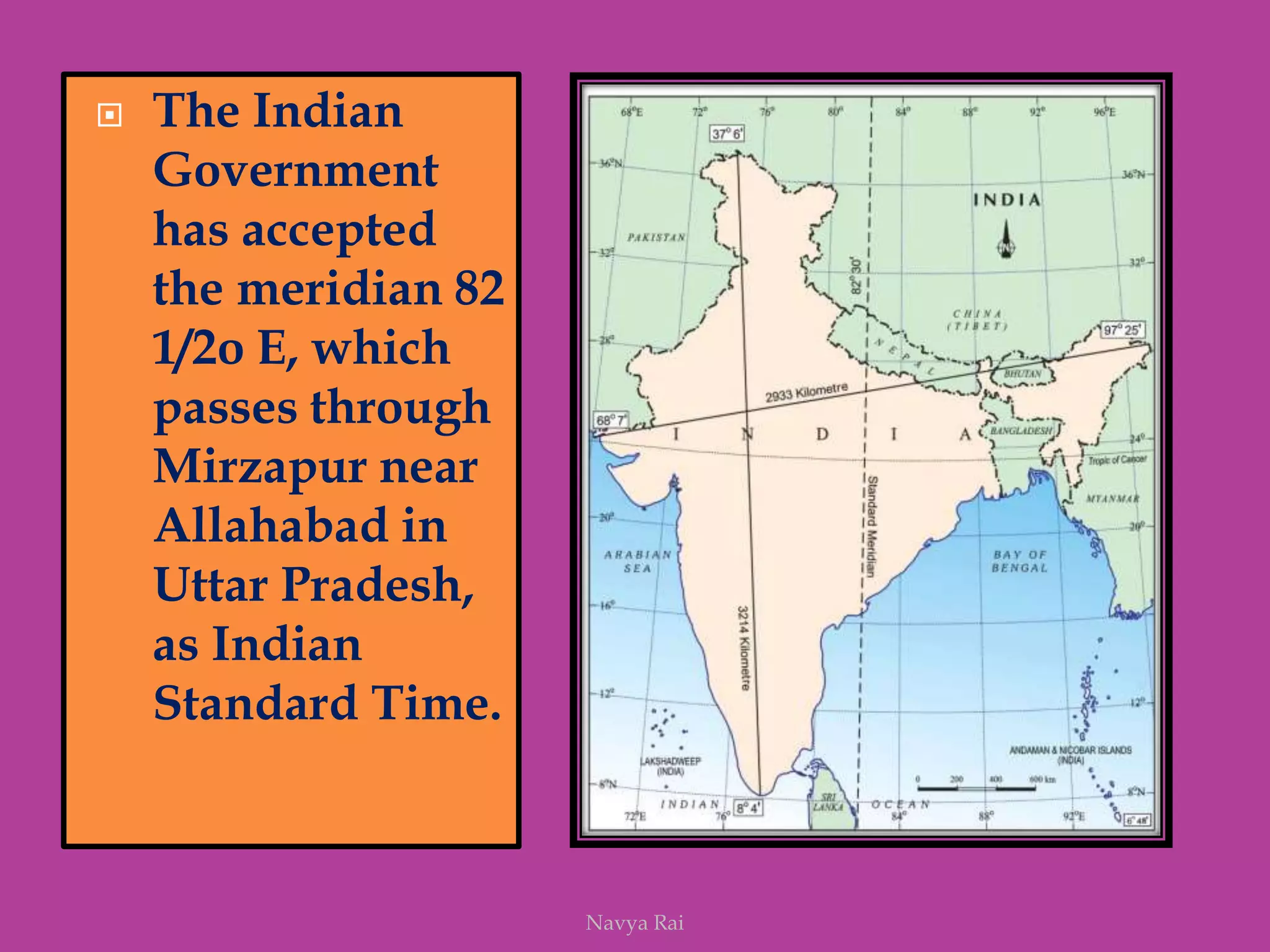
The document explains the geoid shape of the Earth, its rotation, and the significance of poles, with the north pointed towards the pole star and the south as the opposite end. It covers the concepts of latitude and longitude, including the division of the Earth into different zones such as frigid, temperate, and torrid, and the establishment of time zones based on meridians. Additionally, it discusses the Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) and the International Date Line, emphasizing the need for standard time to avoid discrepancies across different regions.