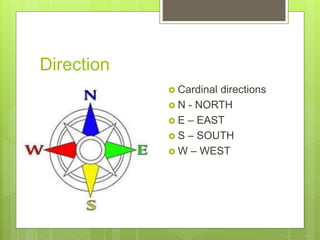
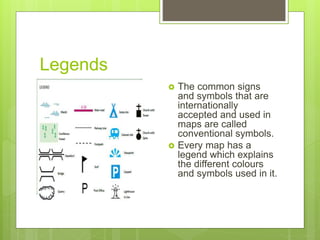
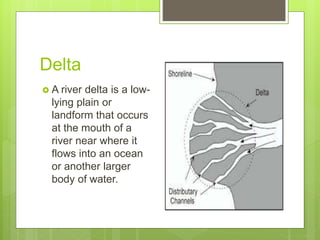
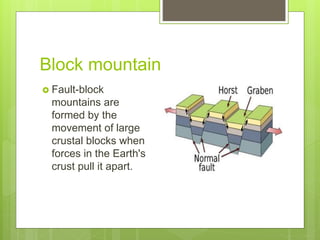
This document outlines key features and components of maps. It discusses that maps symbolically represent characteristics of places on flat surfaces. The two essential features are a title, which provides information about the map's content, and direction indicators like cardinal and intermediate directions. Other components covered include scale, legends, common geographic symbols, and grid systems using parallels of latitude and meridians of longitude.