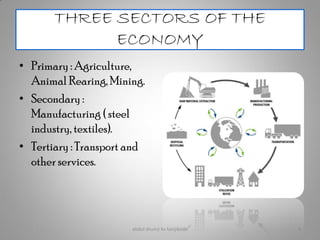
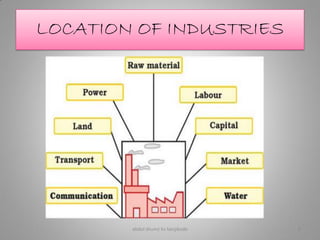
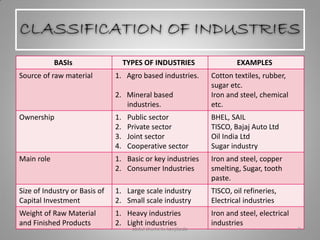
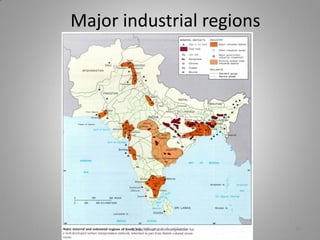
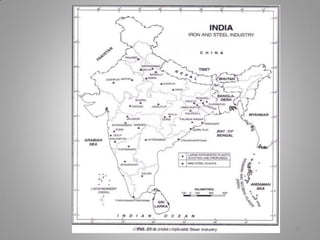
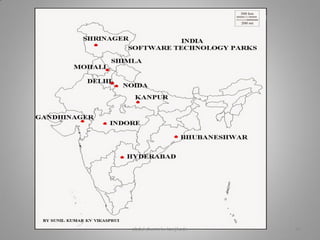
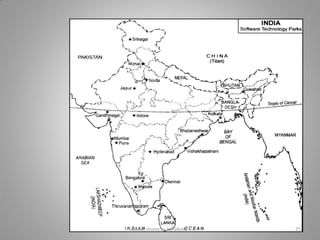
Manufacturing transforms raw materials into finished goods through processing. It is an important sector that contributes to economic development by providing jobs, income, and value-added products. The document outlines key industries like textiles, sugar, iron and steel, chemicals, cement, automobiles and information technology. It also discusses factors influencing industry location, classification of industries, issues like pollution, and measures to control pollution. Manufacturing is divided into primary, secondary and tertiary economic sectors and plays a vital role in modernizing agriculture and reducing poverty.