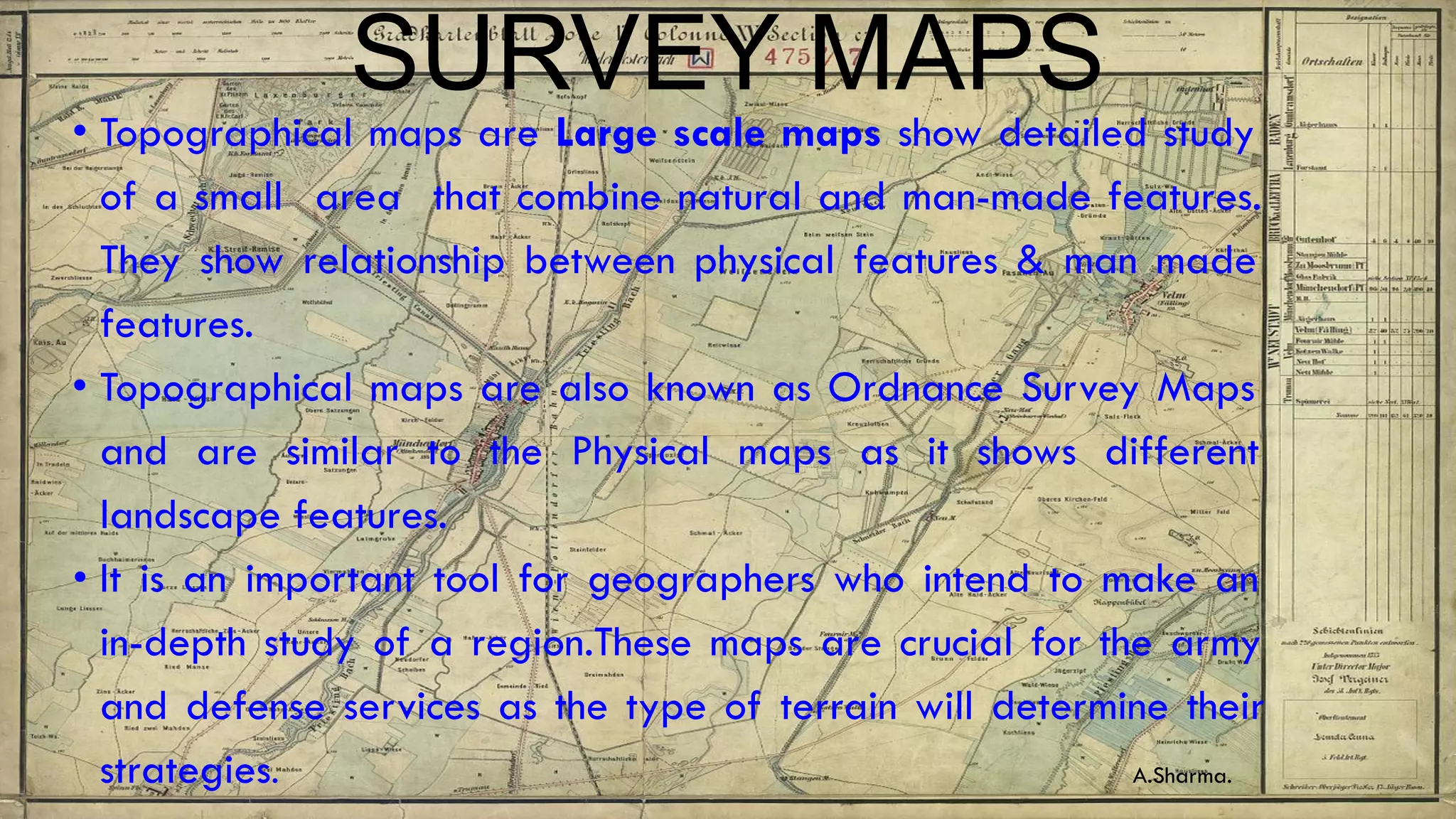
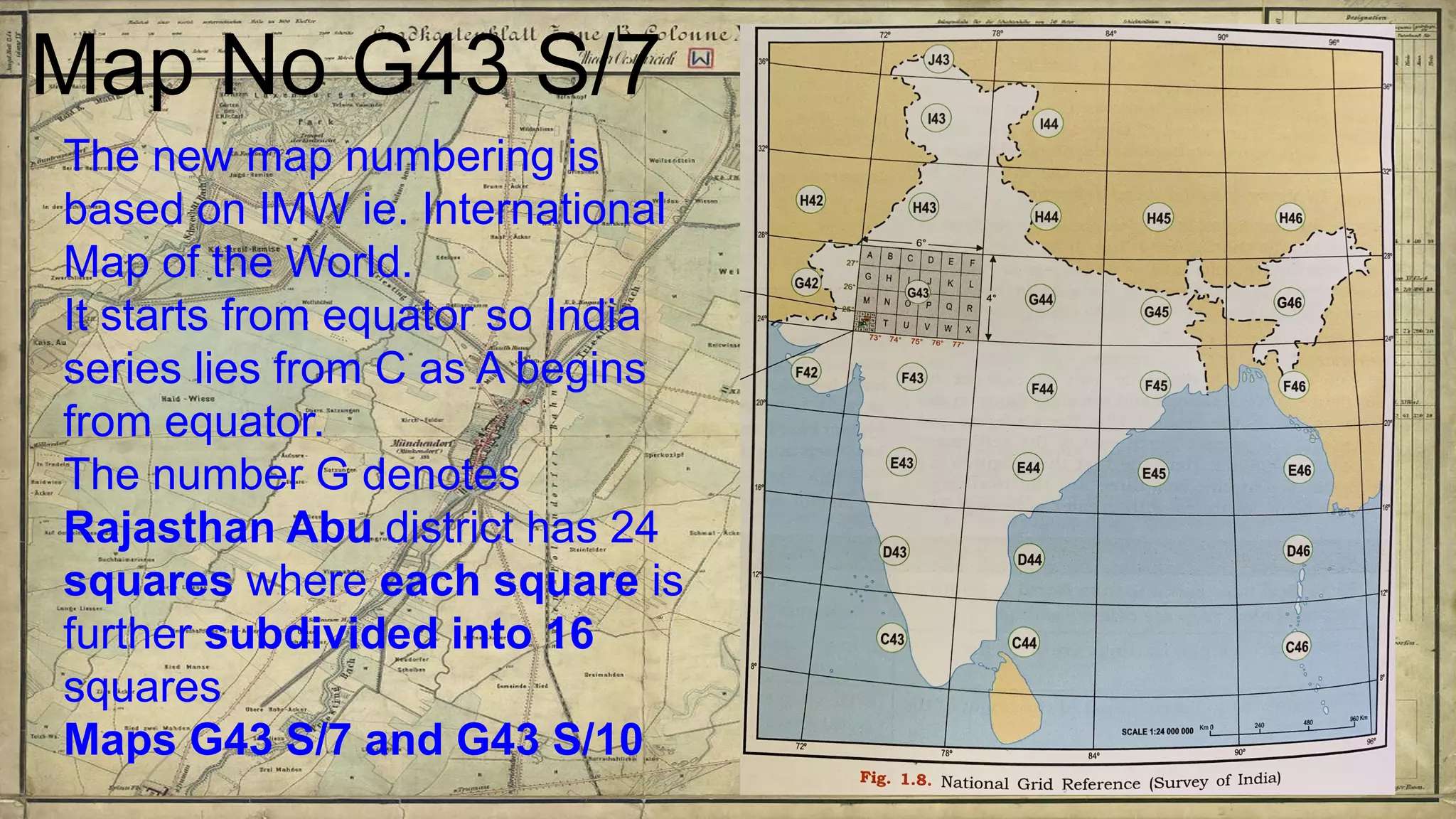
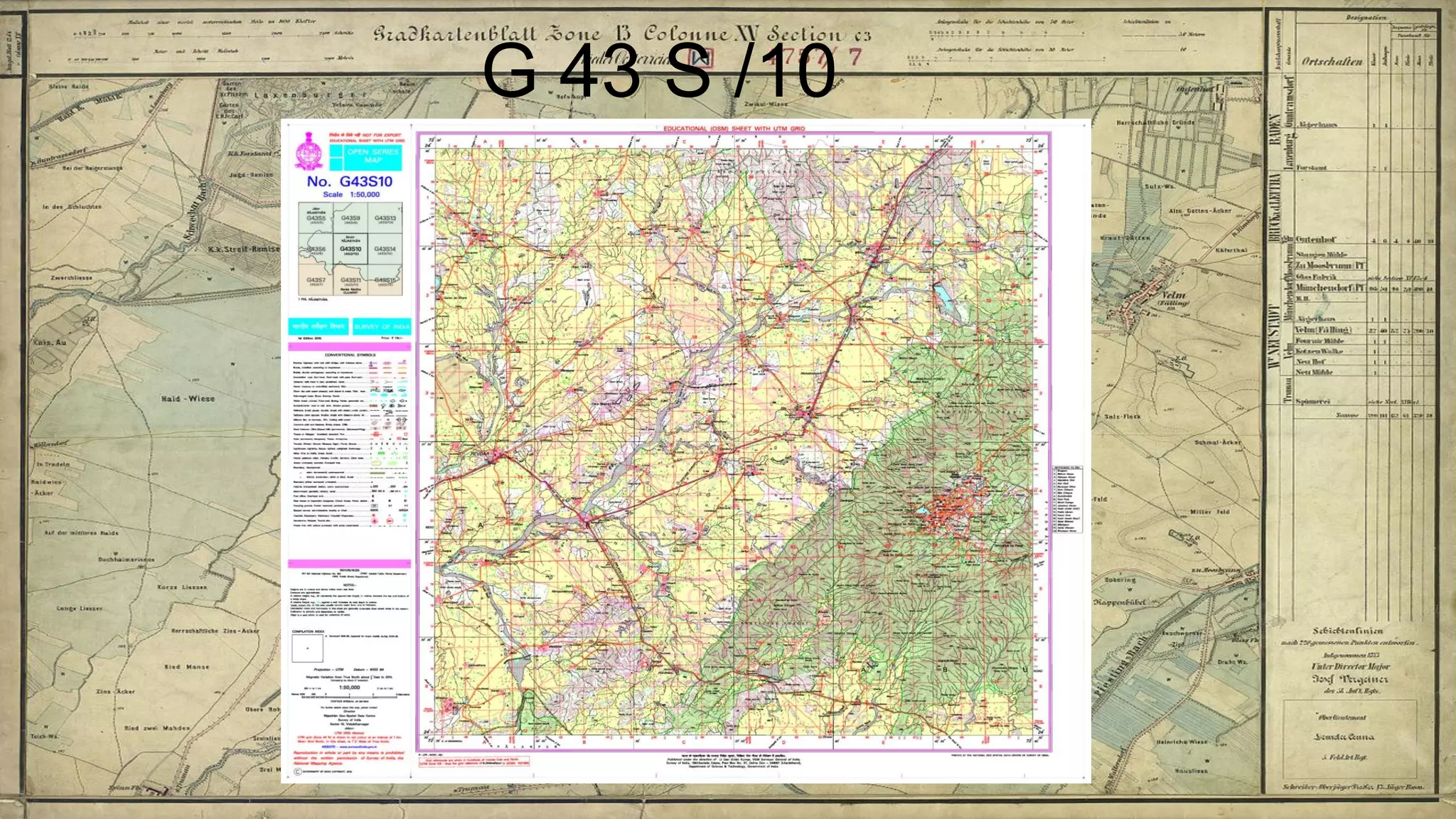
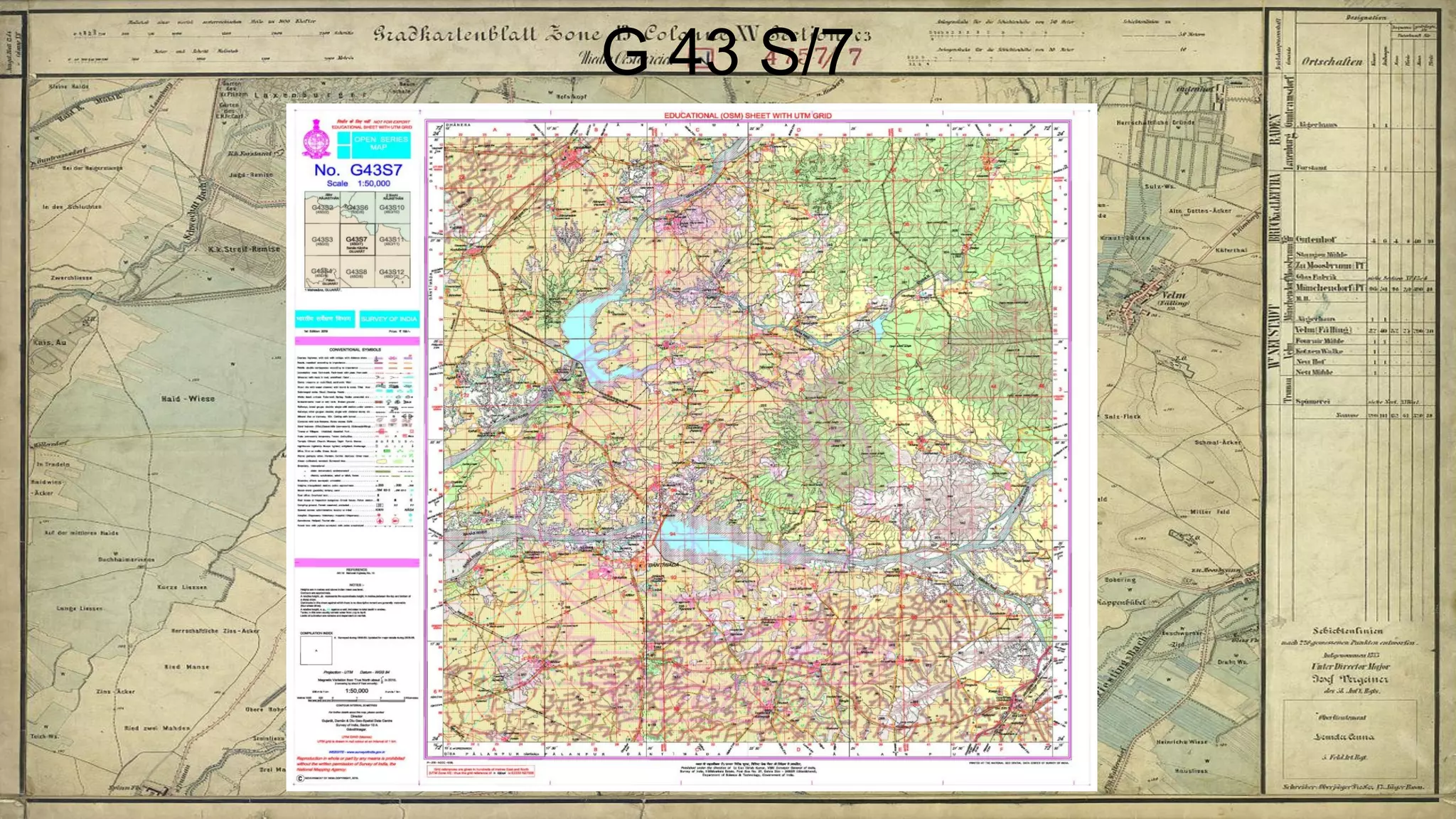
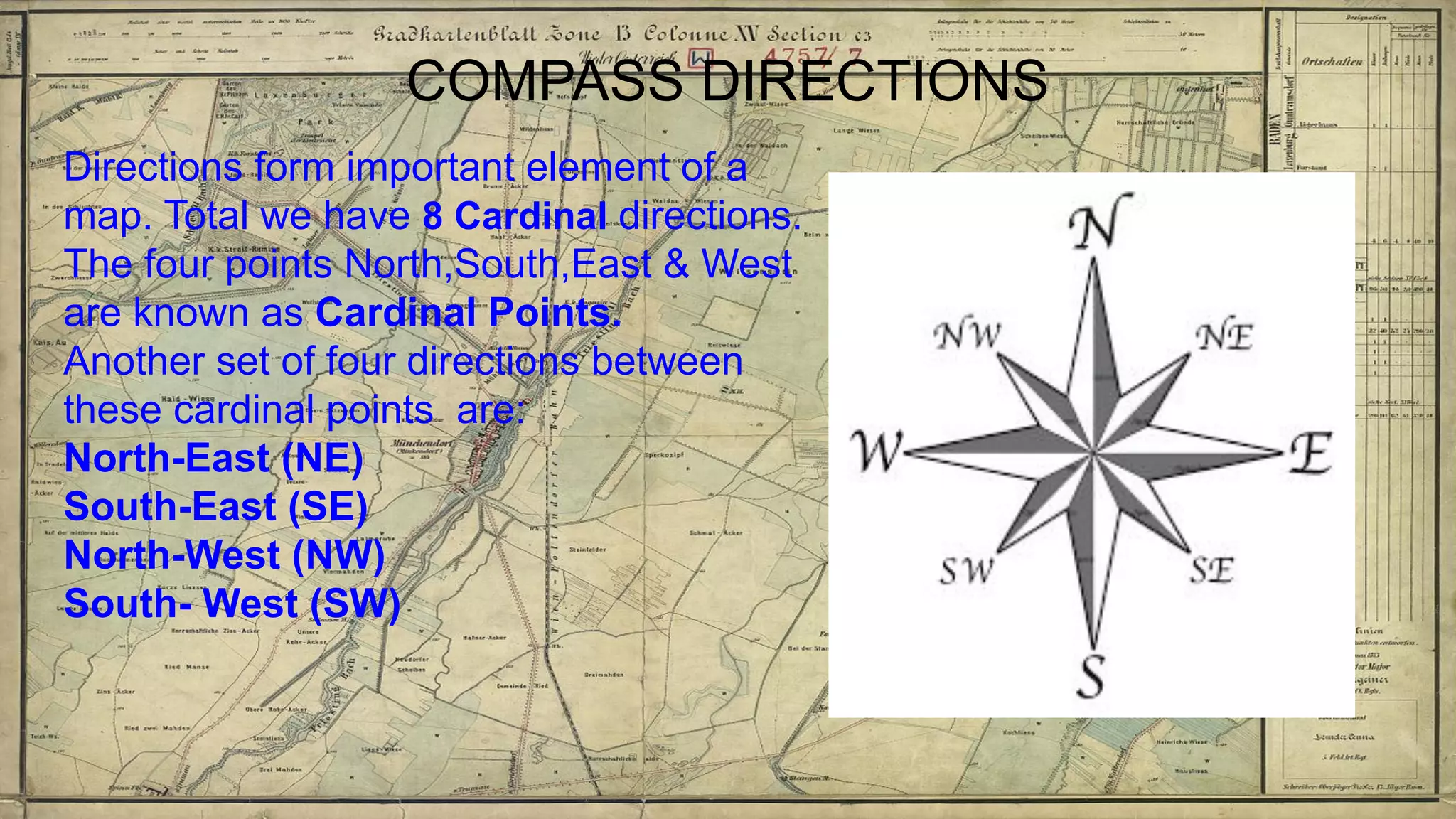
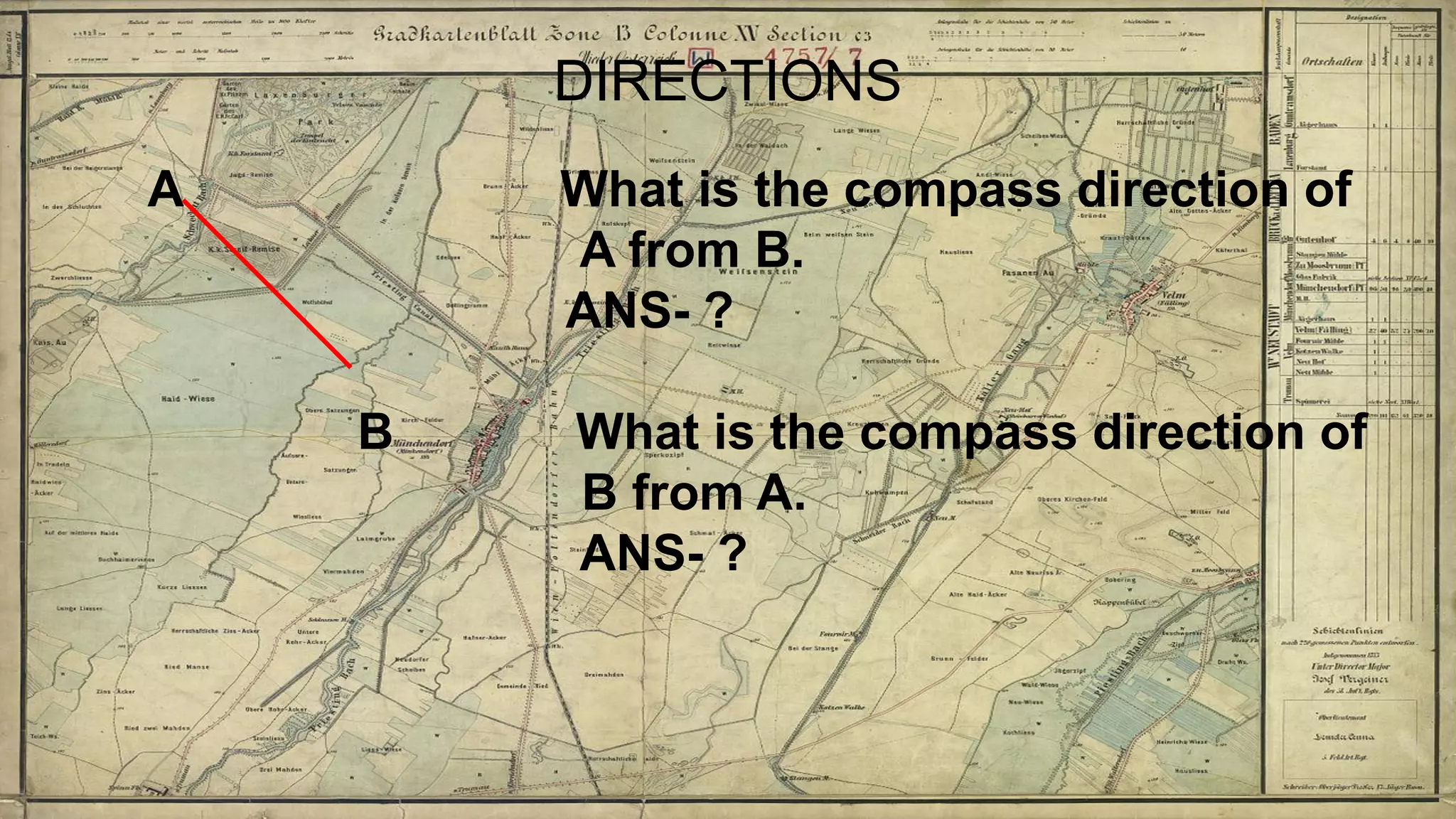
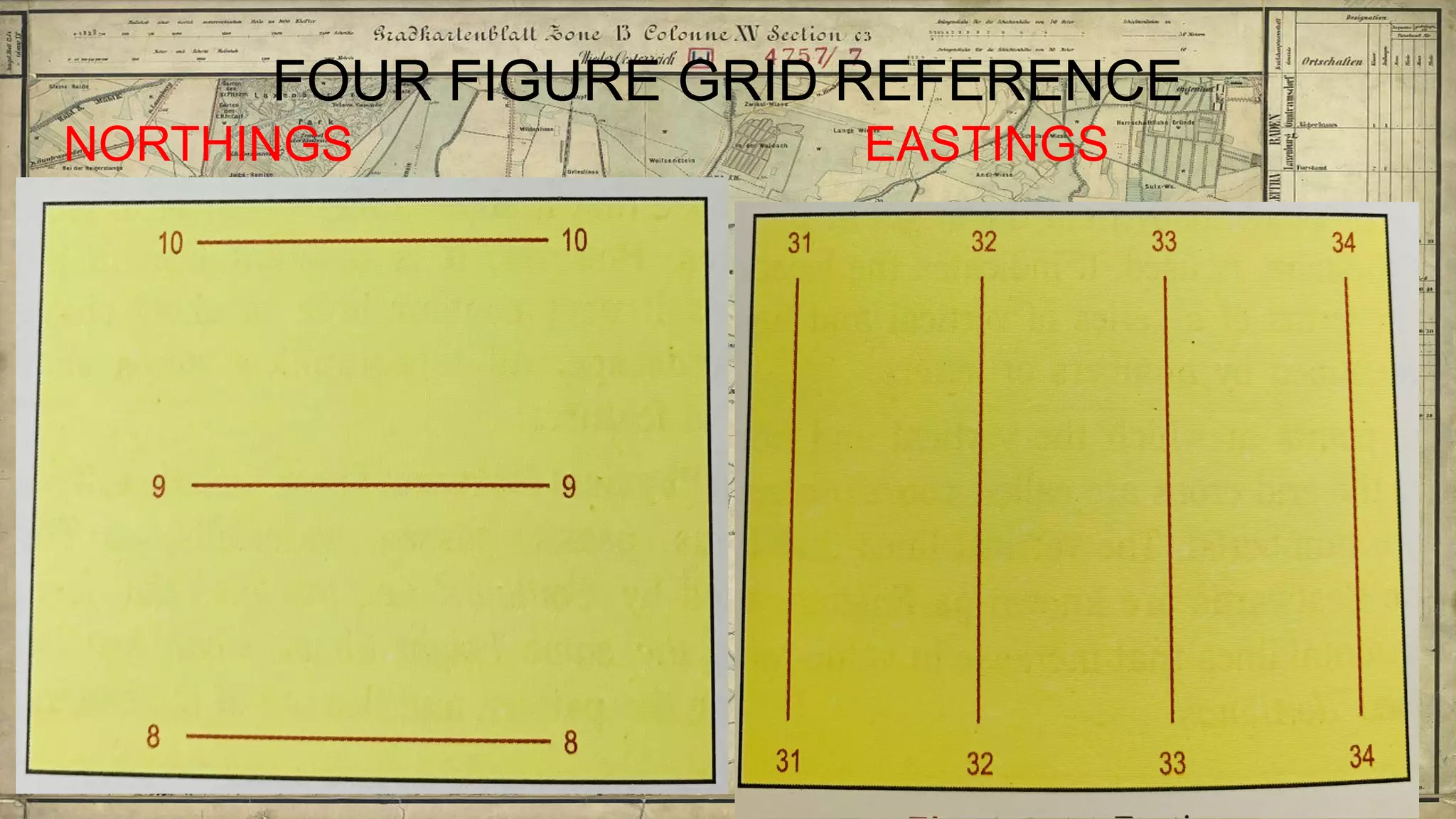
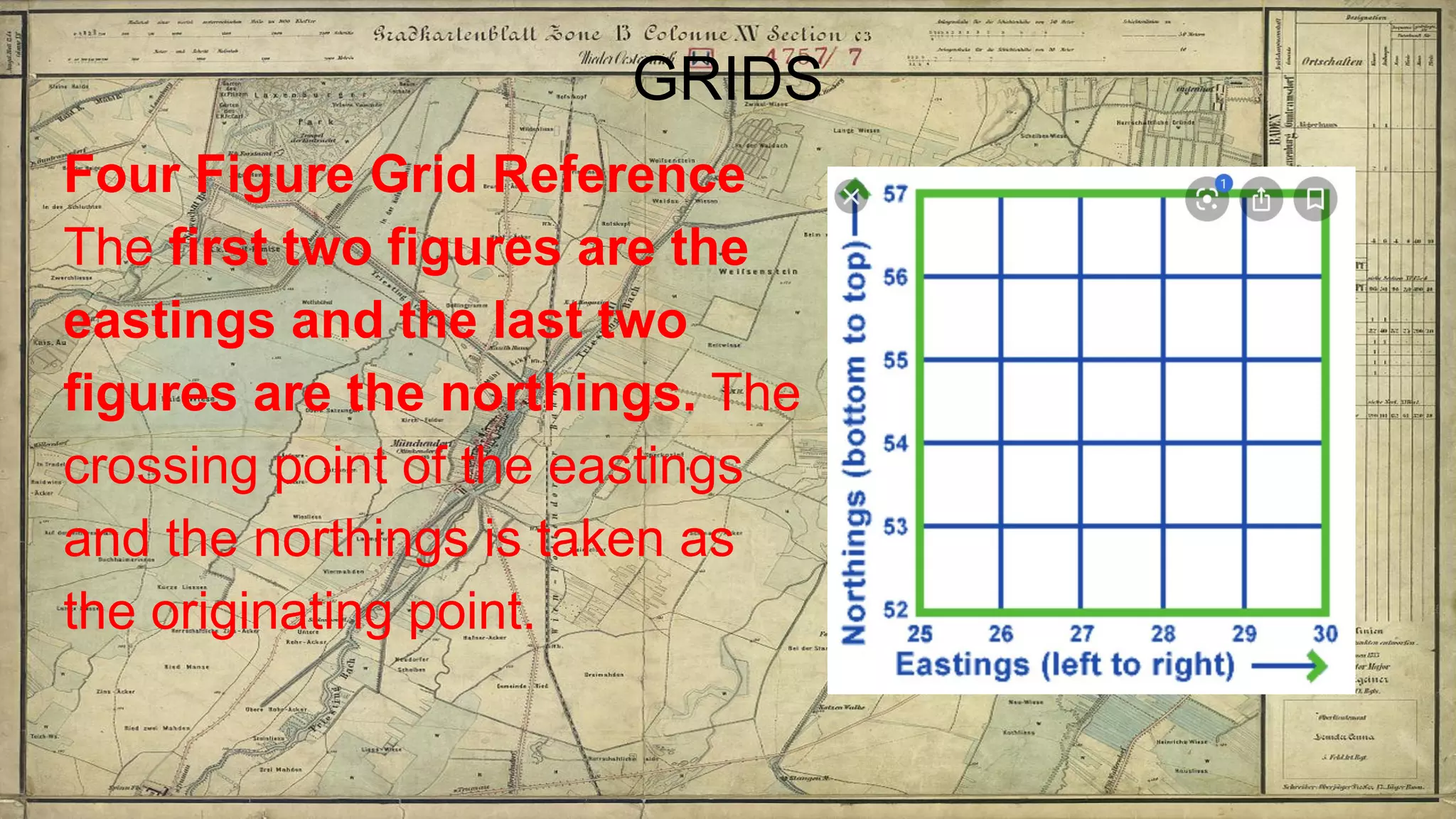
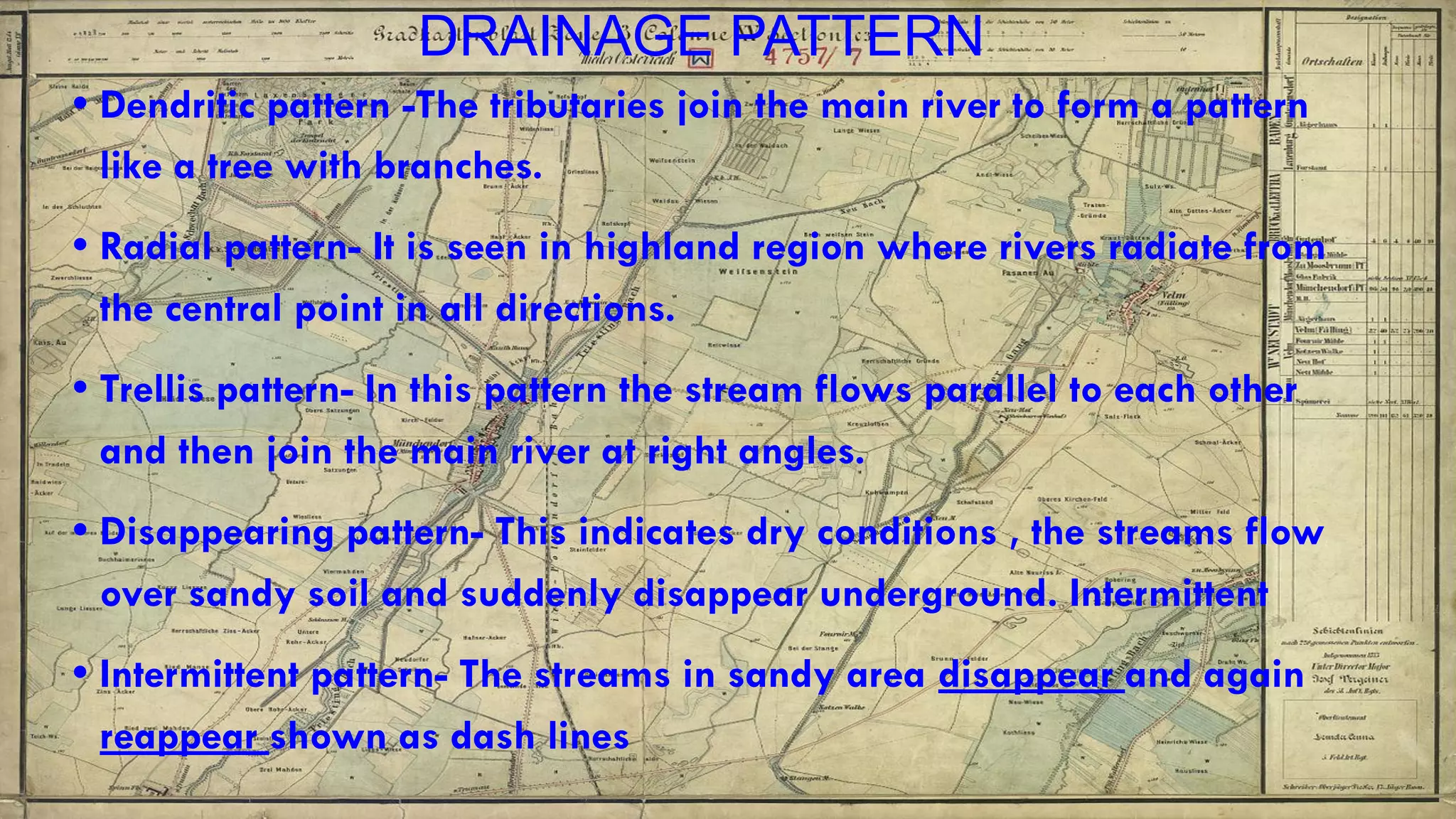
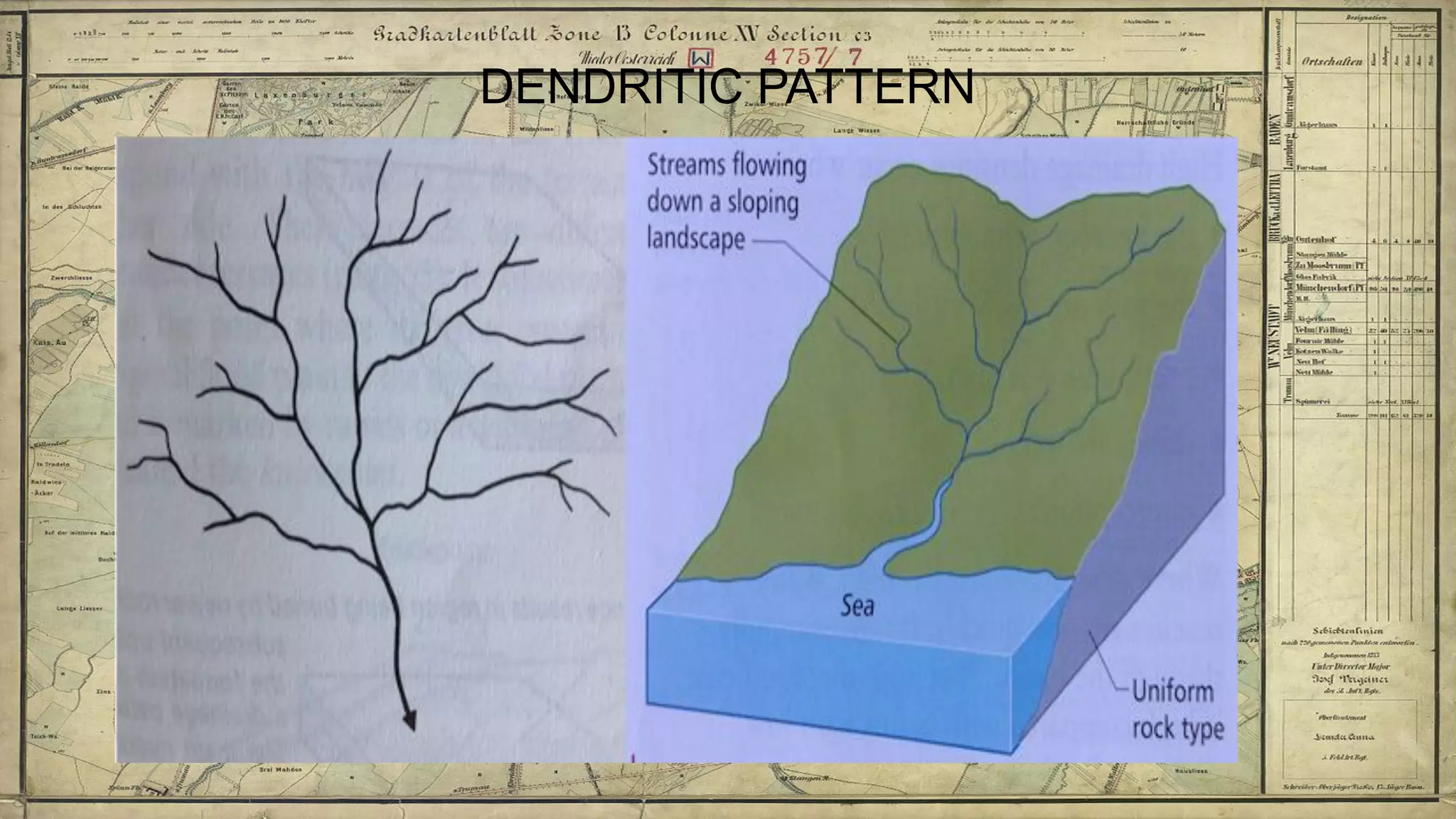
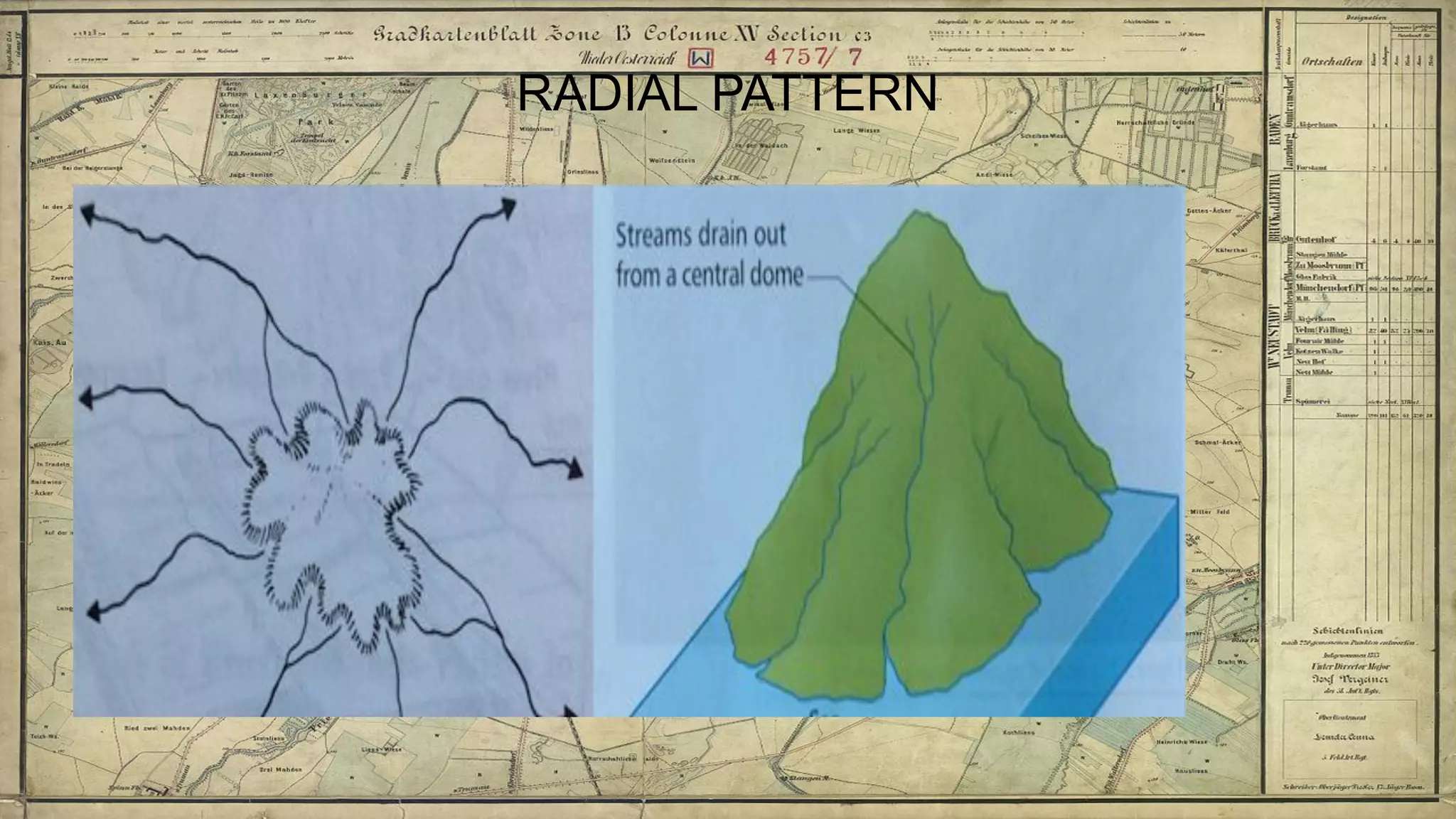
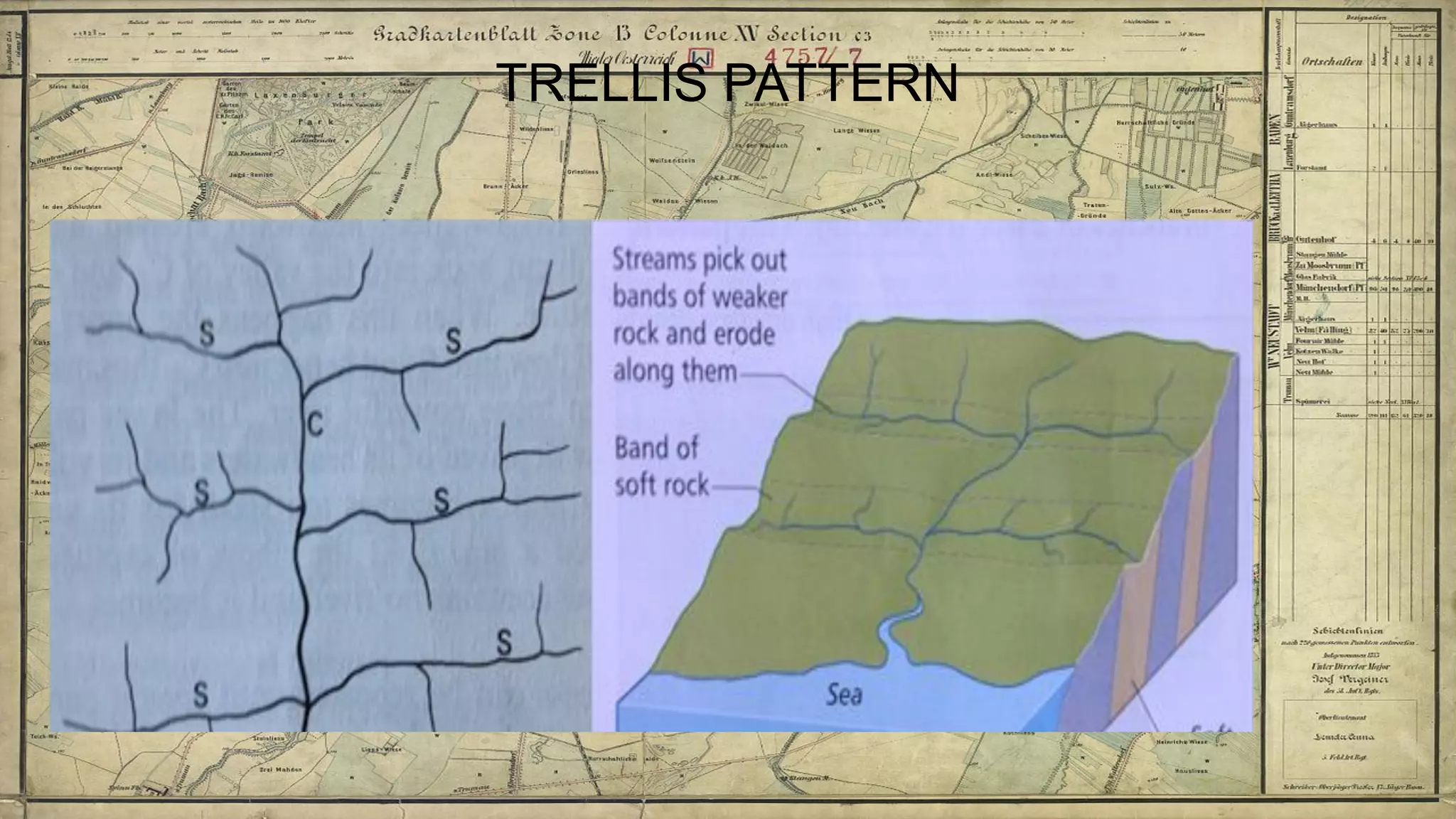
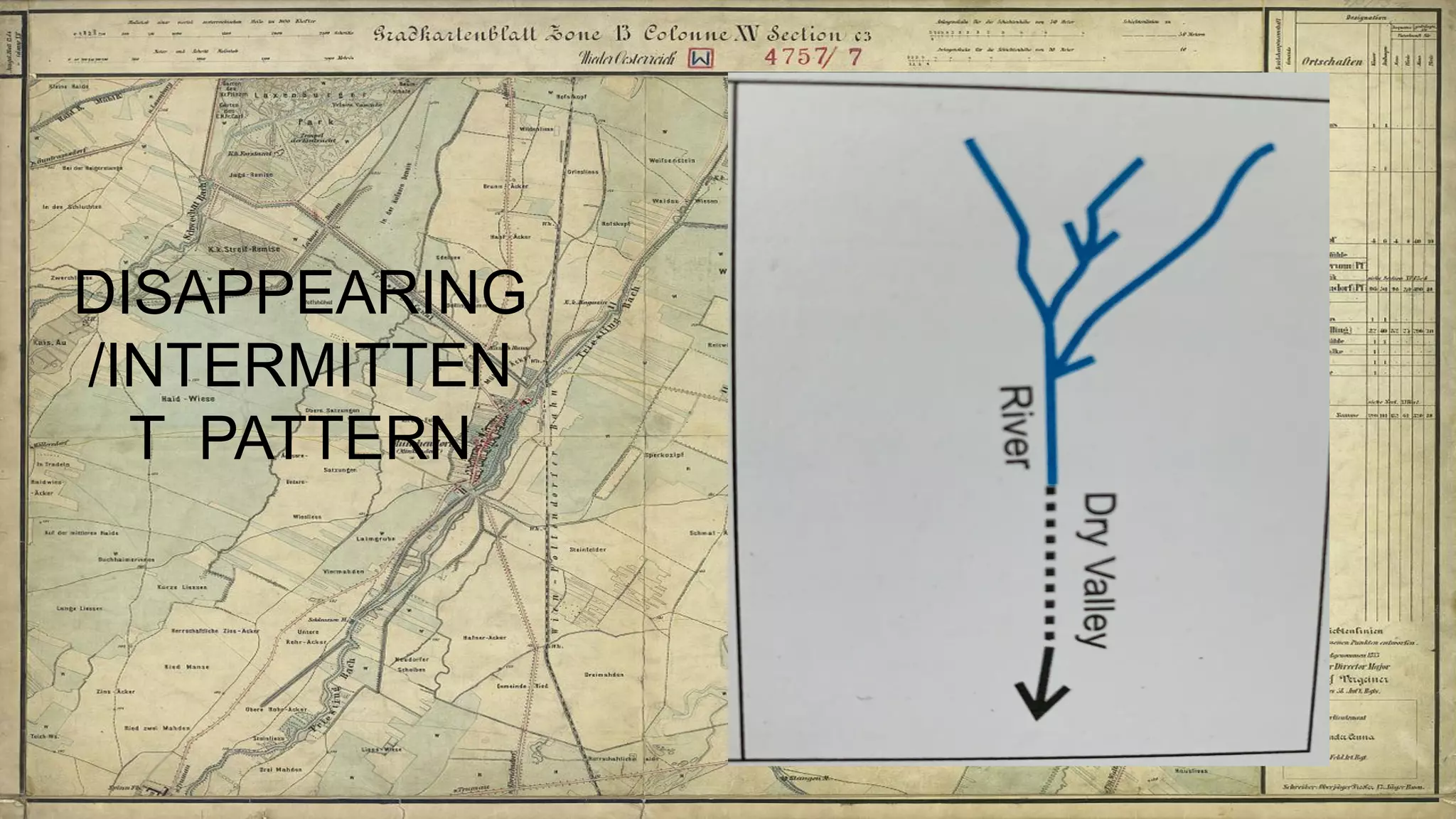
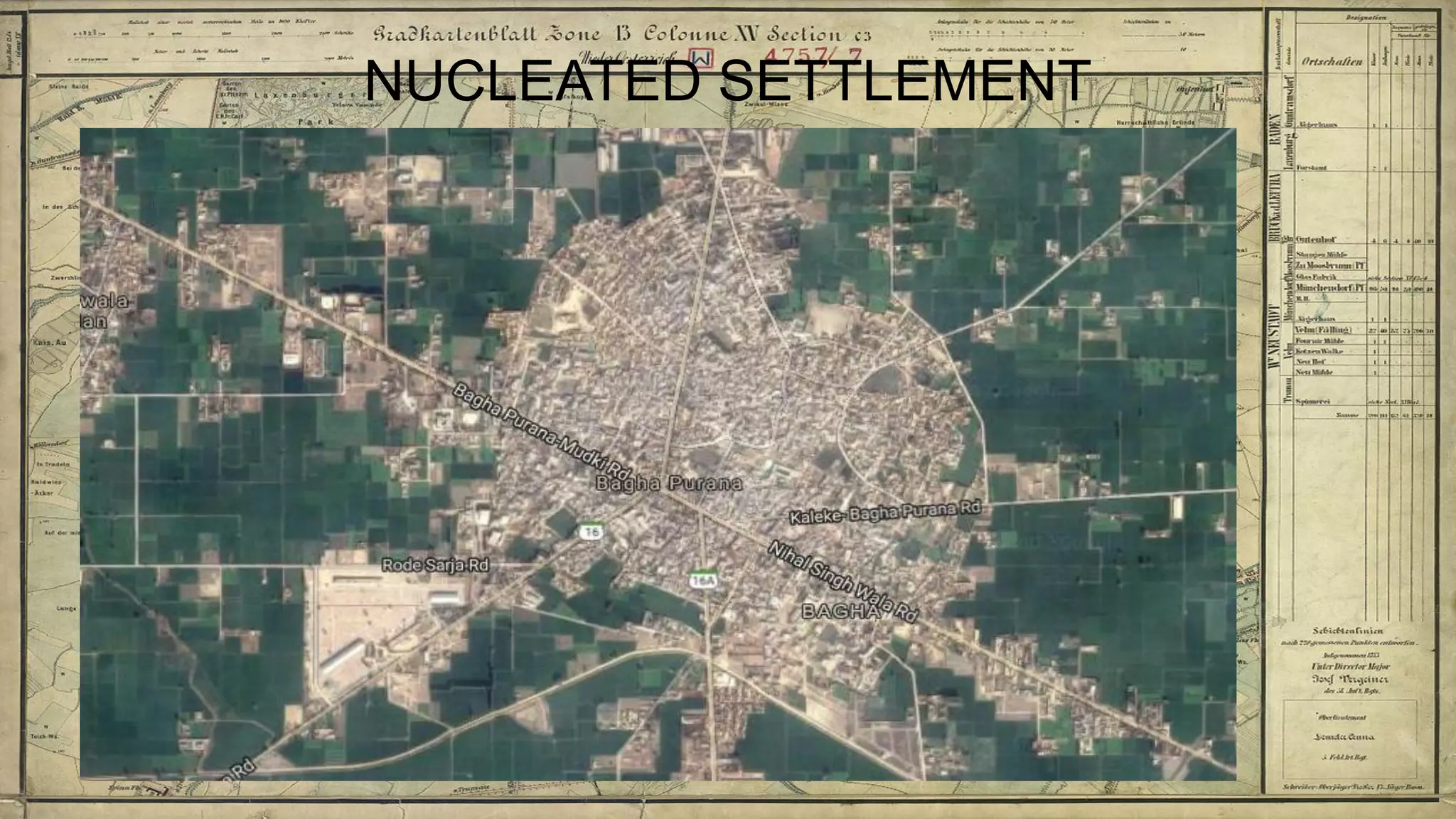
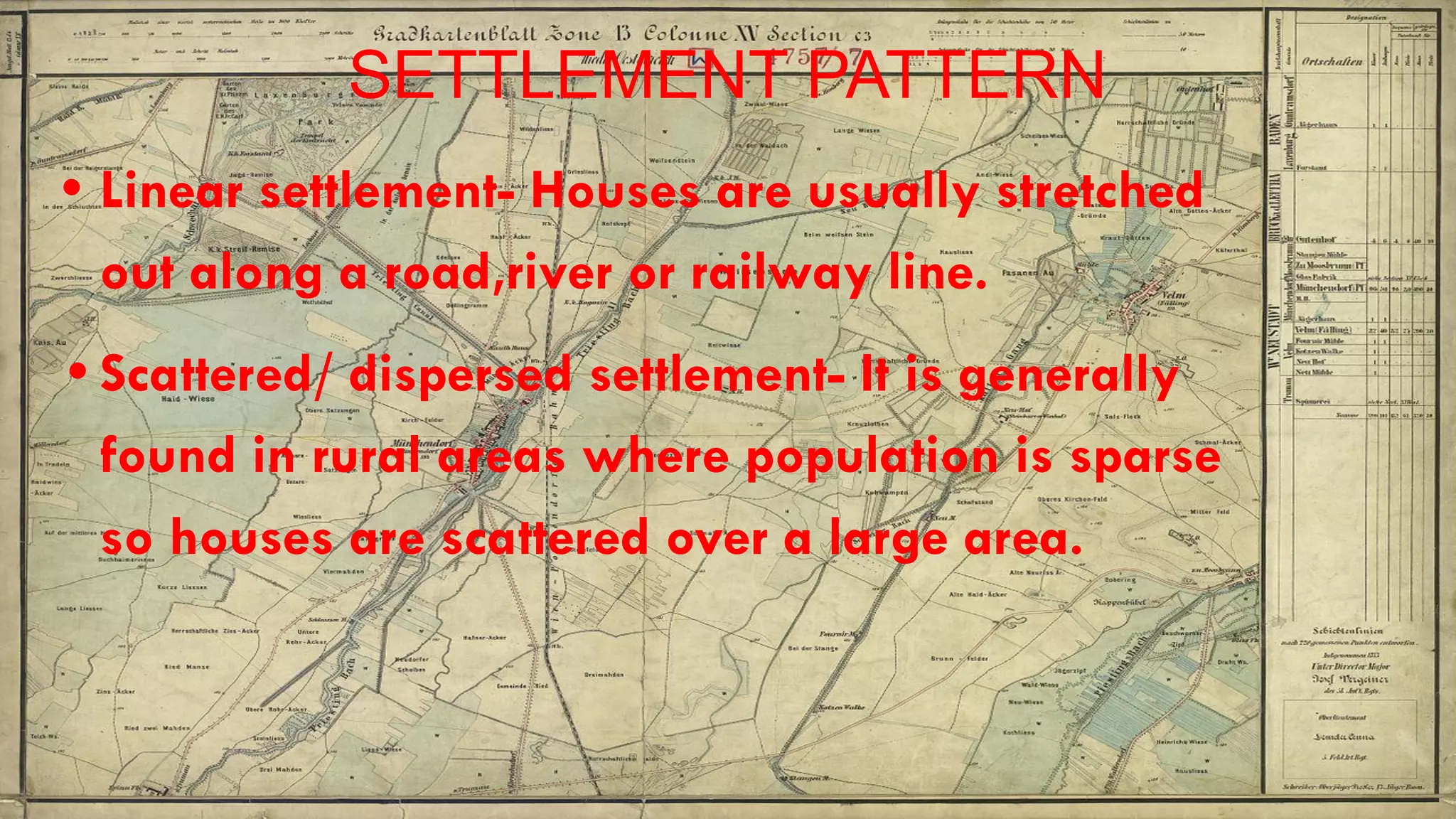
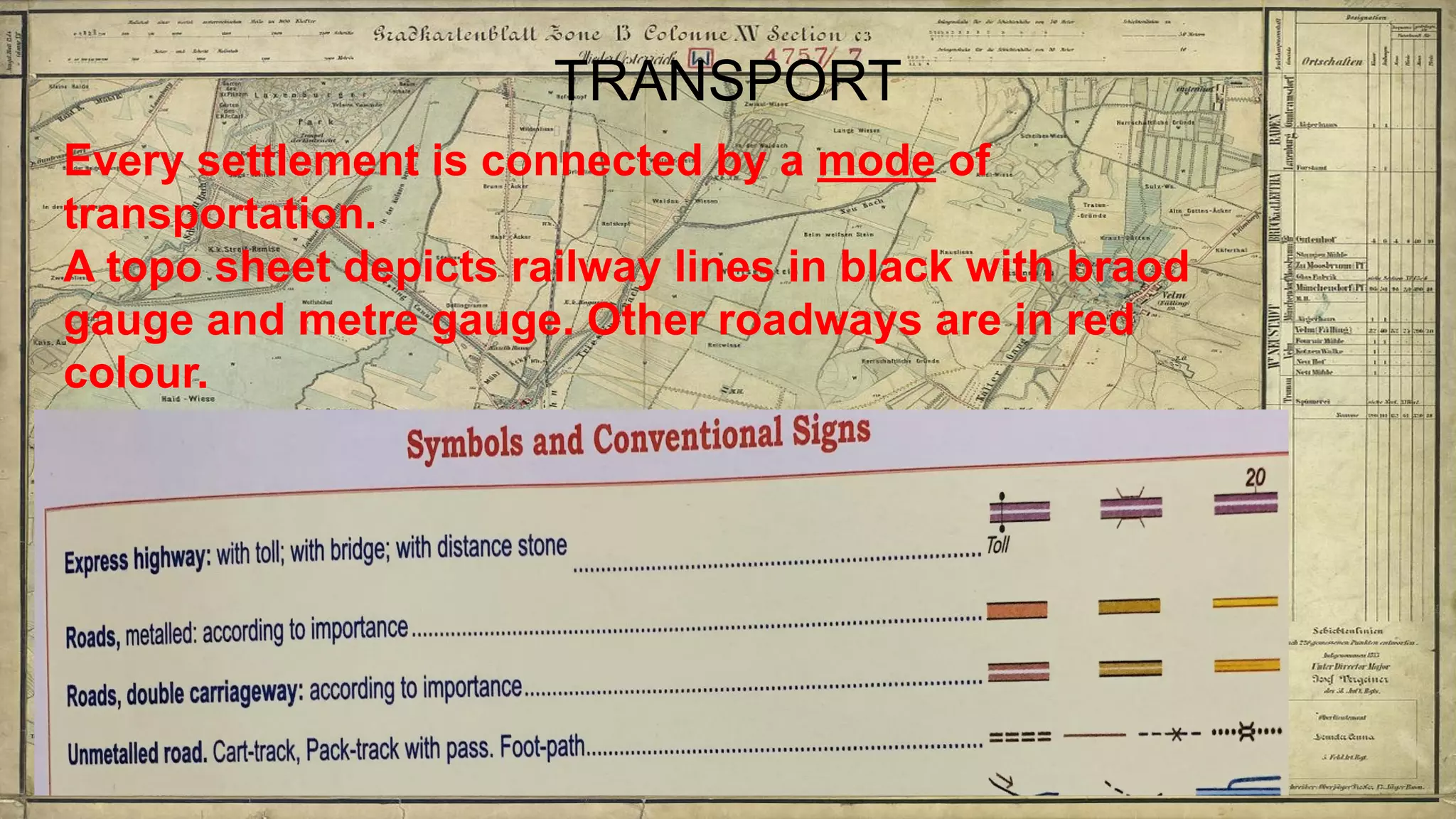
Topographical maps provide detailed studies of small areas, showing both natural and man-made features. They are important tools for geographers studying a region and the military in determining strategies based on terrain. Topographical maps use colors, symbols, contour lines, and grid systems to indicate features such as elevation, drainage patterns, settlements, transportation routes, and other relevant information about a mapped area.