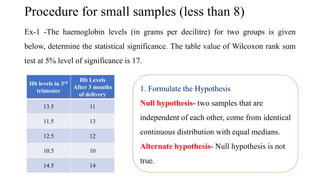
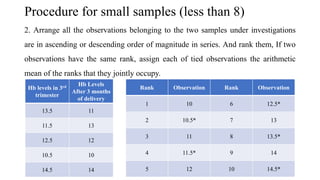
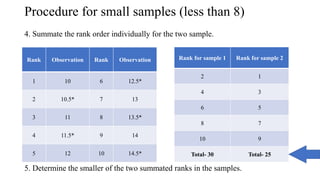
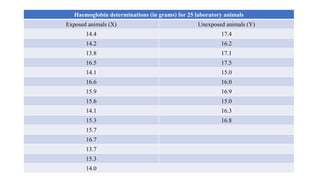
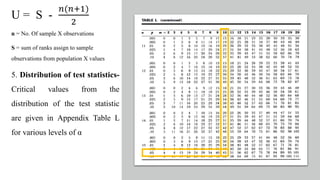
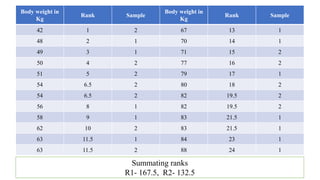
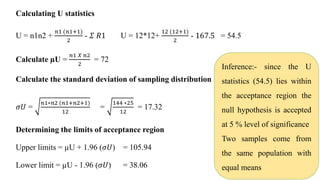
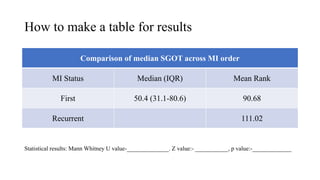
The document discusses the history and procedures for conducting the Mann-Whitney U test. It originated from the work of Frank Wilcoxon, Henry Mann, and Donald Whitney in the late 19th/early 20th century. The test is a nonparametric alternative to the independent t-test that can be used to compare two independent groups when the dependent variable is either ordinal or continuous. It works by ranking the data from both groups together and comparing the sums of the ranks for each group to determine if they are significantly different, indicating differences in central tendency. Examples are provided demonstrating how to calculate the test statistic U and conduct statistical inferences.