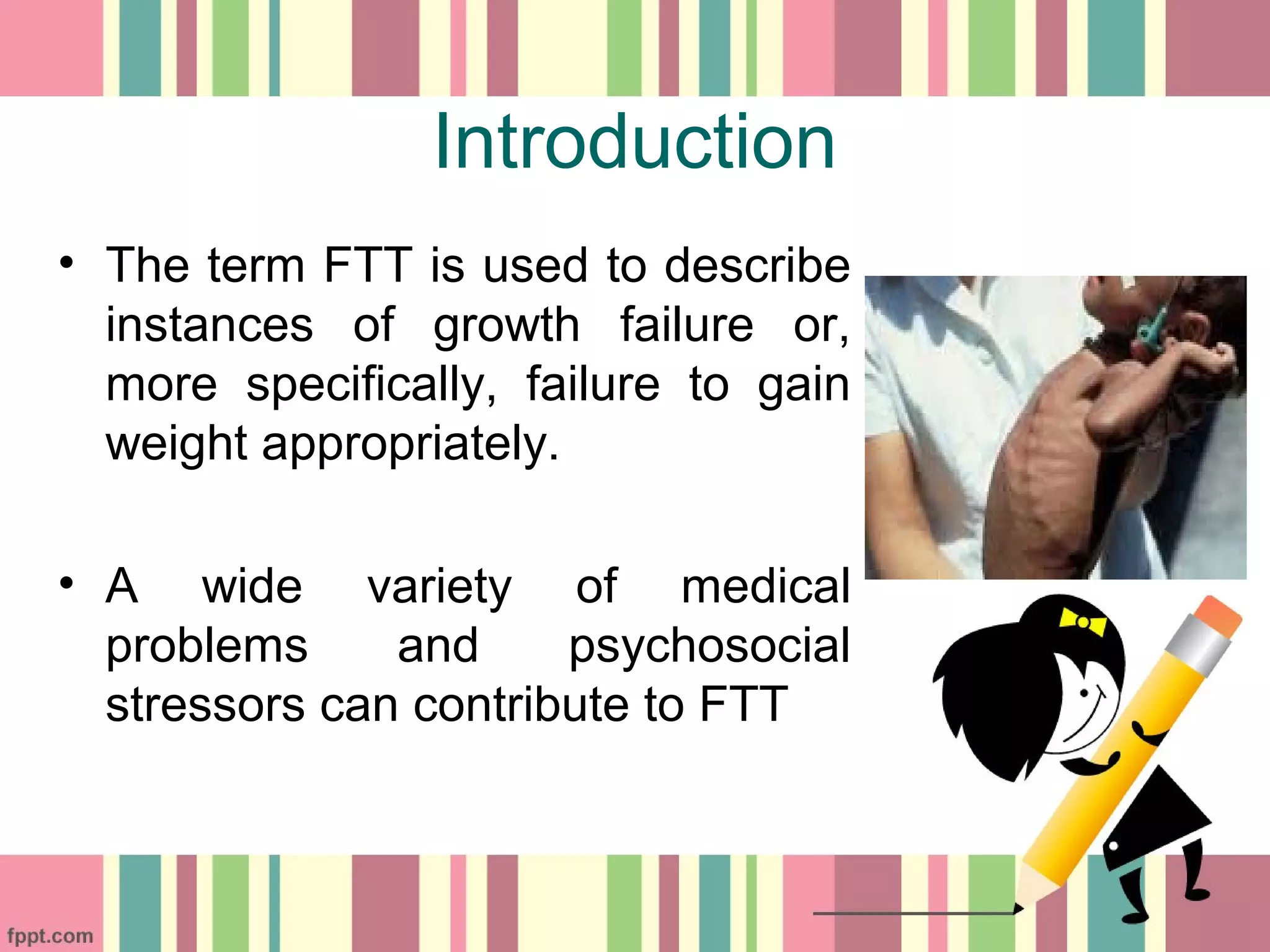
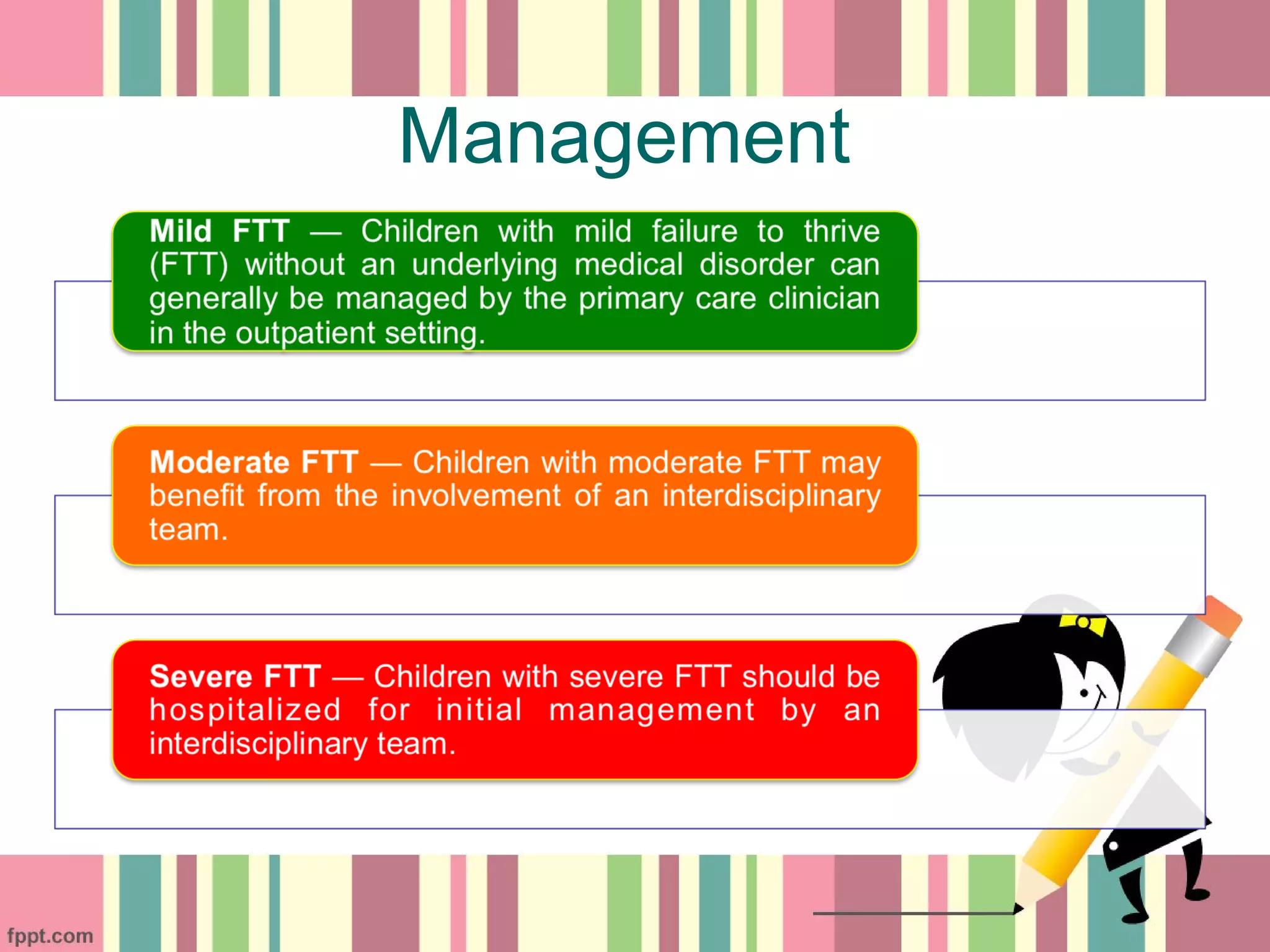
The document discusses the management of failure to thrive (FTT) in children, emphasizing the importance of nutritional therapy to improve dietary intake for catch-up growth. It outlines individualized management plans that address medical, nutritional, developmental, and psychosocial factors, recommending high energy and nutrient-rich diets along with multivitamin supplementation. Additionally, it highlights the need for medical, developmental, and psychosocial interventions to support overall treatment effectiveness.