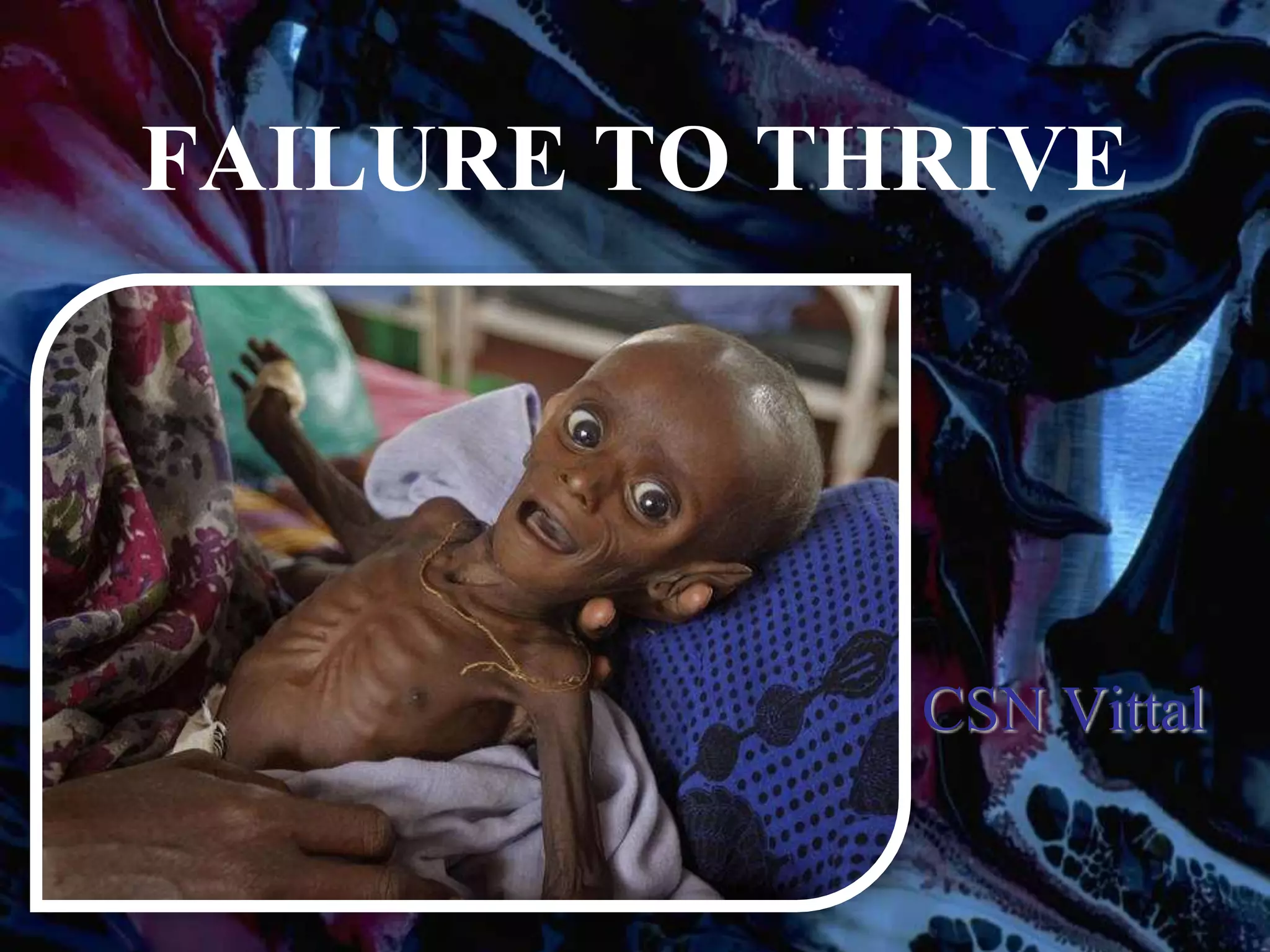
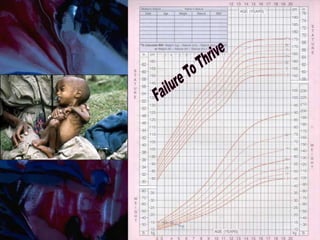
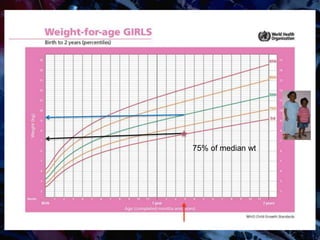
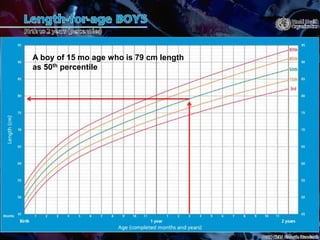
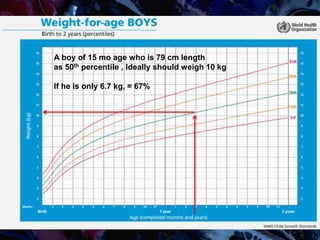
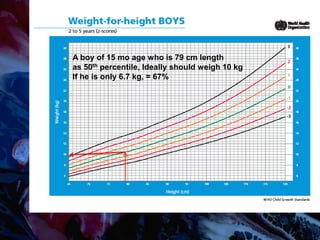
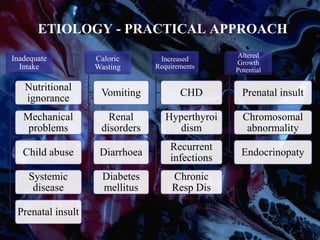
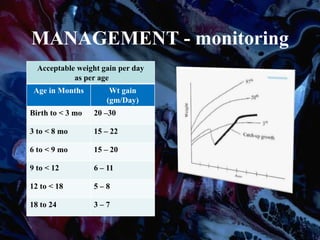
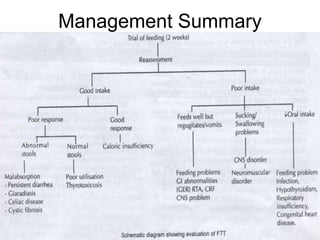
Failure to thrive (FTT) is defined as a lack of appropriate weight gain or a persistent weight loss from a child's normal growth curve. It can be classified as organic, caused by medical issues, or non-organic, caused by psychosocial factors. A thorough history, physical exam, and lab tests are needed to determine the etiology and develop an appropriate treatment plan focused on nutritional rehabilitation and addressing the underlying cause. Prognosis depends on the etiology, with FTT in the first year generally having a poorer outcome. Prevention efforts include exclusive breastfeeding, parental education, and early detection and intervention.