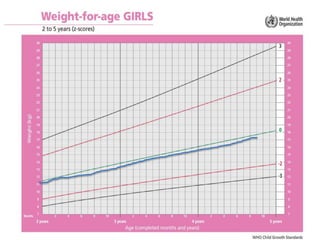
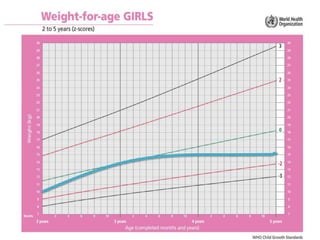
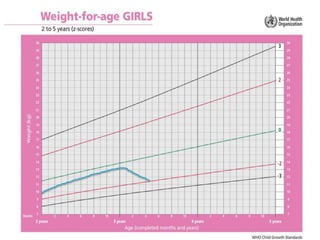
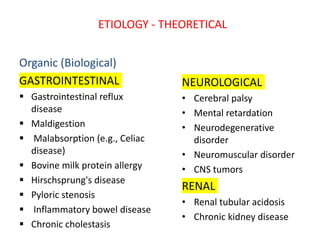
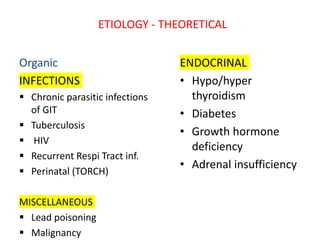
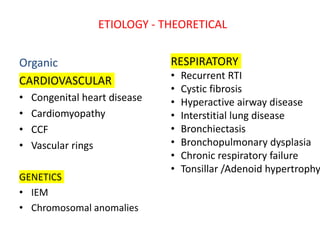
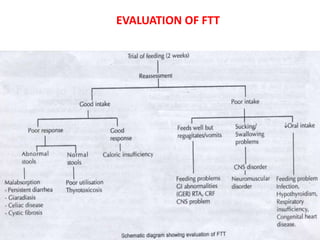
Failure to thrive is defined as sustained weight loss or failure to gain weight resulting in a child's weight falling below normal growth curves. It can be caused by inadequate nutrition intake, increased calorie needs, or issues with absorption. Evaluation involves assessing growth charts, nutrition intake, physical exam for signs of organic disease, and laboratory tests if indicated. Management goals are nutritional rehabilitation, treating any underlying medical causes, and addressing psychosocial factors. The prognosis depends on the etiology, with psychosocial causes having risks of developmental delays and organic causes having variable outcomes based on the specific condition.