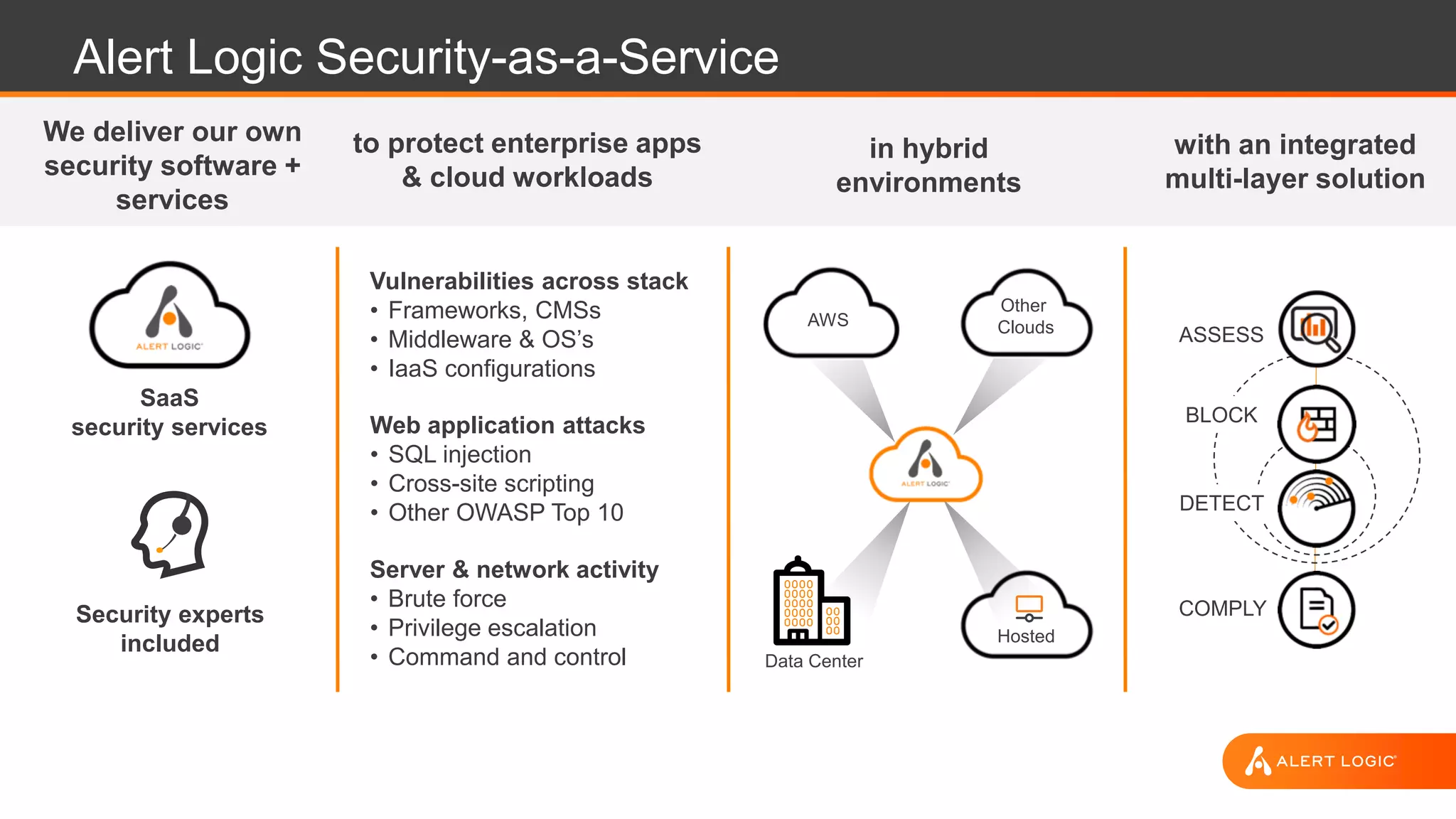
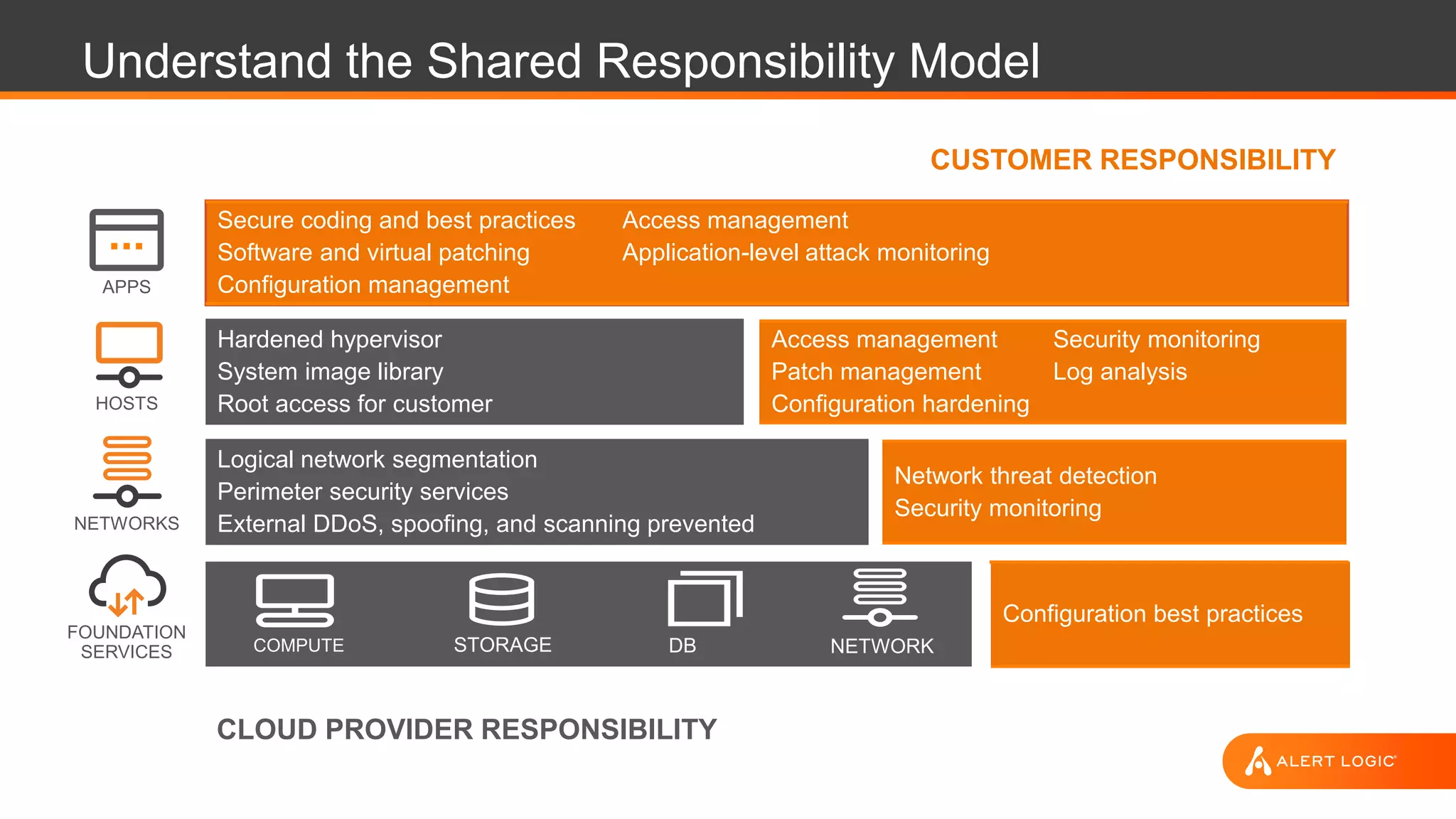
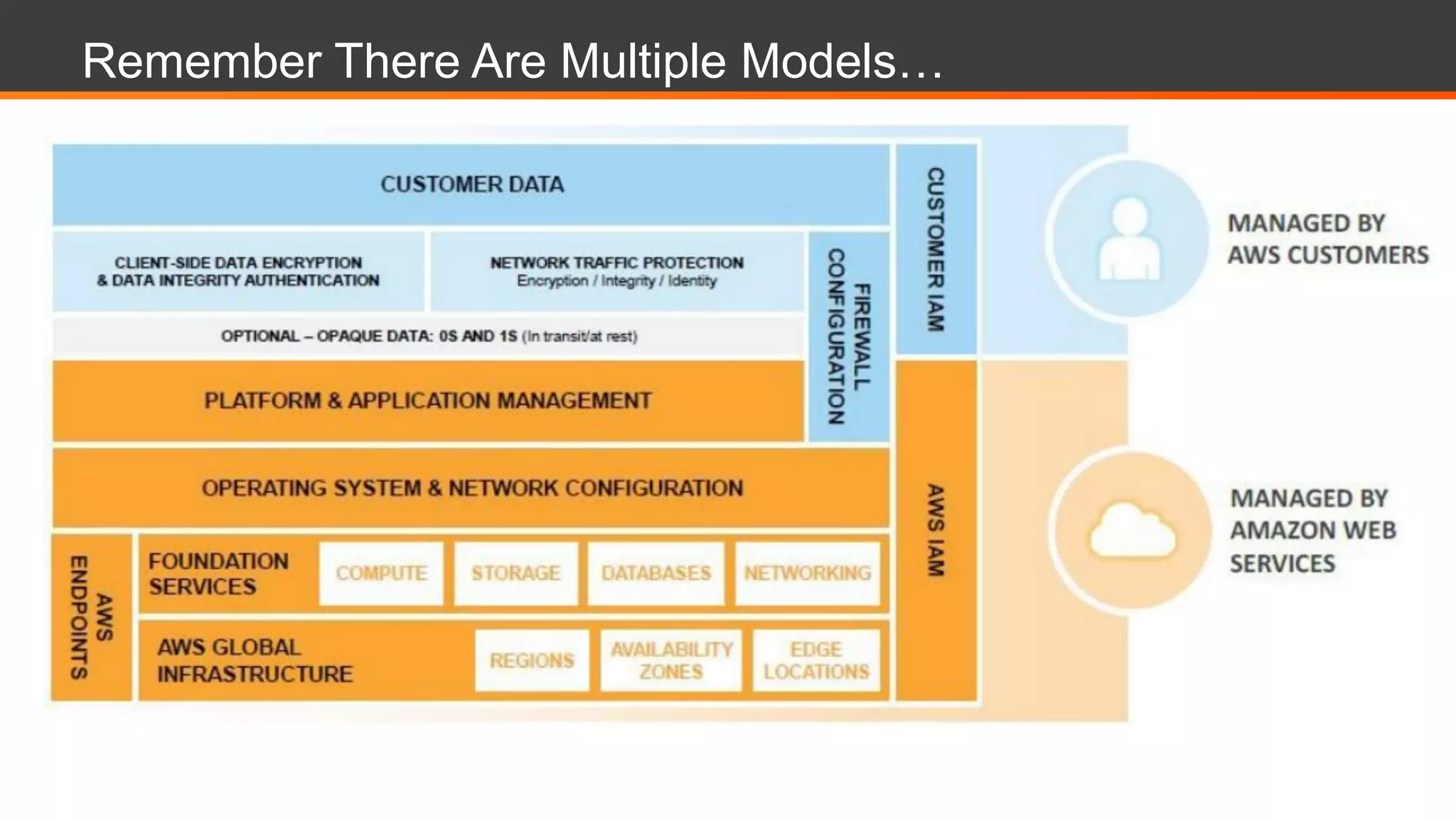
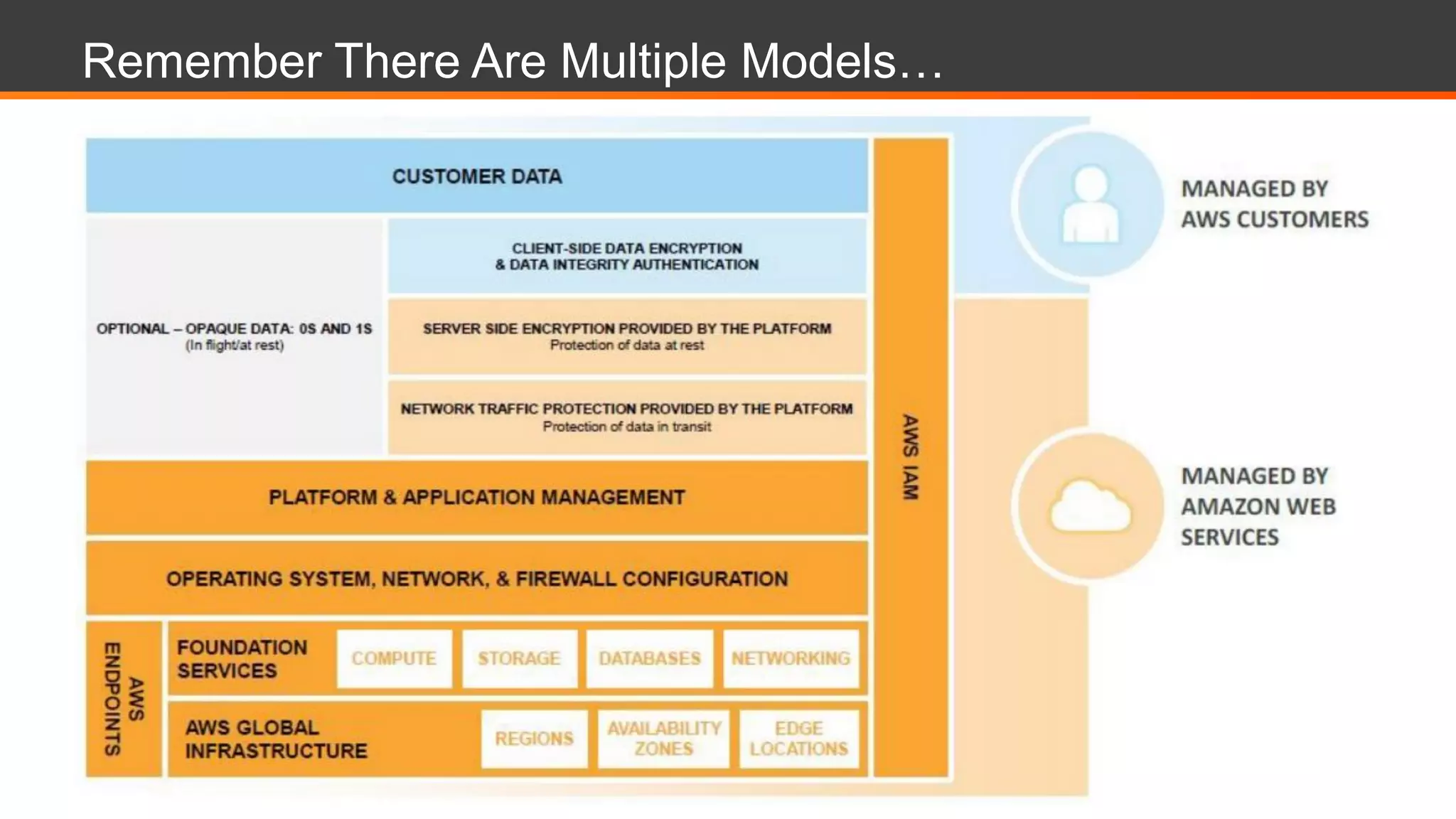
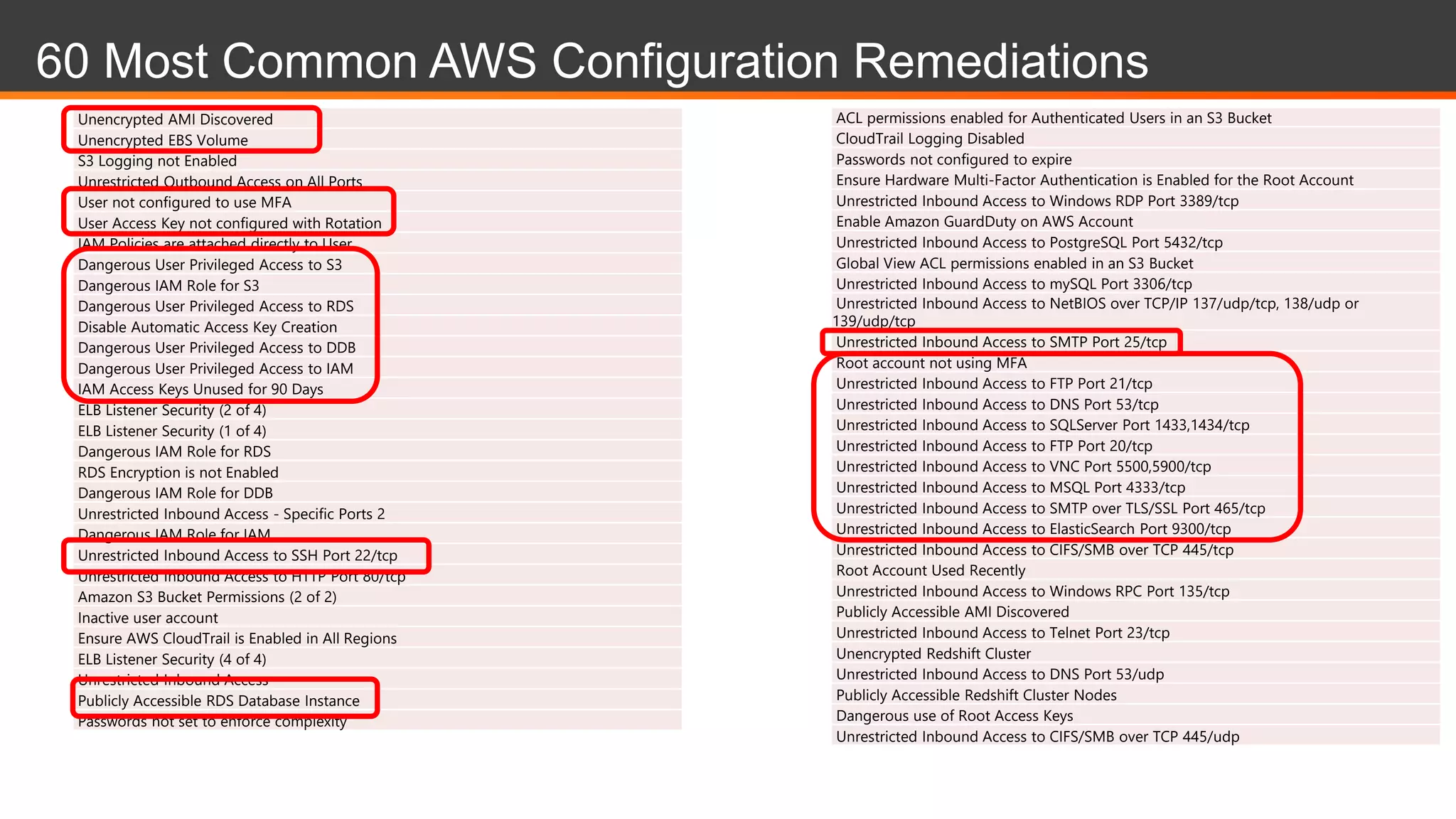
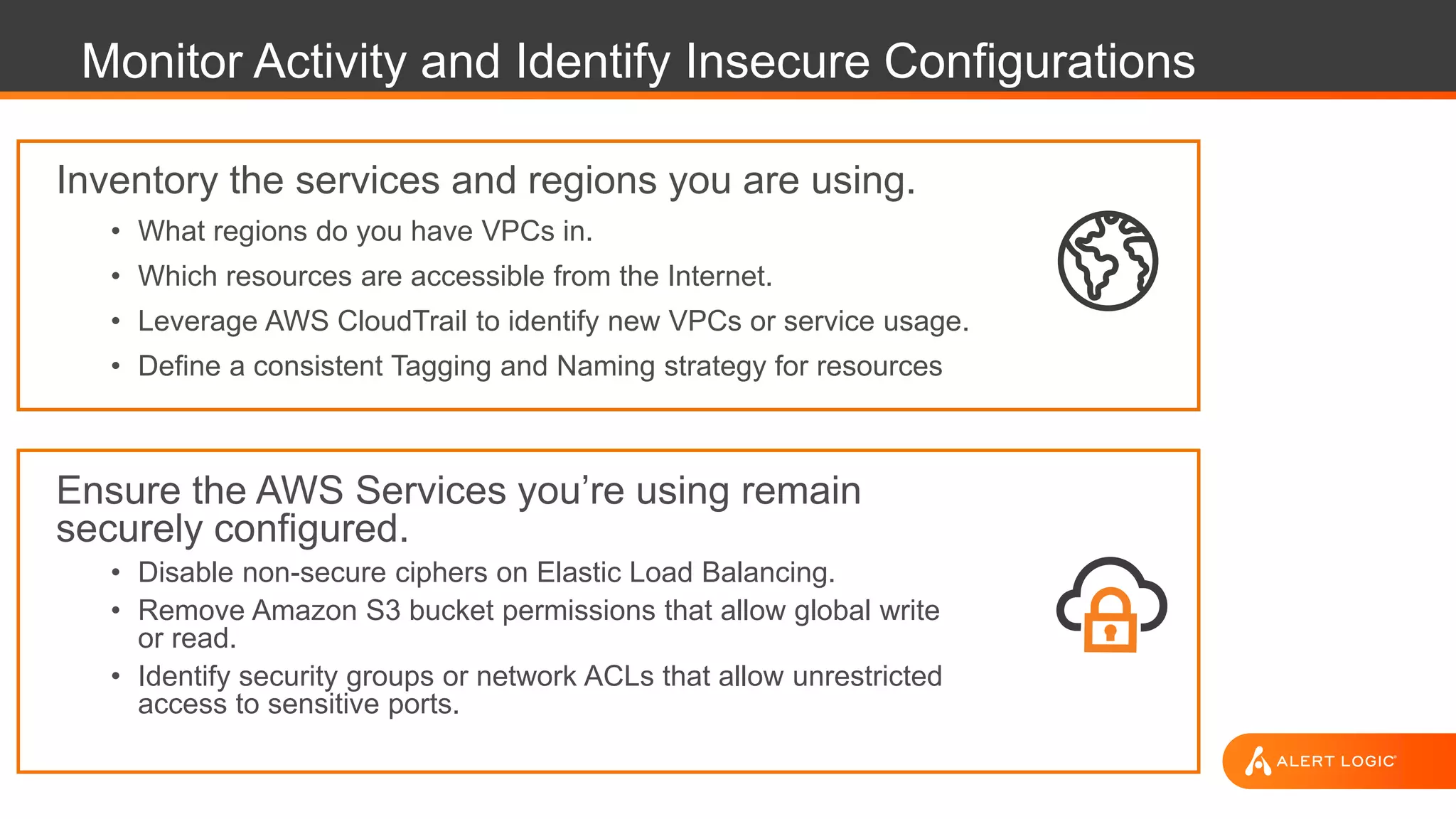
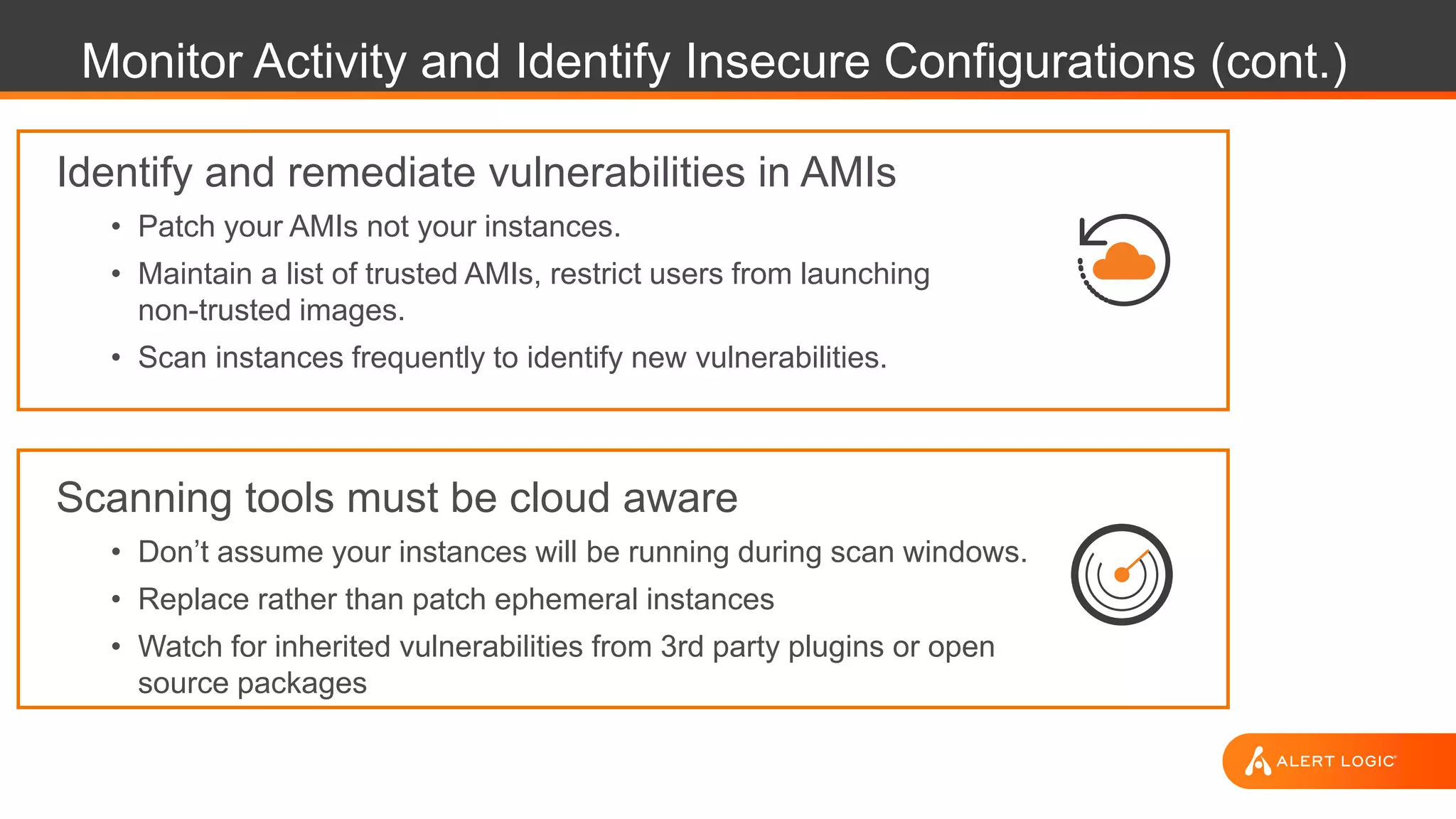
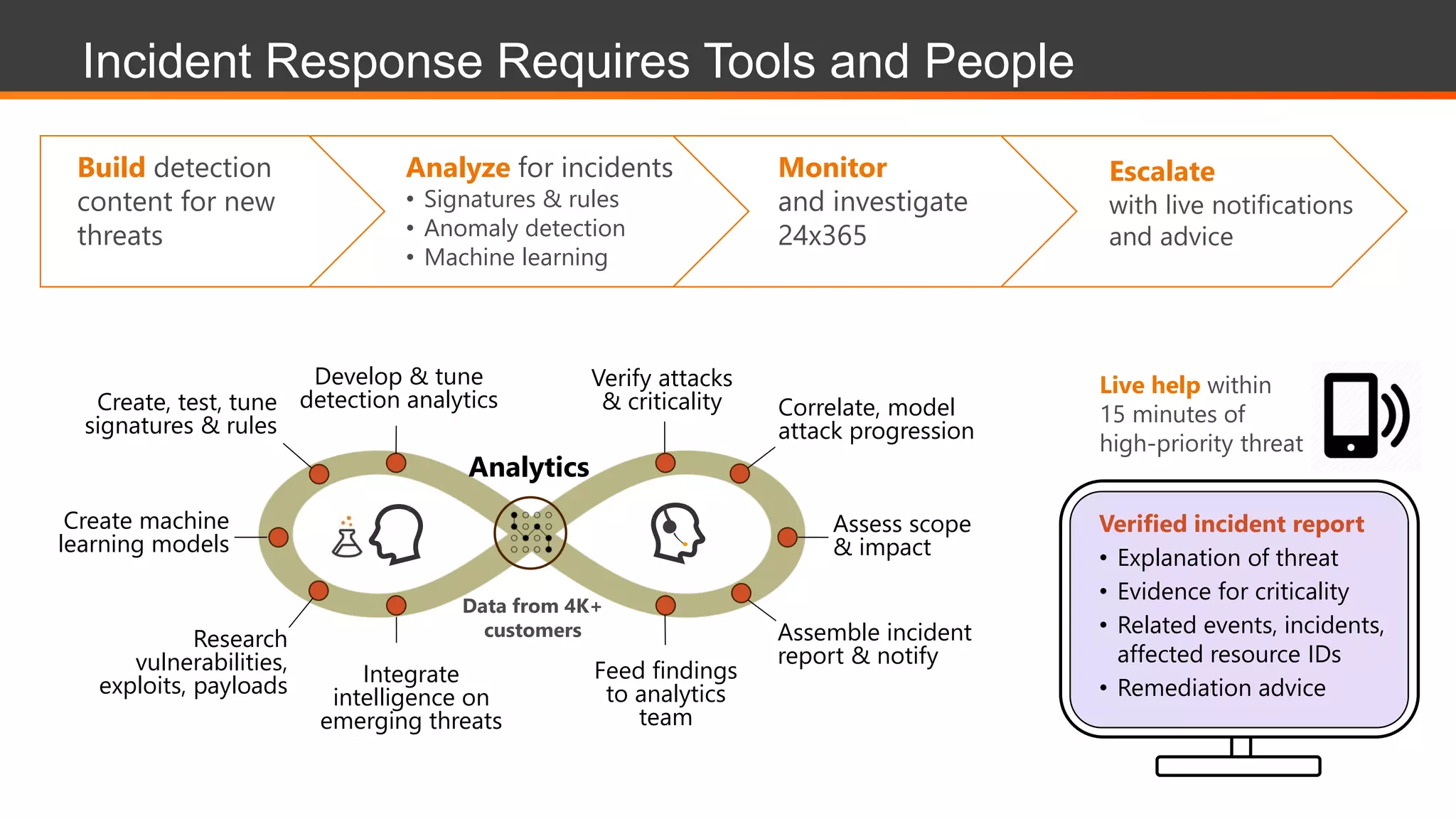
This document discusses Alert Logic's Security-as-a-Service offering which provides an integrated multi-layer security solution to protect enterprise applications and cloud workloads across hosted data centers and hybrid environments. It protects against web application attacks, server and network activity, and vulnerabilities across software stacks. Alert Logic also provides security experts and services including assessment, blocking, detection, and compliance. The document then discusses best practices for securing an AWS environment including logical network segmentation, access management, configuration management, and understanding the shared responsibility model between cloud providers and customers.