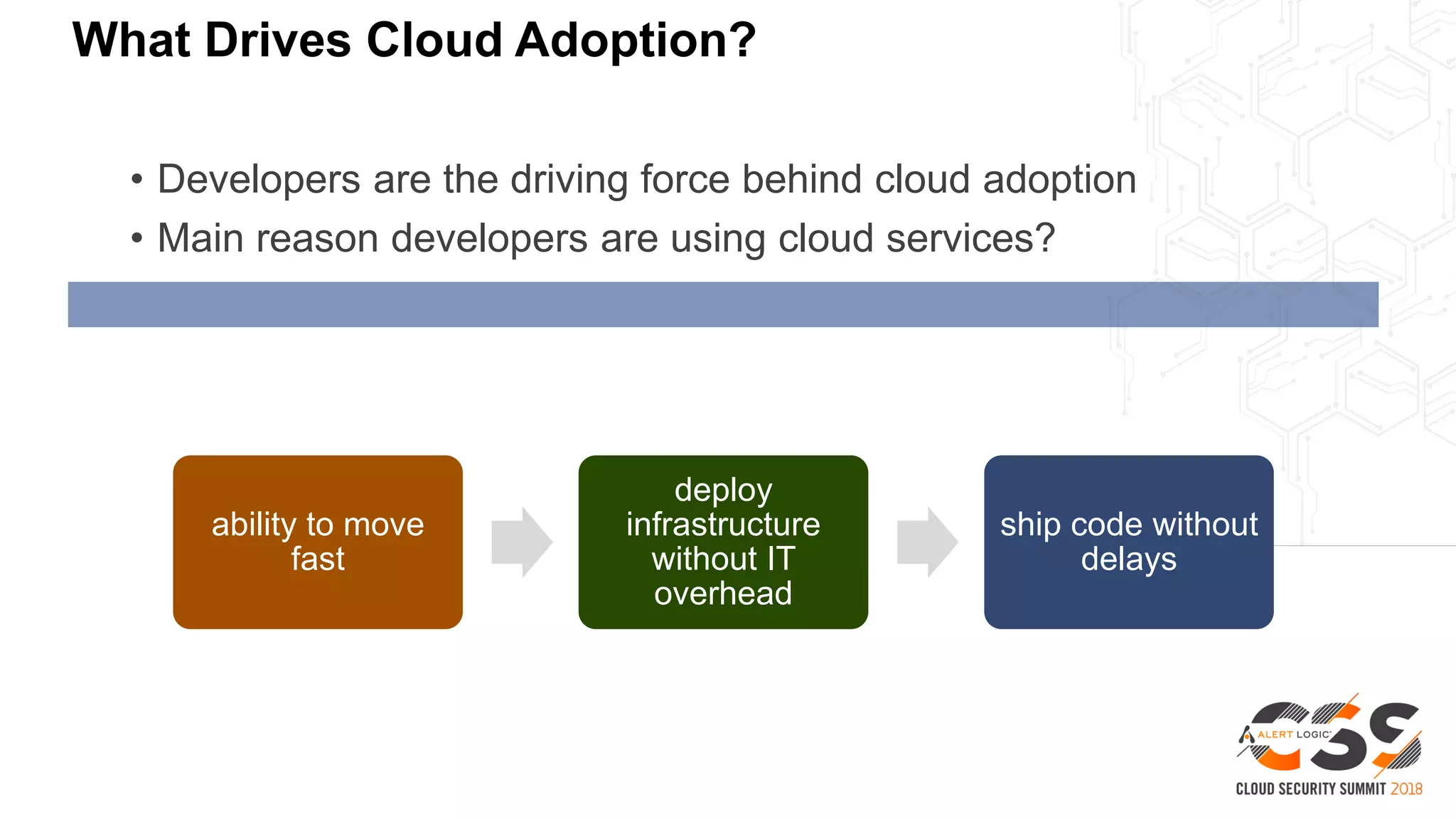
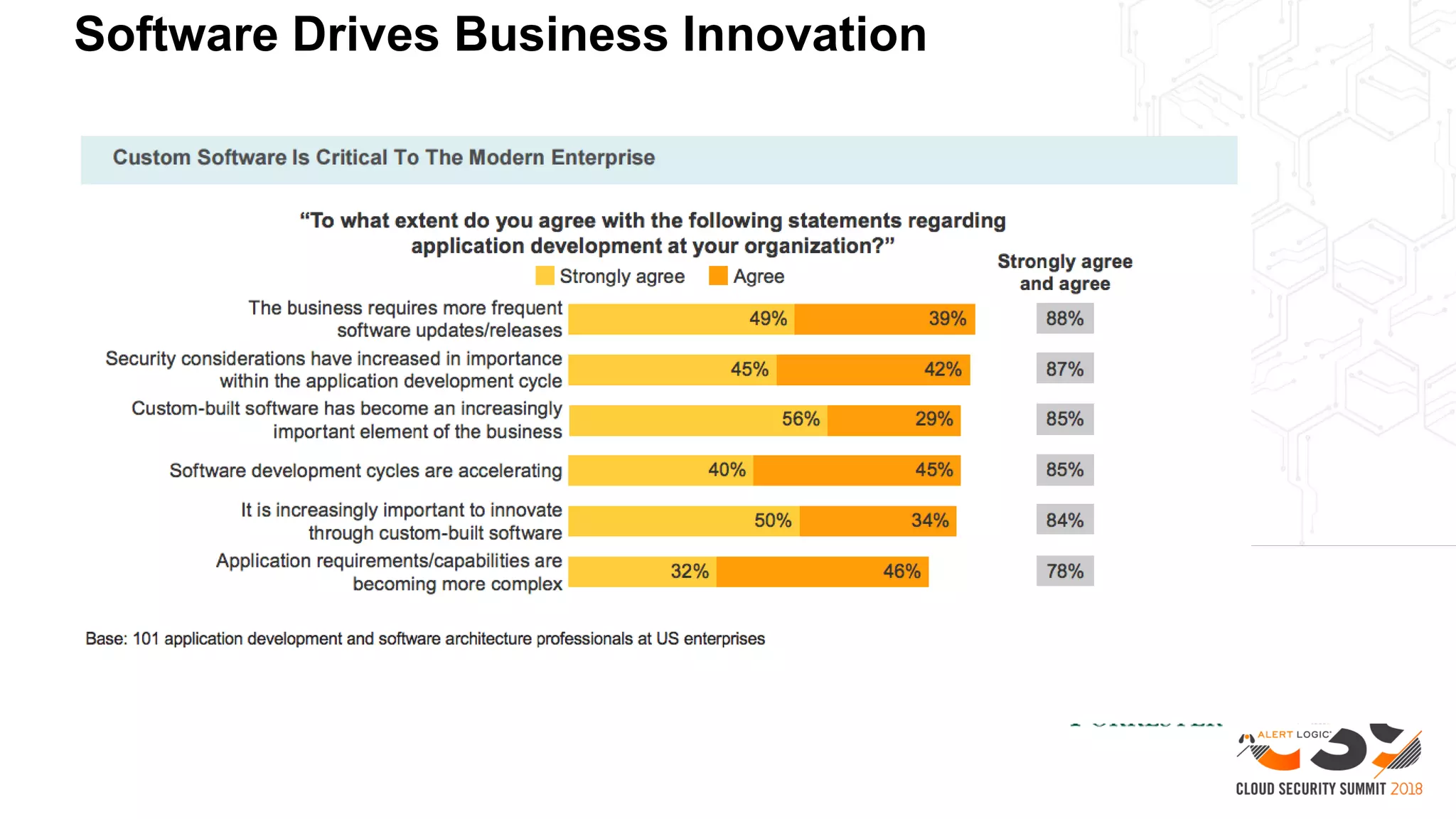
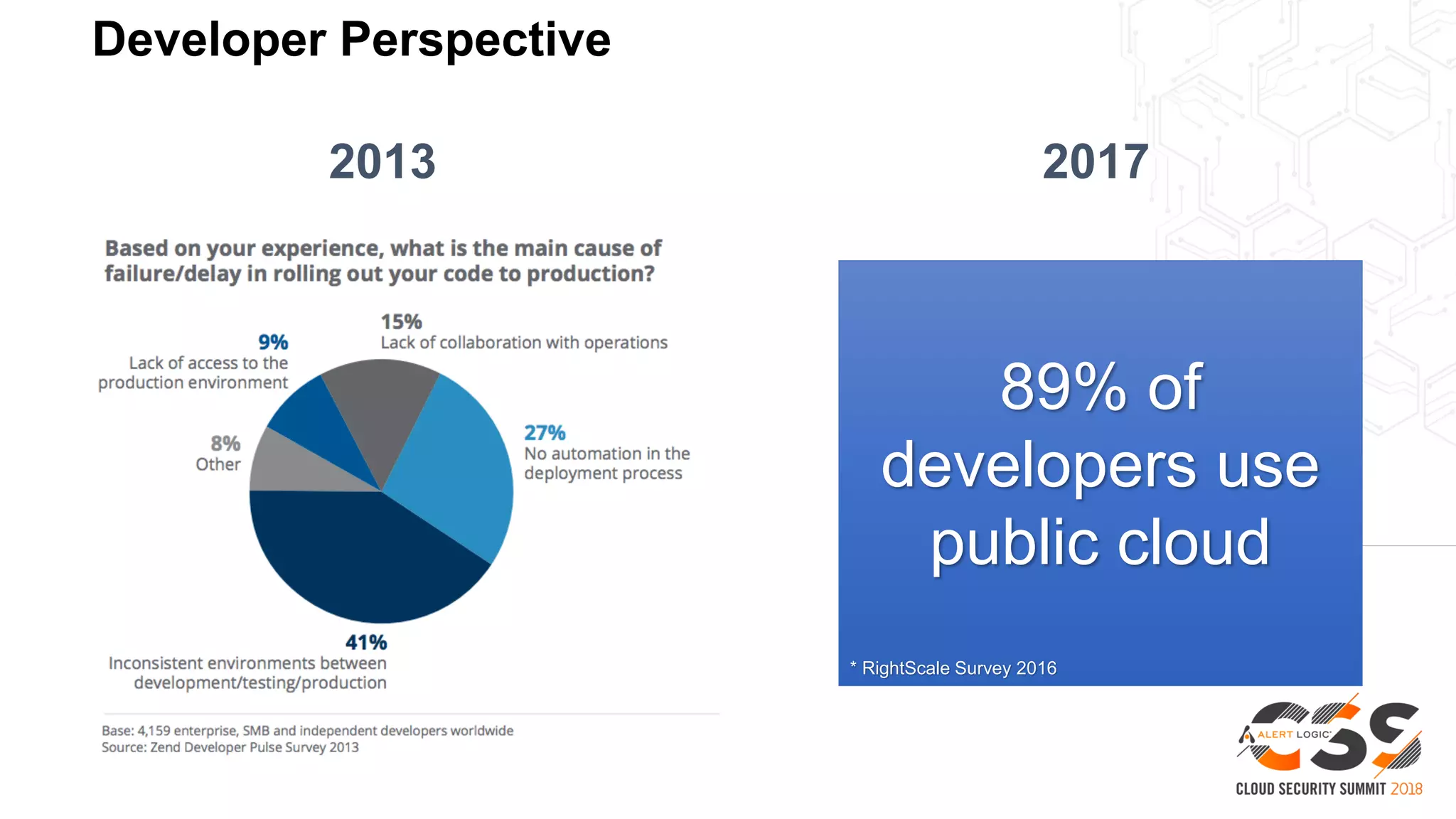
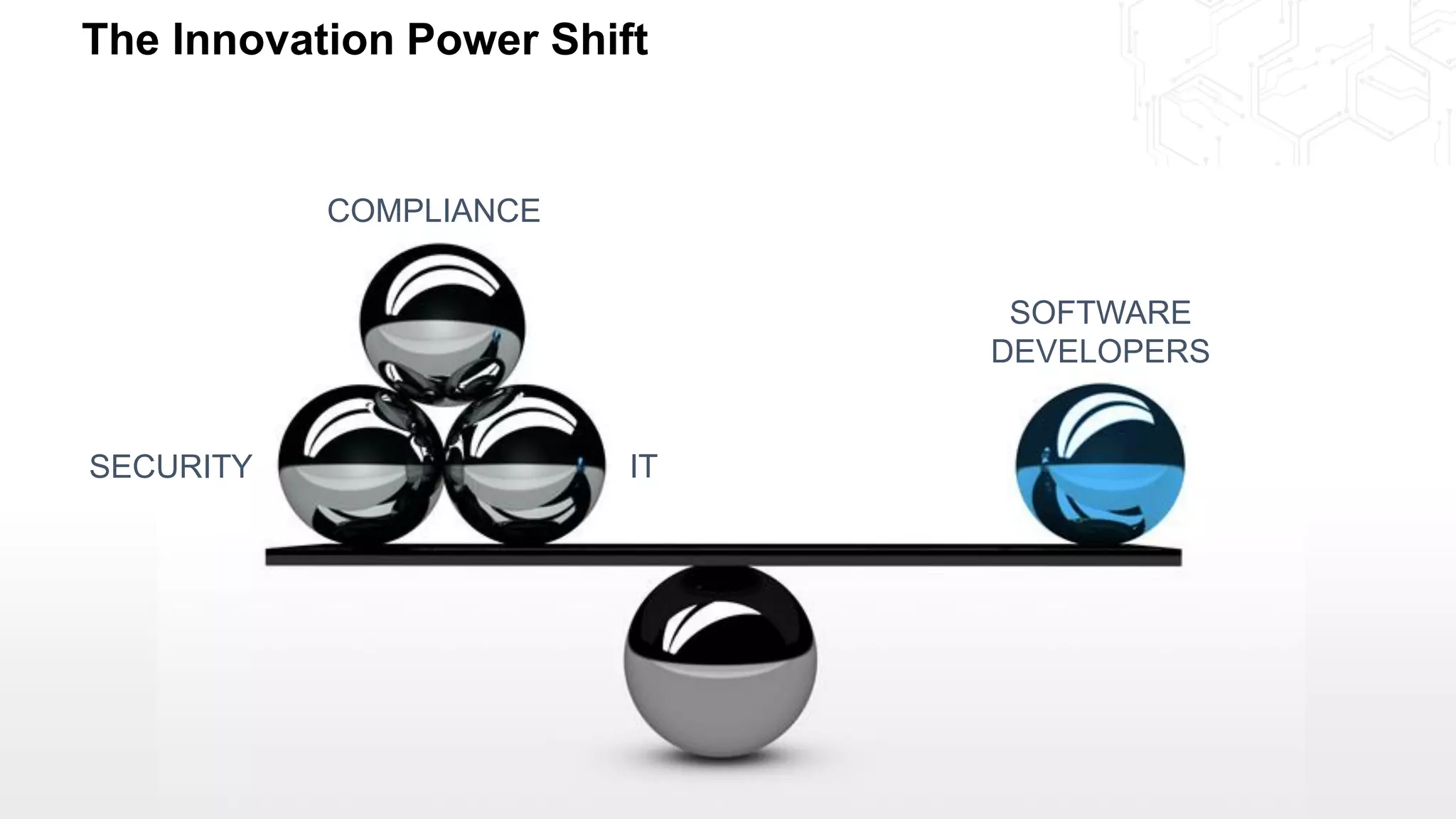
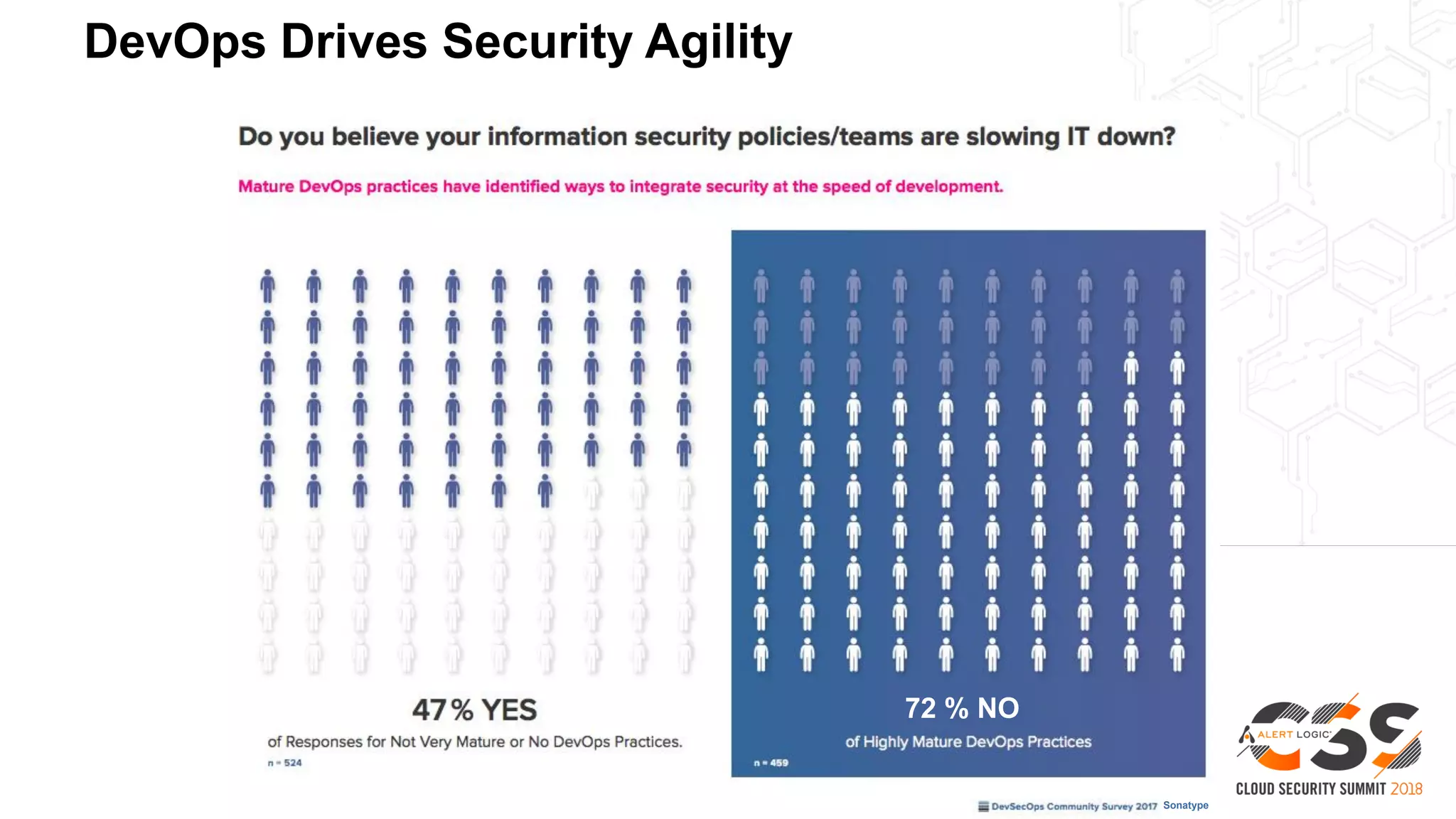
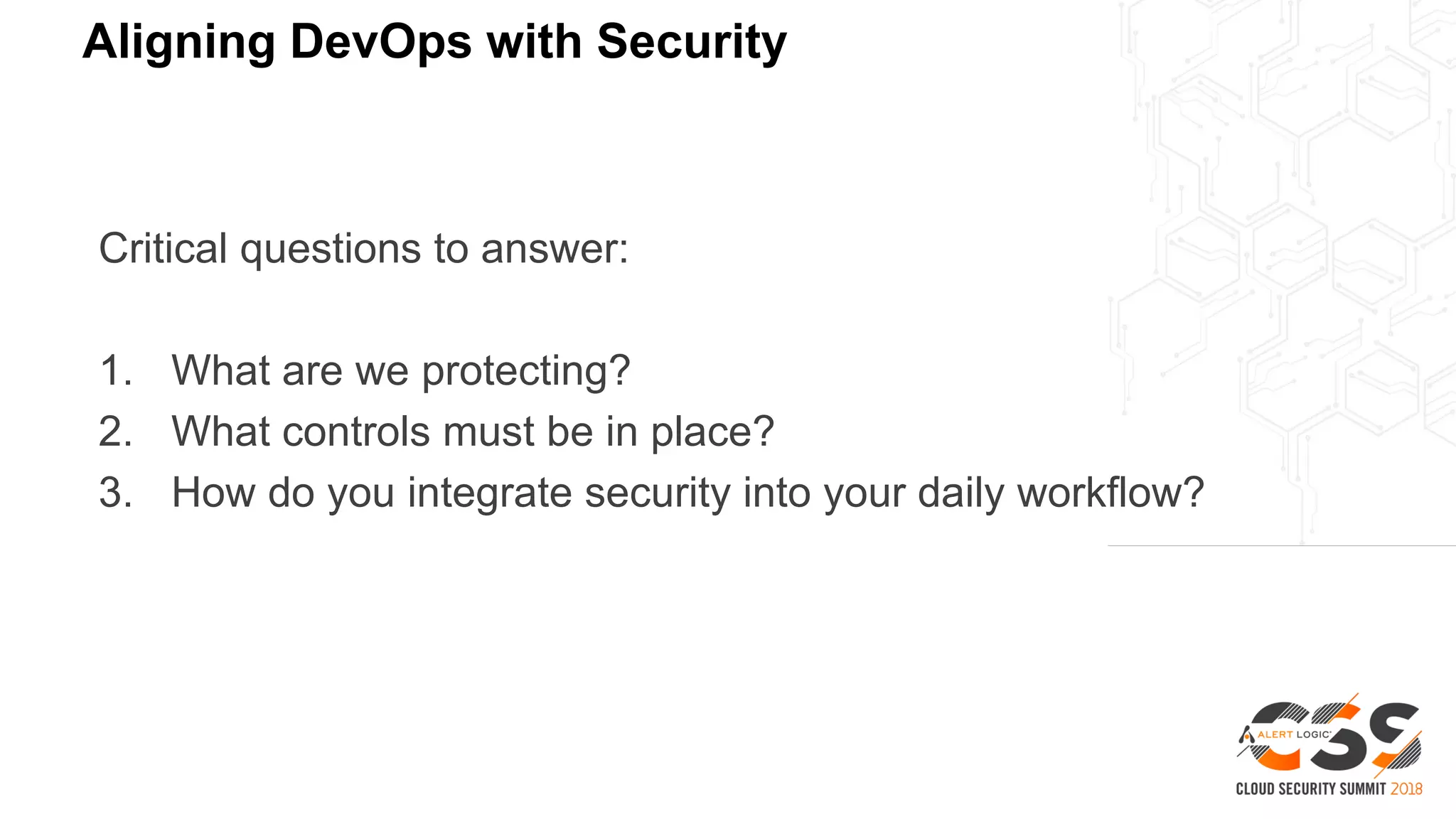
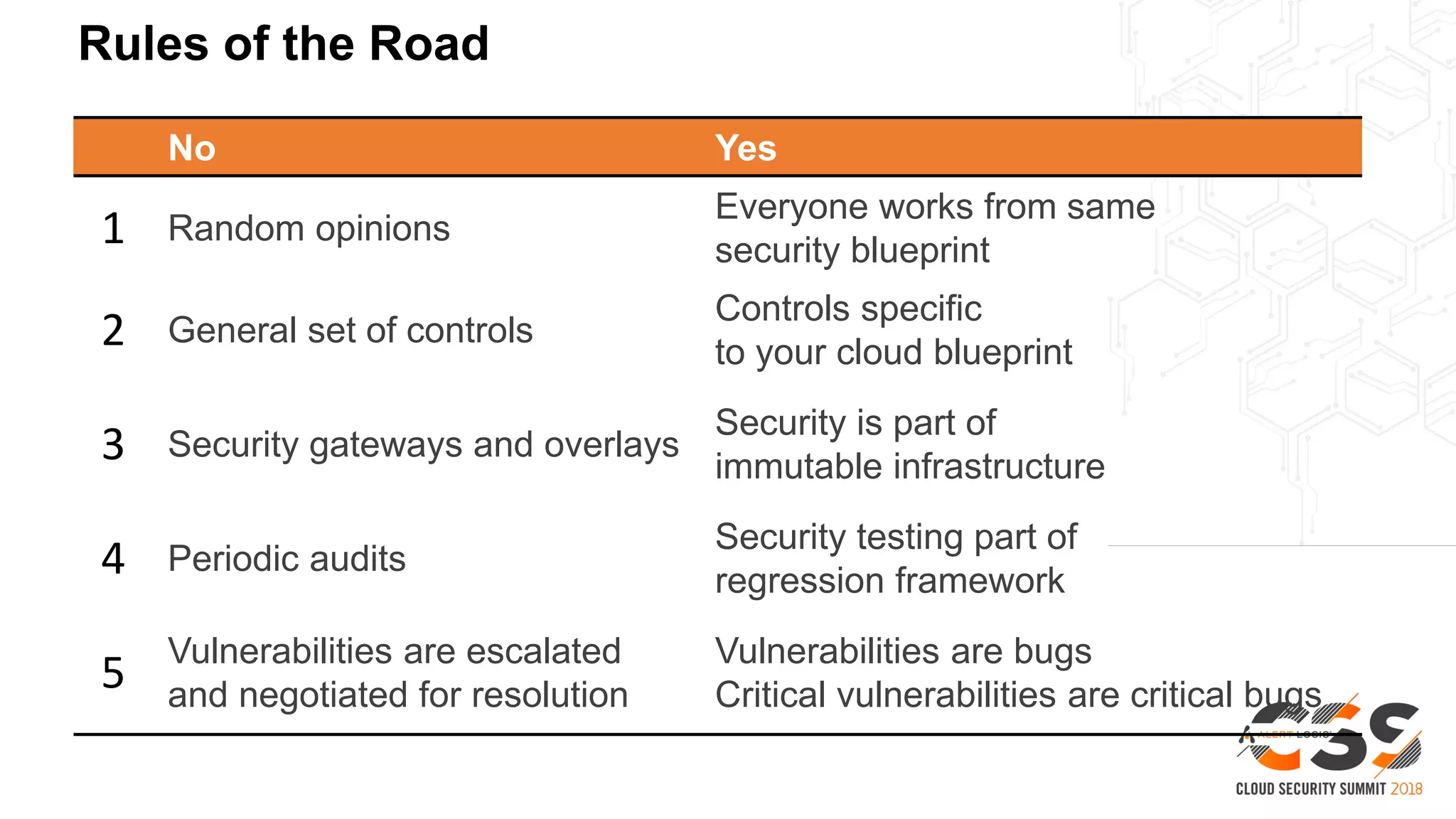
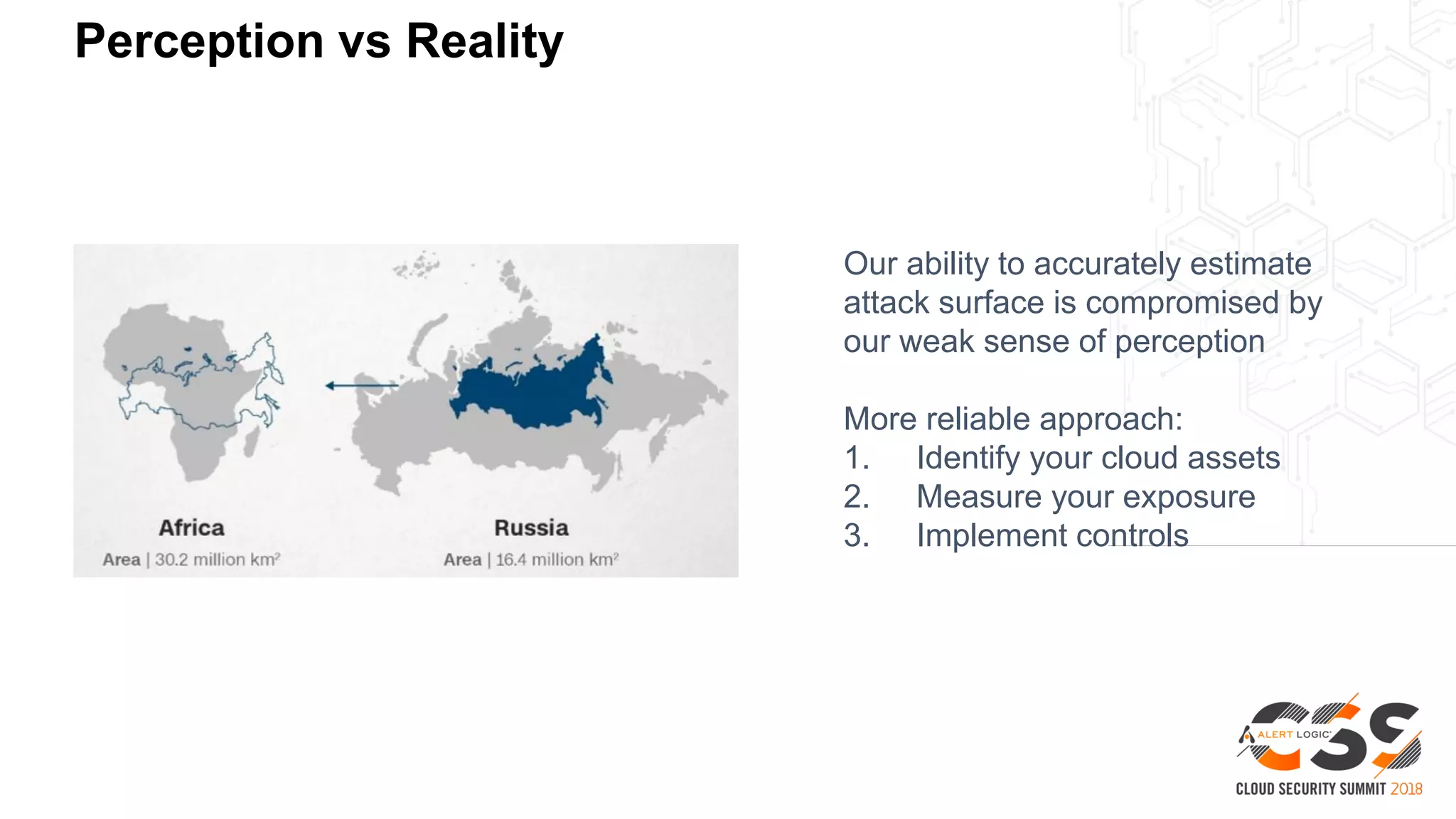
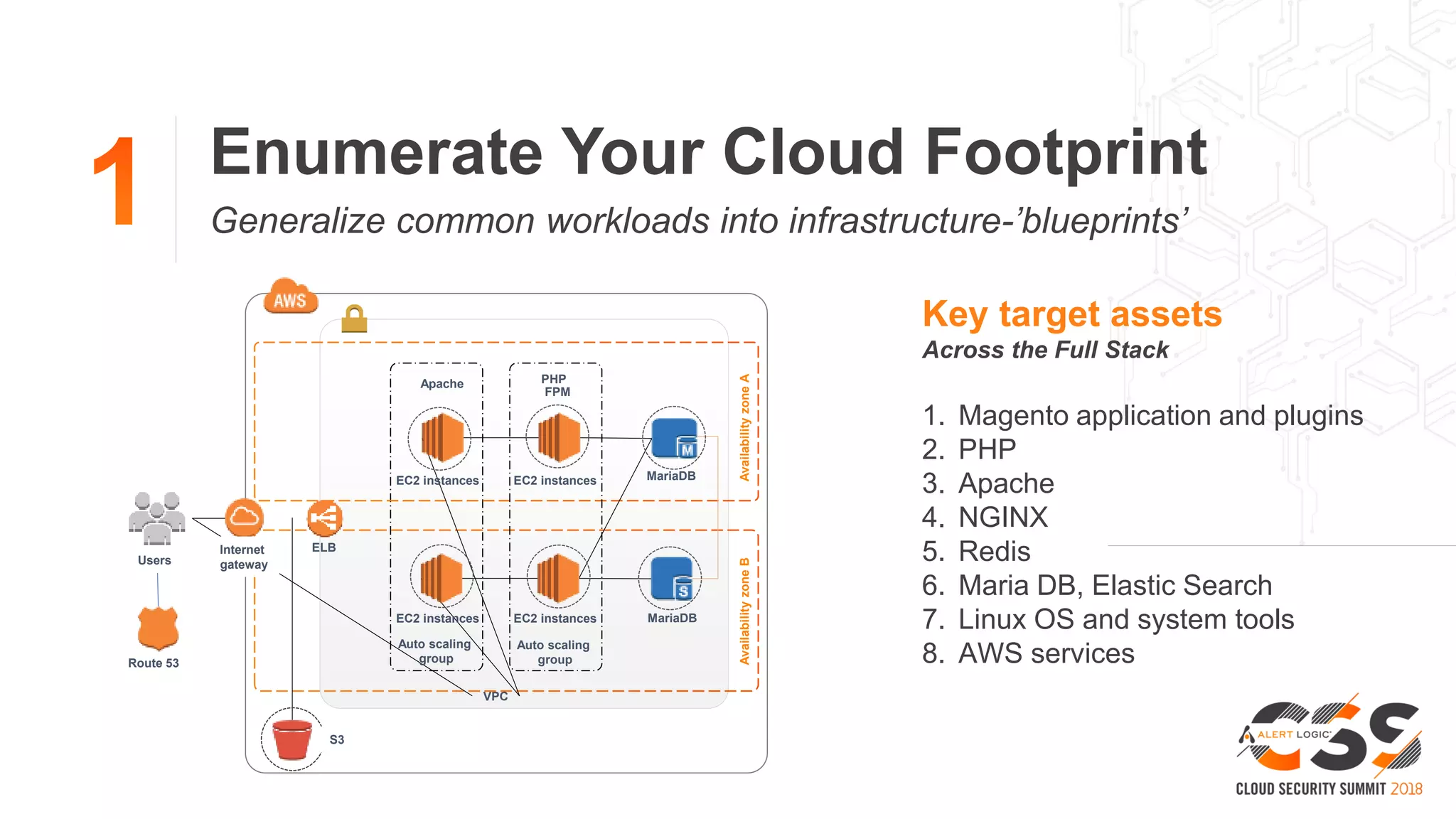
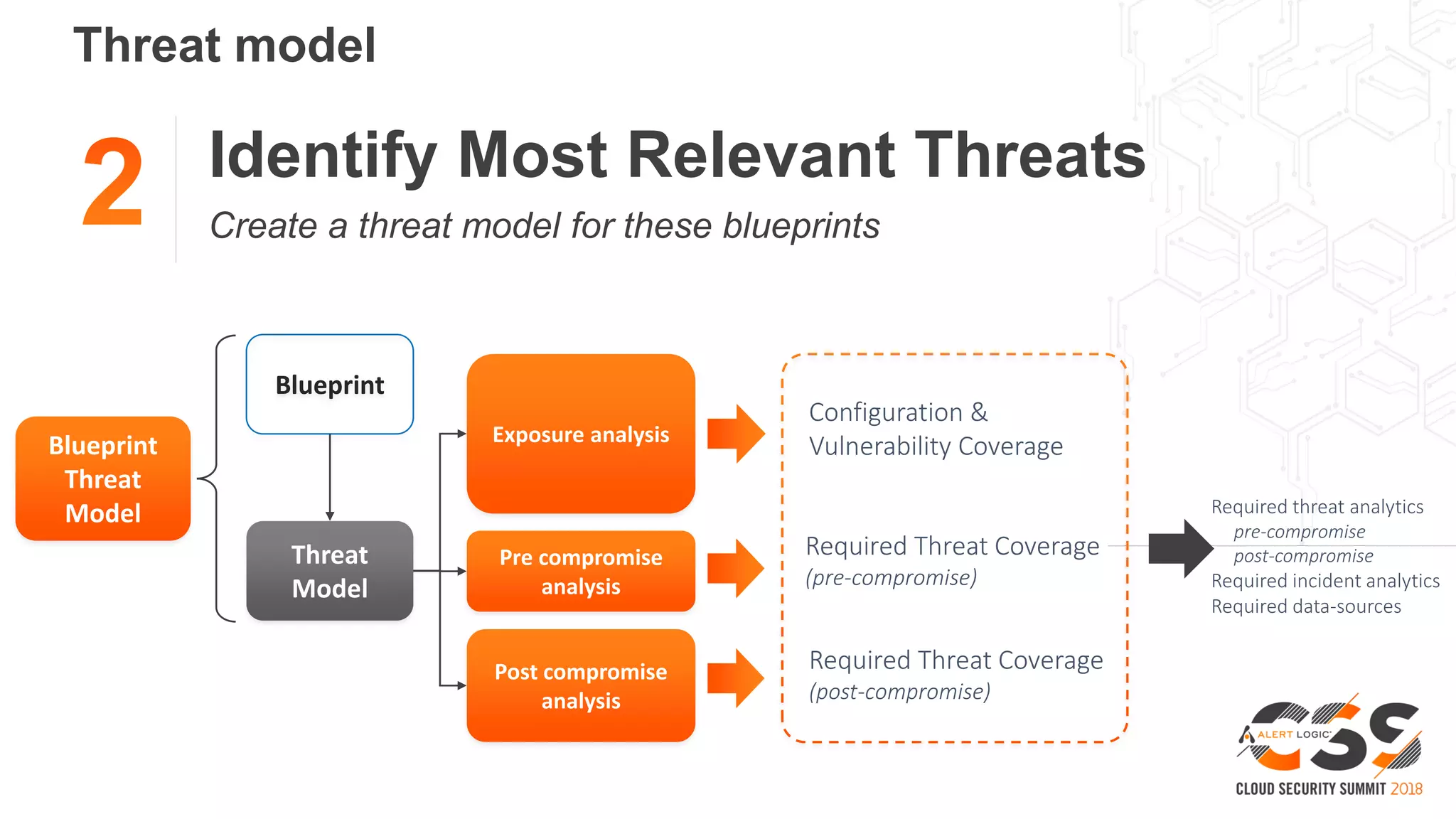
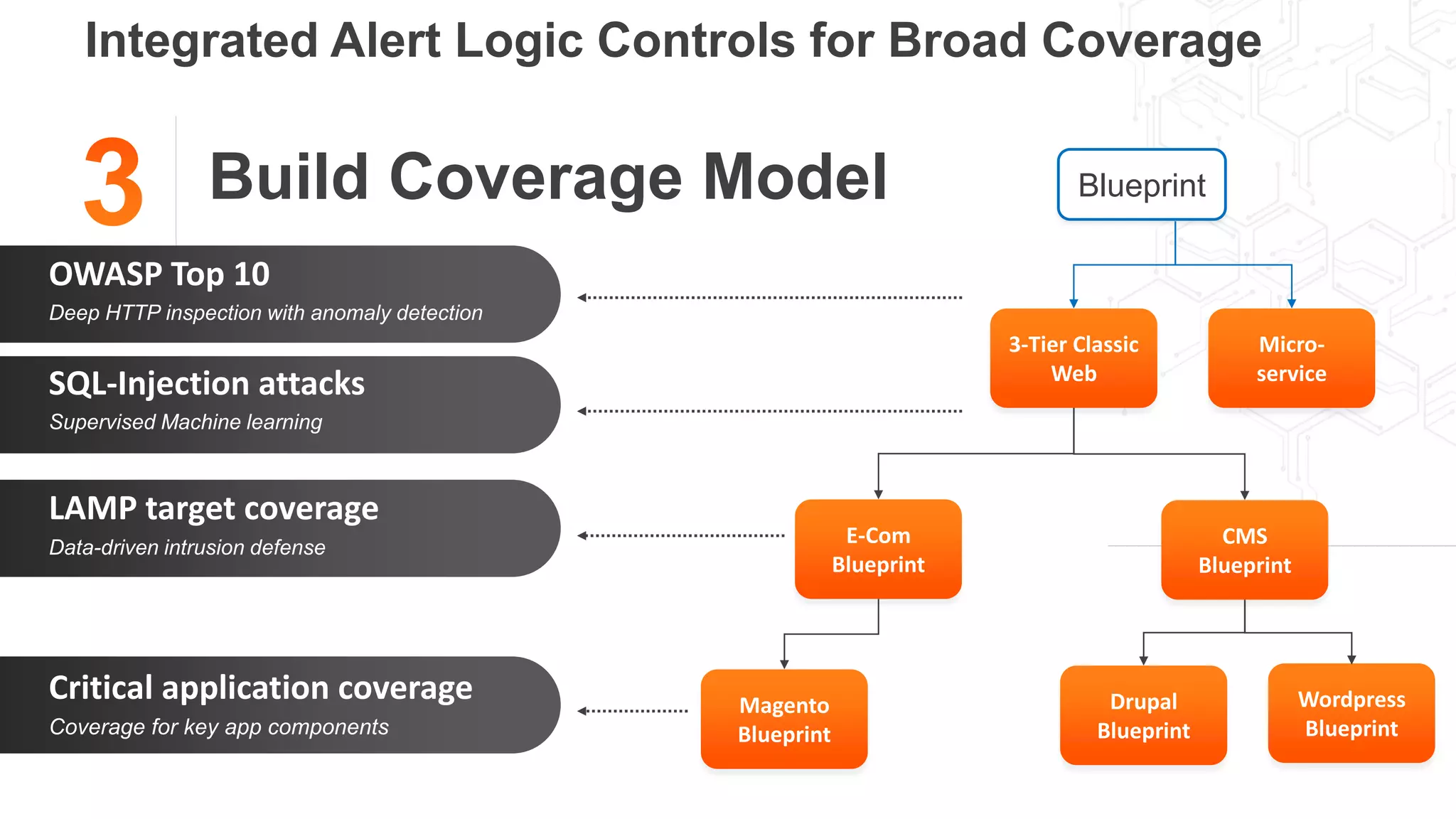
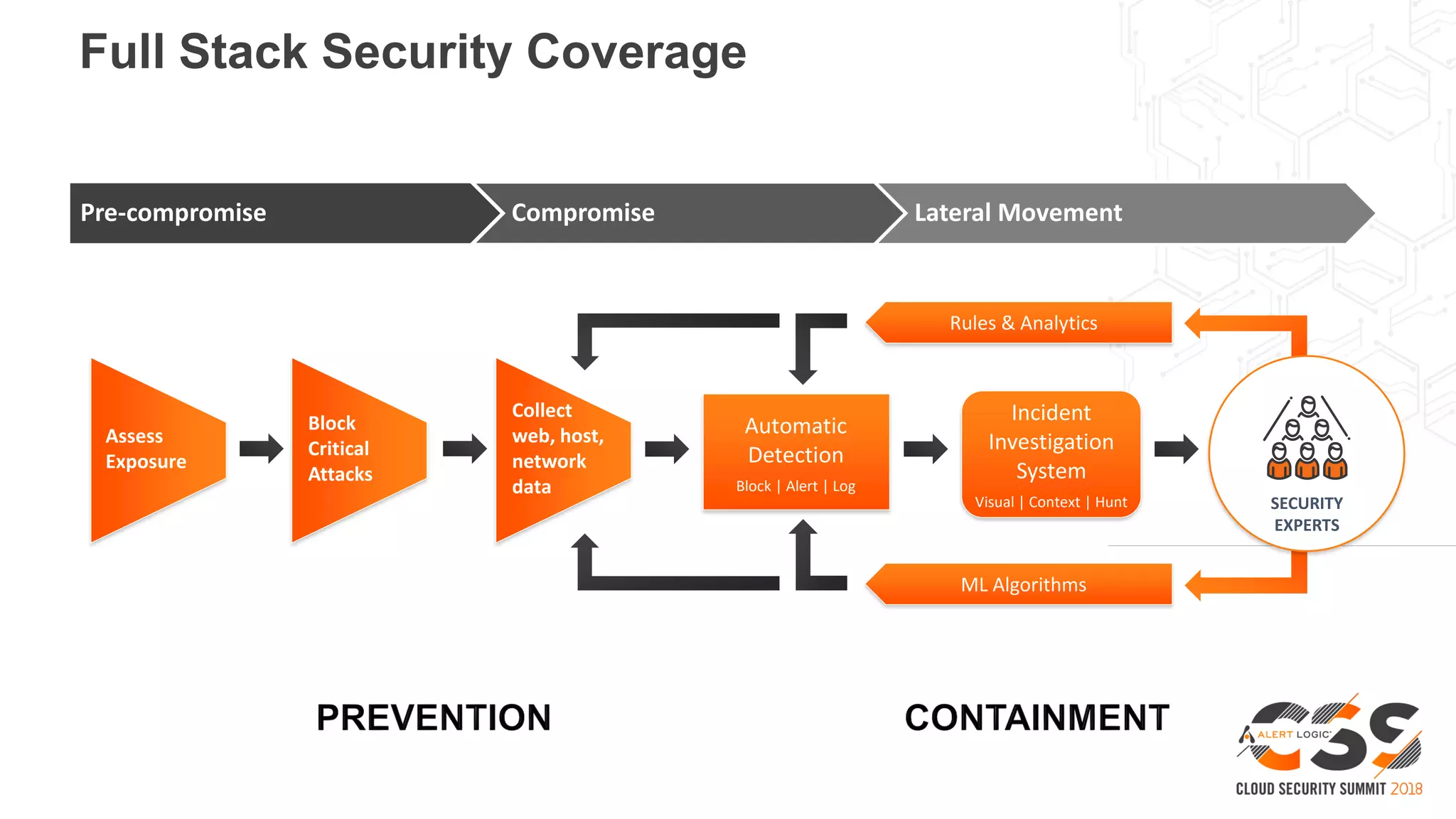
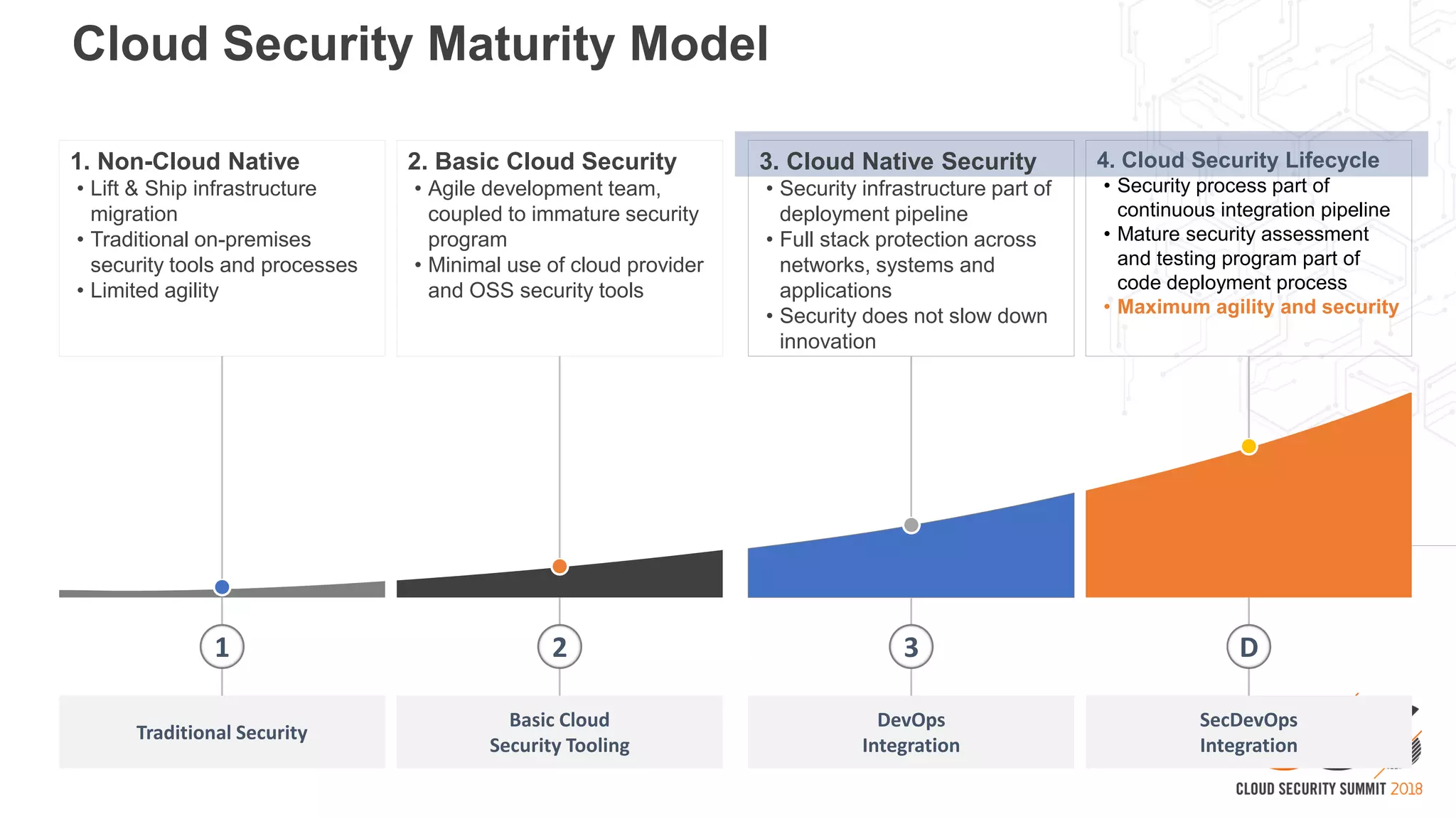
The document discusses the intersection of security and DevOps, emphasizing the role of developers in driving cloud adoption for innovation. It outlines critical questions for integrating security into DevOps workflows and proposes a blueprint model for cloud security that includes threat modeling and exposure analysis. The document also describes various security maturity levels, from basic cloud security to mature DevOps security integration, highlighting the importance of agility without compromising security.