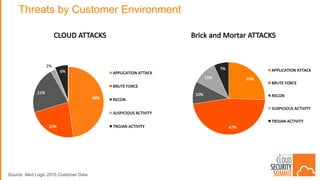
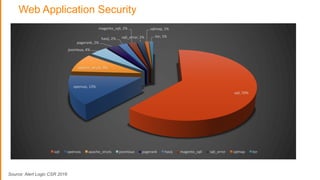
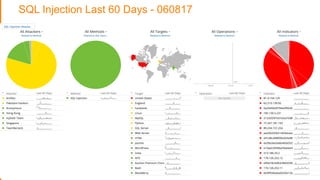
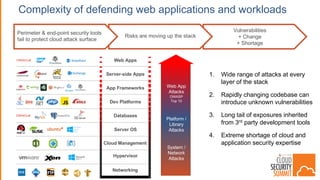
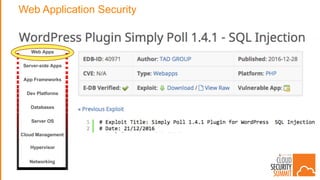
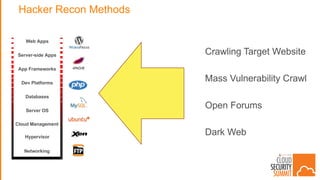
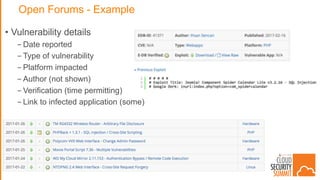
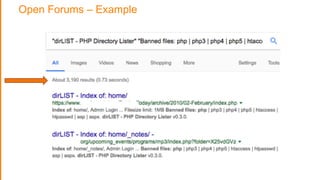
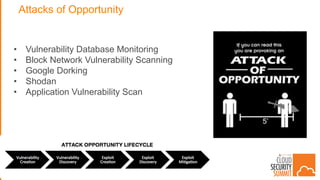
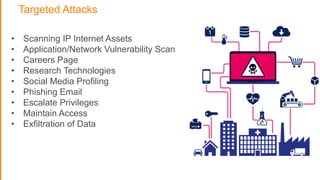
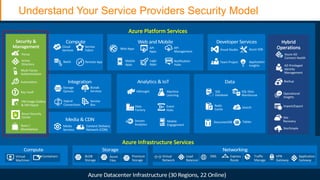
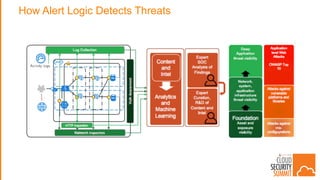
The document discusses strategies for protecting web applications from security threats. It begins by examining the types of attacks organizations face, including application attacks, brute force attacks, and suspicious activity. It then covers hacker reconnaissance methods such as crawling websites, using vulnerability scanners, and searching open forums and the dark web. The document outlines how attacks can escalate from exploiting web applications to gaining privileged access. It concludes by providing recommendations for developing a secure code, access management policies, patch management, monitoring strategies, and staying informed of the latest vulnerabilities.