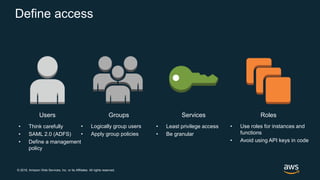
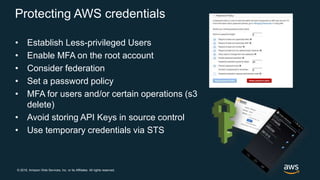
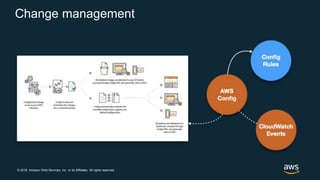
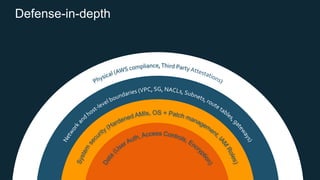
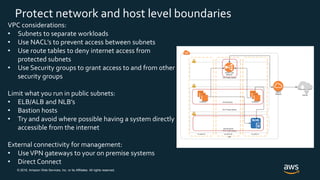
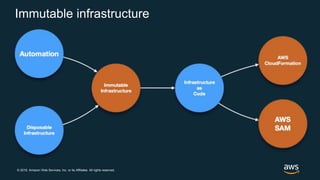
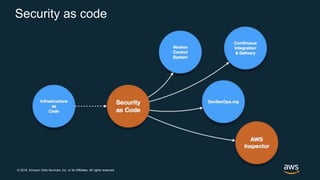
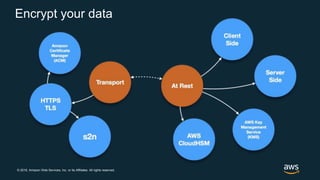
The document discusses AWS security best practices, including implementing a strong identity foundation with IAM, enabling traceability with logging and monitoring tools, applying security at all layers with a defense-in-depth approach, automating security best practices through templates and CI/CD pipelines, protecting data through encryption, and preparing for security events with incident response planning.