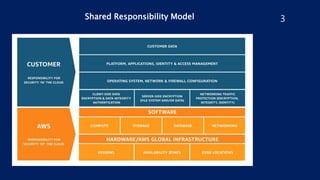
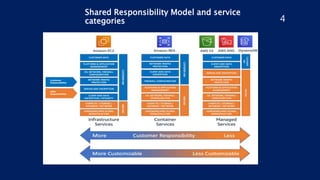
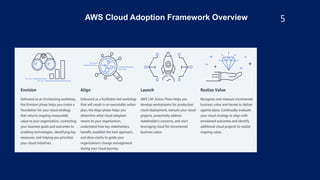
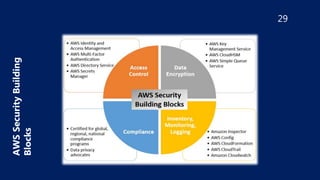
The document outlines security best practices for AWS including:
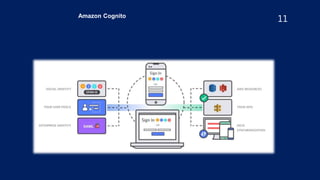
- Using IAM roles instead of long-term access keys, enabling MFA authentication, and granting least privilege access.
- Encrypting data at rest using AES-256 encryption, limiting network access using security groups, and enabling logging.
- Ensuring S3 buckets, RDS instances, and Redshift clusters are not publicly accessible and their access is encrypted.
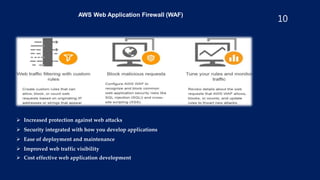
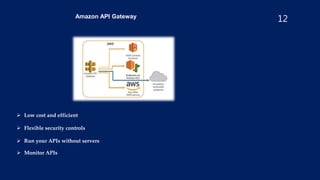
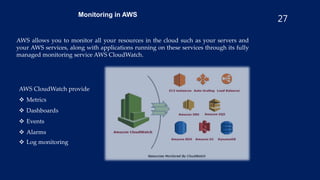
- Implementing monitoring with CloudWatch and using security tools like Inspector, Shield, and WAF.