This document provides an overview of malaria, including its epidemiology, life cycle, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment. Some key points:
- Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasites and transmitted via the bites of infected Anopheles mosquitoes. P. falciparum causes the most severe form of the disease.
- It is widespread in tropical and subtropical regions, especially sub-Saharan Africa. An estimated 1-3 million people die from malaria each year.
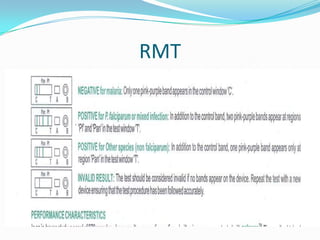
- Symptoms include fever, chills, fatigue and headaches. Severe malaria can lead to coma, organ failure or death if not promptly treated. Diagnosis involves blood smear examination and rapid tests.
-