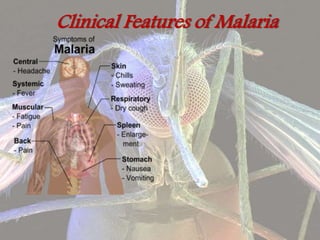
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease caused by Plasmodium parasites. P. falciparum is the most dangerous species and a major cause of mortality in developing countries. It is transmitted via the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. Symptoms include fever, chills, and flu-like illness. Diagnosis involves examining blood films under a microscope for parasites. Treatment depends on the species and severity, but uncomplicated cases are typically treated with artemisinin-based combination therapies over 3 days. Nursing care, chemoprophylaxis, and controlling the mosquito vector are also important aspects of malaria control and management.