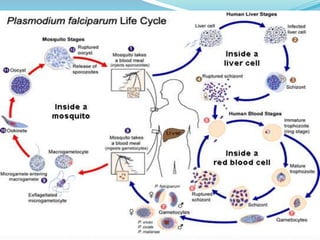
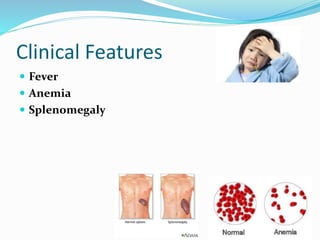
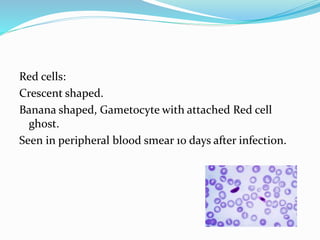
Over 200 million malaria cases and 655,000 deaths occurred globally in 2010 according to WHO estimates. Plasmodium falciparum causes the most severe form of malaria, characterized by high parasitemia levels and life-threatening complications such as cerebral malaria and acute renal failure. The malaria parasite has a complex life cycle involving sexual reproduction in mosquitoes and asexual reproduction in human hosts, causing cyclic fever symptoms. Definitive diagnosis of malaria requires microscopic examination of blood films to identify the plasmodium species. Treatment depends on the identified species, with chloroquine used for chloroquine-sensitive P. falciparum and P. ovale infections.