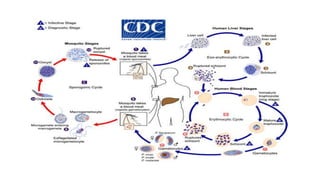
The document summarizes the four main Plasmodium species that cause malaria in humans: P. falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale, and P. malariae. It describes their life cycles, which involve sexual reproduction in mosquitos and asexual reproduction in human liver and red blood cells. P. falciparum causes the most severe disease and is the most likely to result in complications like cerebral malaria and blackwater fever. The life cycle and symptoms of the different species are discussed in detail.