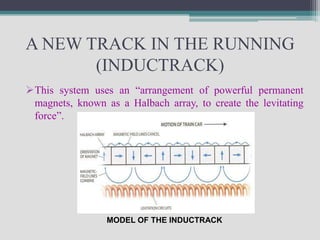
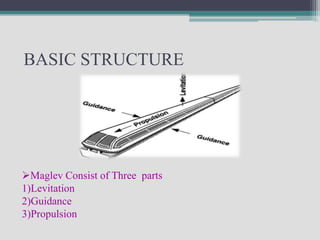
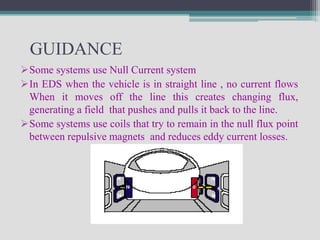
Maglev trains use magnetic levitation for guidance and propulsion instead of wheels on rails. There are two main types - electromagnetic suspension (EMS) which uses electromagnets and electrodynamic suspension (EDS) which uses superconducting magnets. Maglev trains have higher maximum speeds than conventional trains, produce less noise and vibration, and require less maintenance due to the lack of physical contact between train and track. Maglev is also more environmentally friendly as it is more energy efficient and does not emit greenhouse gases.