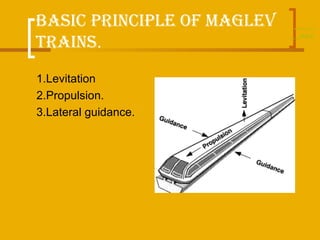
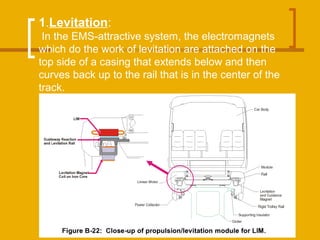
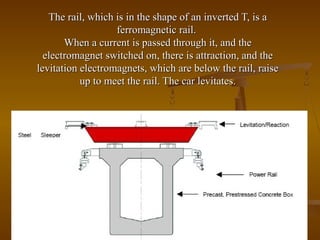
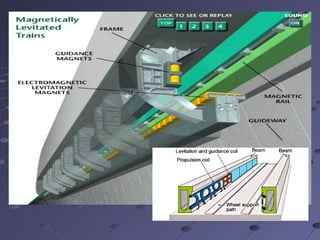
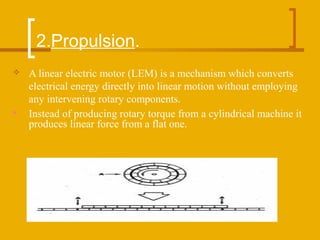
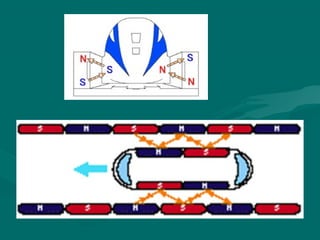
The document discusses magnetic levitation (maglev) trains, detailing their operational principles, types, advantages, and comparisons with conventional trains and aircraft. Maglev trains utilize magnetic fields for levitation and propulsion, achieving higher speeds and lower energy consumption than traditional trains. The conclusion highlights the potential benefits of implementing maglev systems, particularly in countries like India.