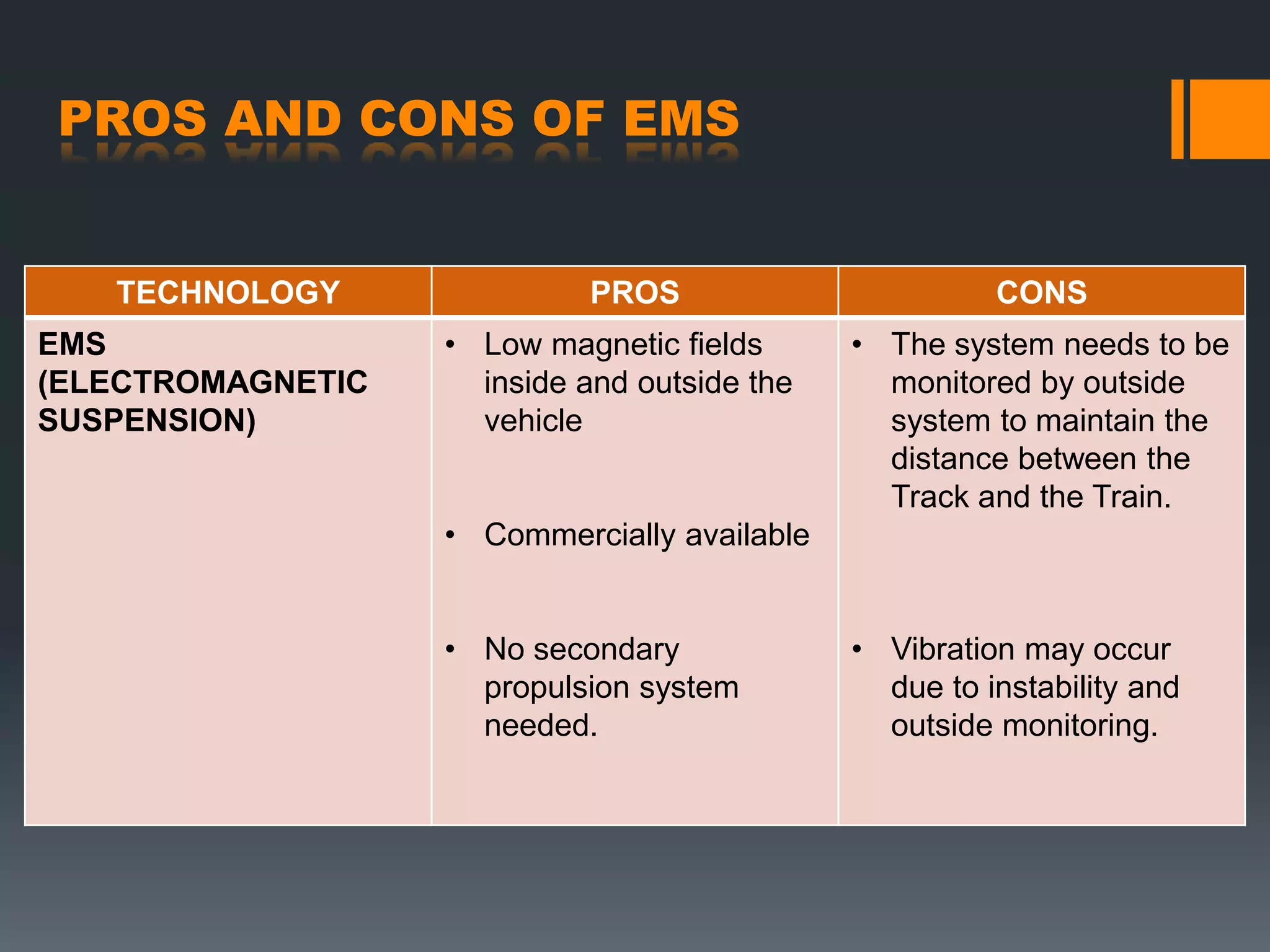
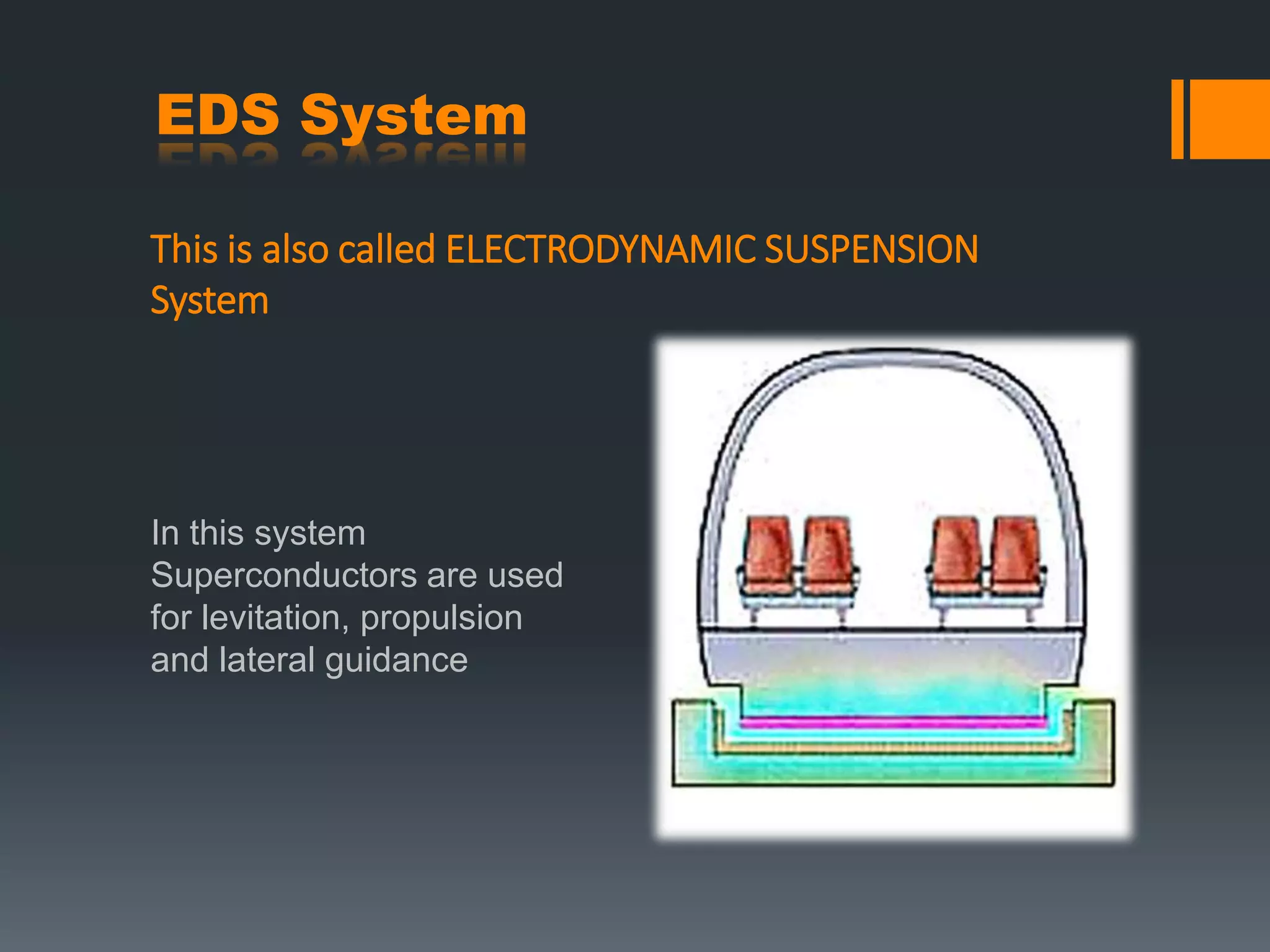
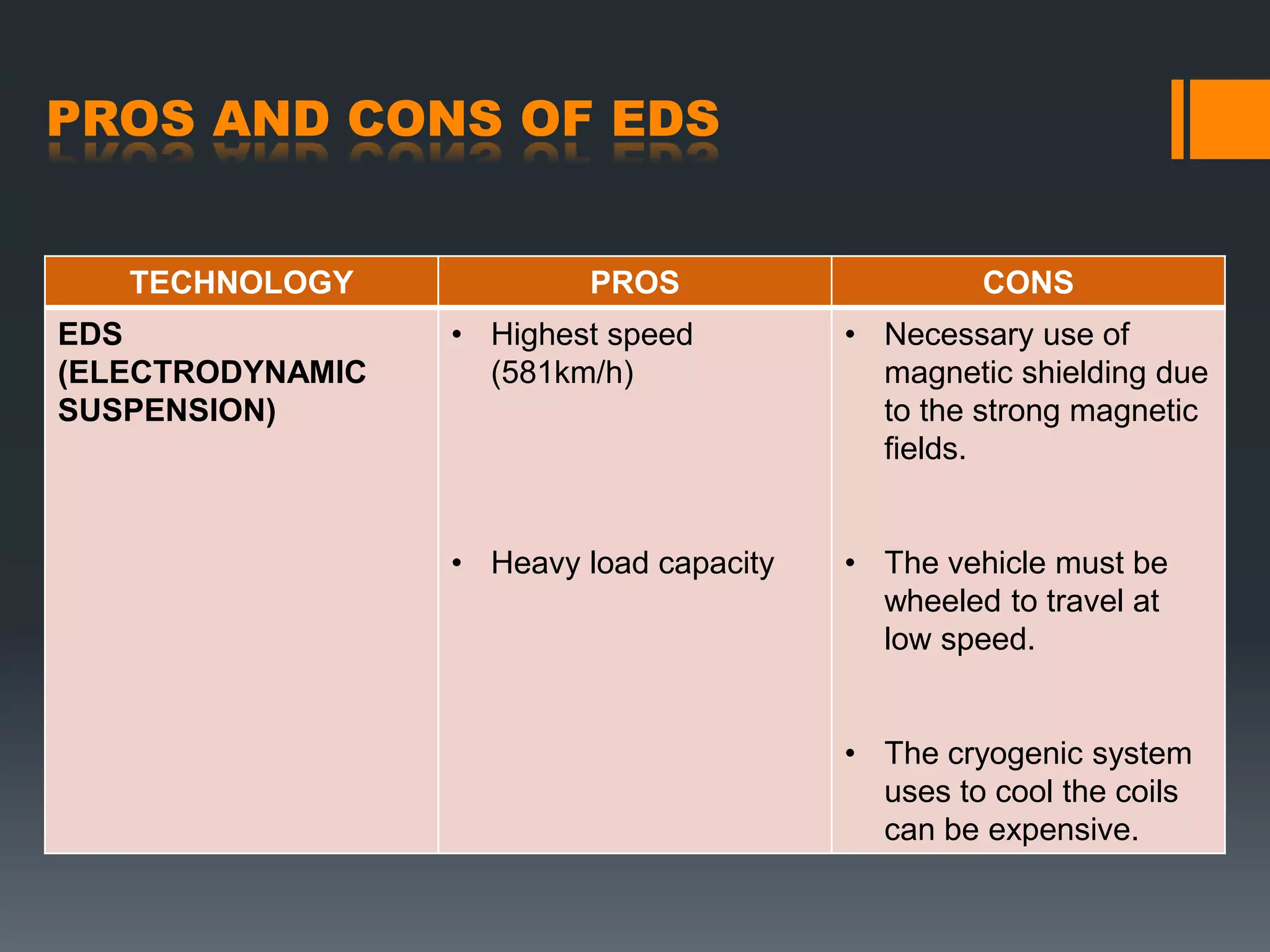
Maglev trains use magnetic levitation to float above the track and propel the train forward. There are two main types of maglev systems - EMS uses electromagnets for levitation while EDS uses superconducting magnets. Maglev trains have the potential for very high speeds since there is no friction, but require complex magnetic systems and can be expensive to implement. The Chuo Shinkansen maglev line under construction in Japan will connect Tokyo and Osaka using EDS technology, with a planned top speed of 350 mph.