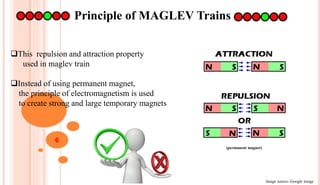
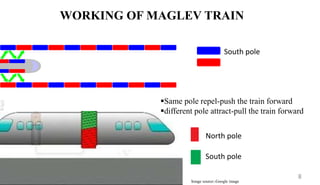
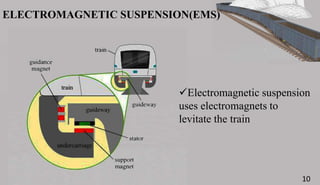
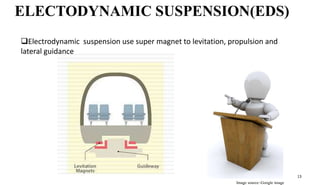
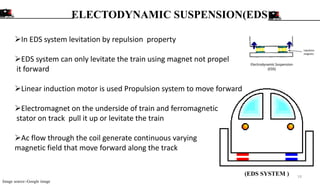
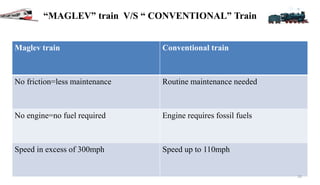
The document is a seminar presentation on maglev trains, covering topics such as their principle of operation, developers, types, and advantages over conventional trains. It emphasizes the technology of magnetic levitation that allows trains to move without contact with the ground, highlighting the differences between electromagnetic and electrodynamic suspension systems. Notable examples include the Shanghai Maglev Train and speed tests conducted by the Central Japan Railway Company.