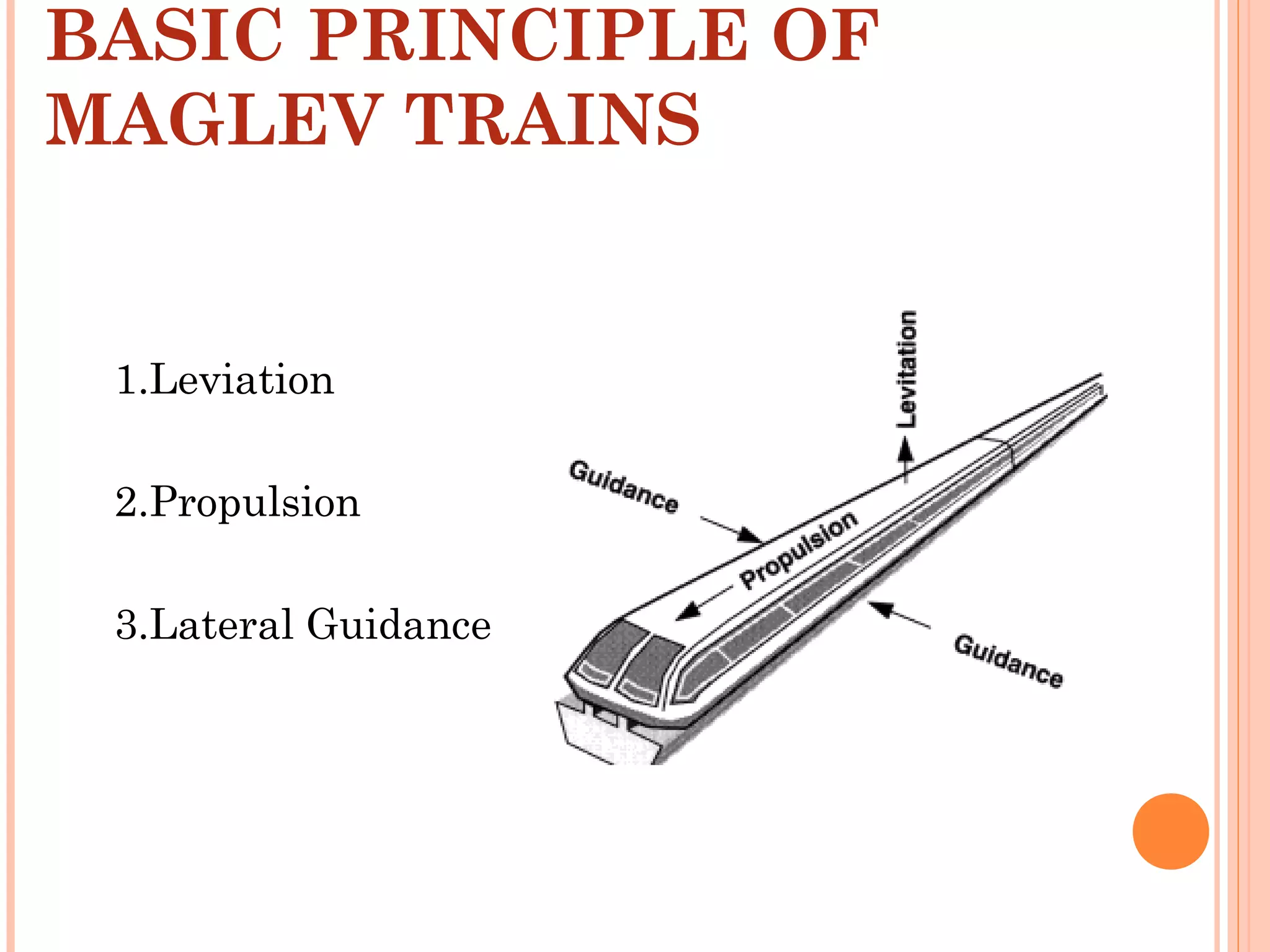
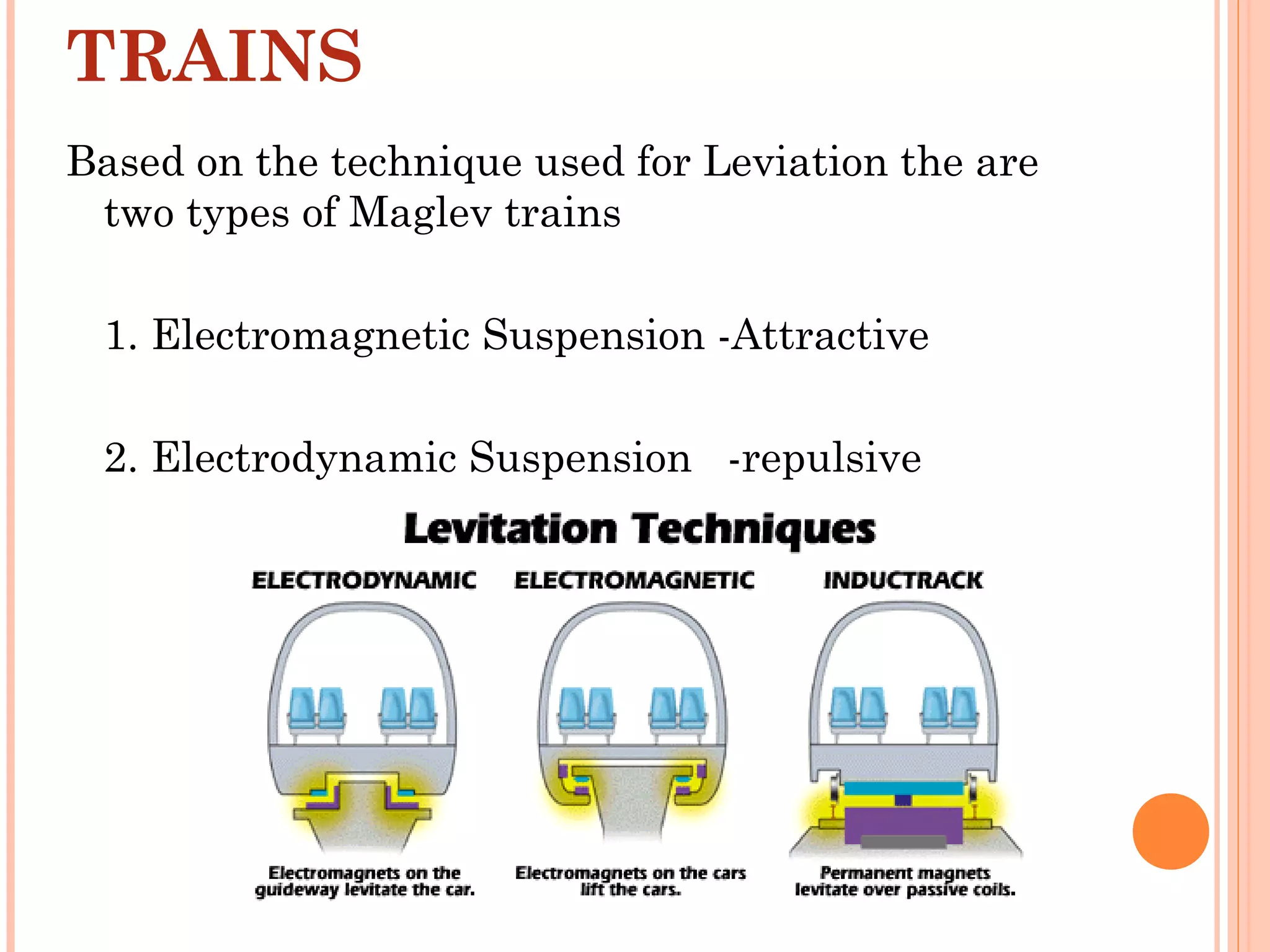
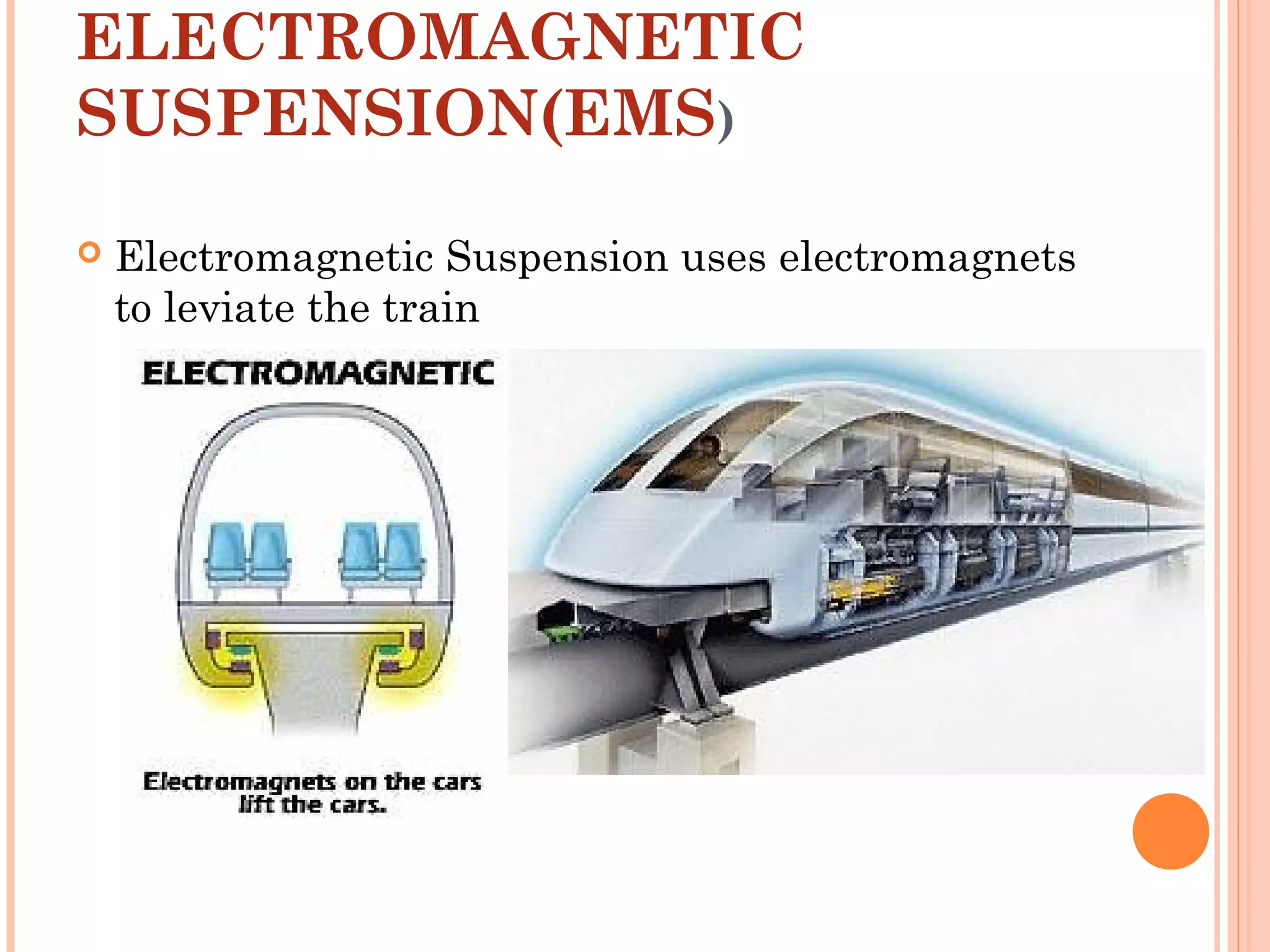
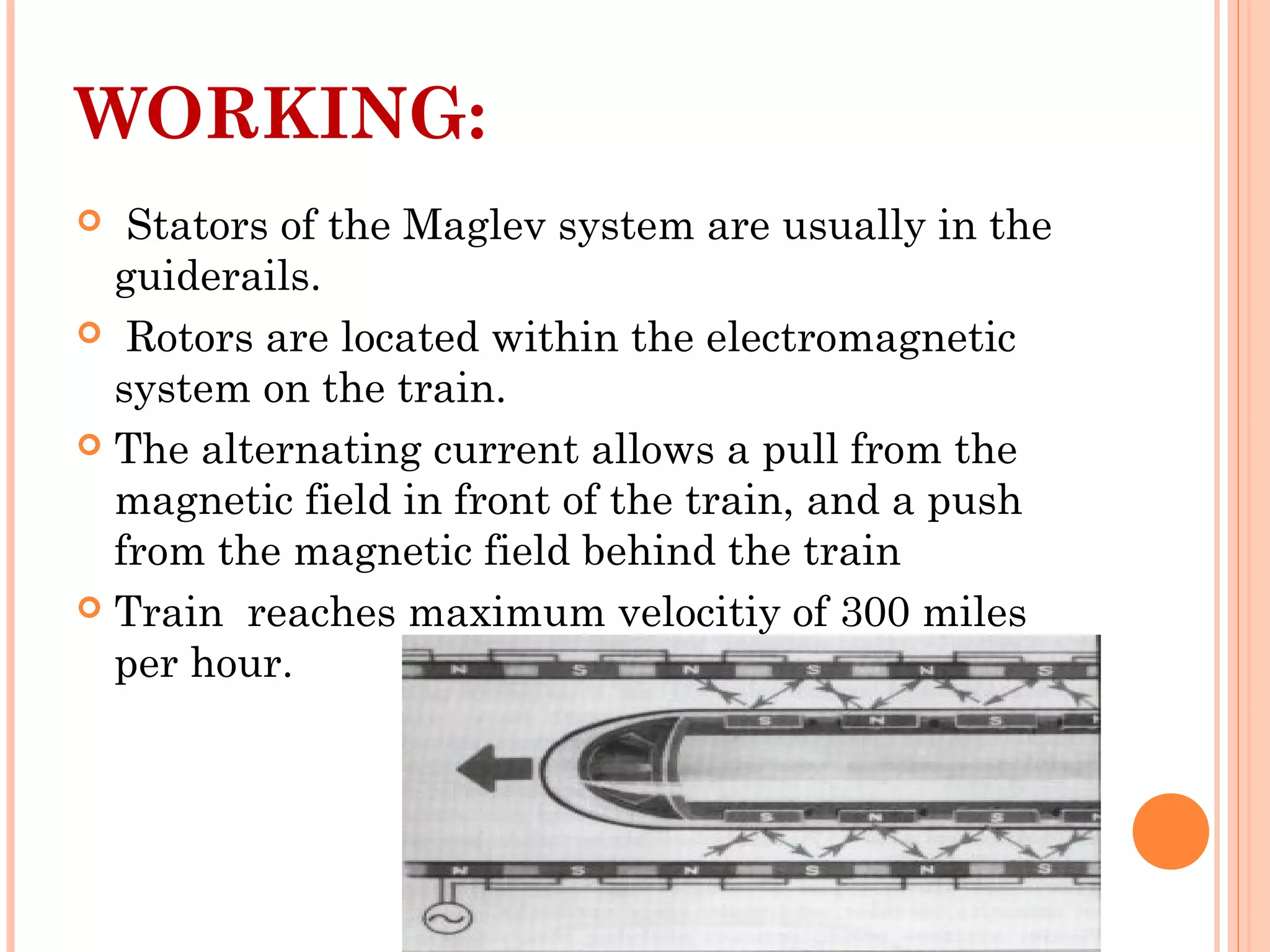
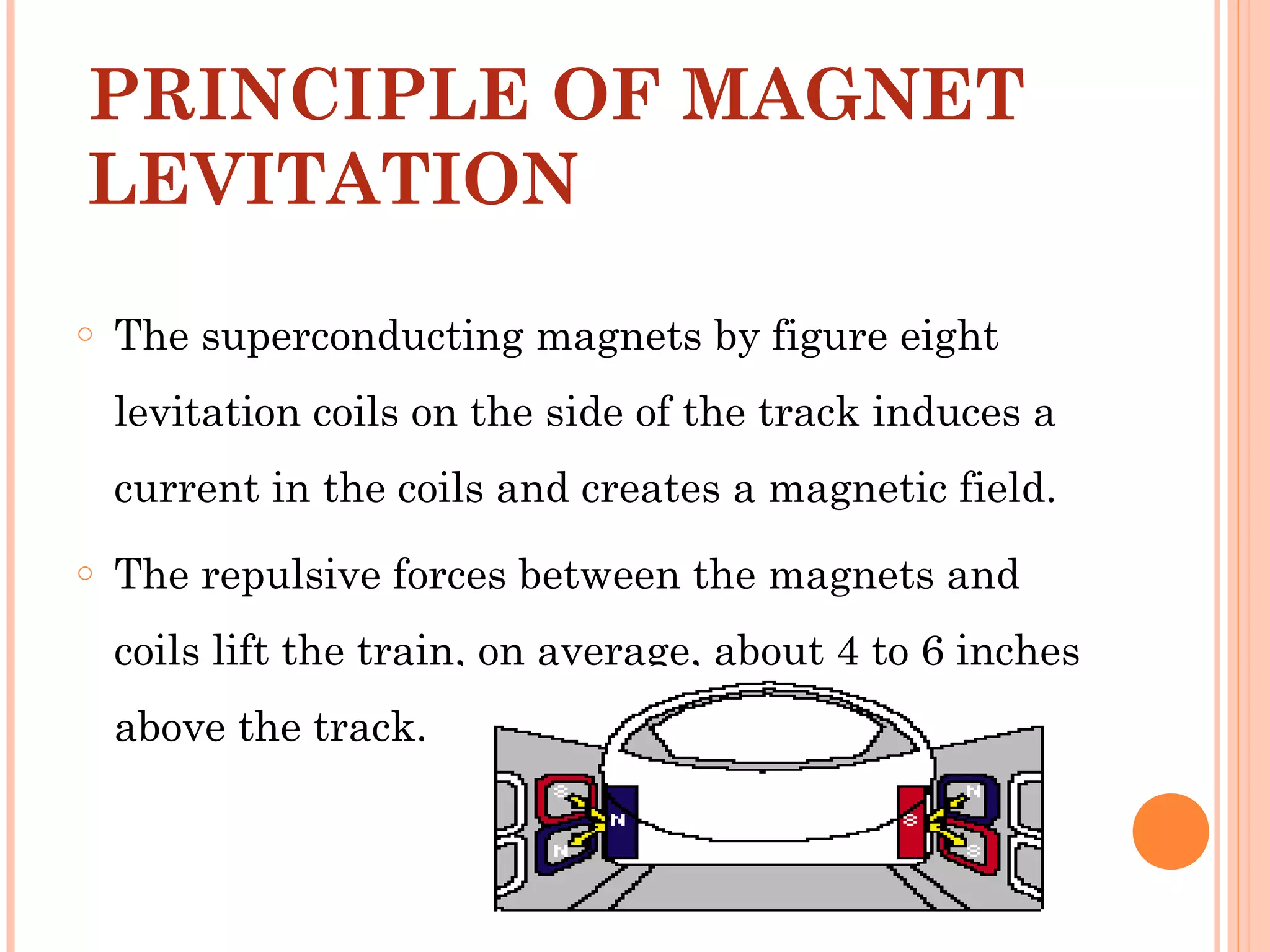
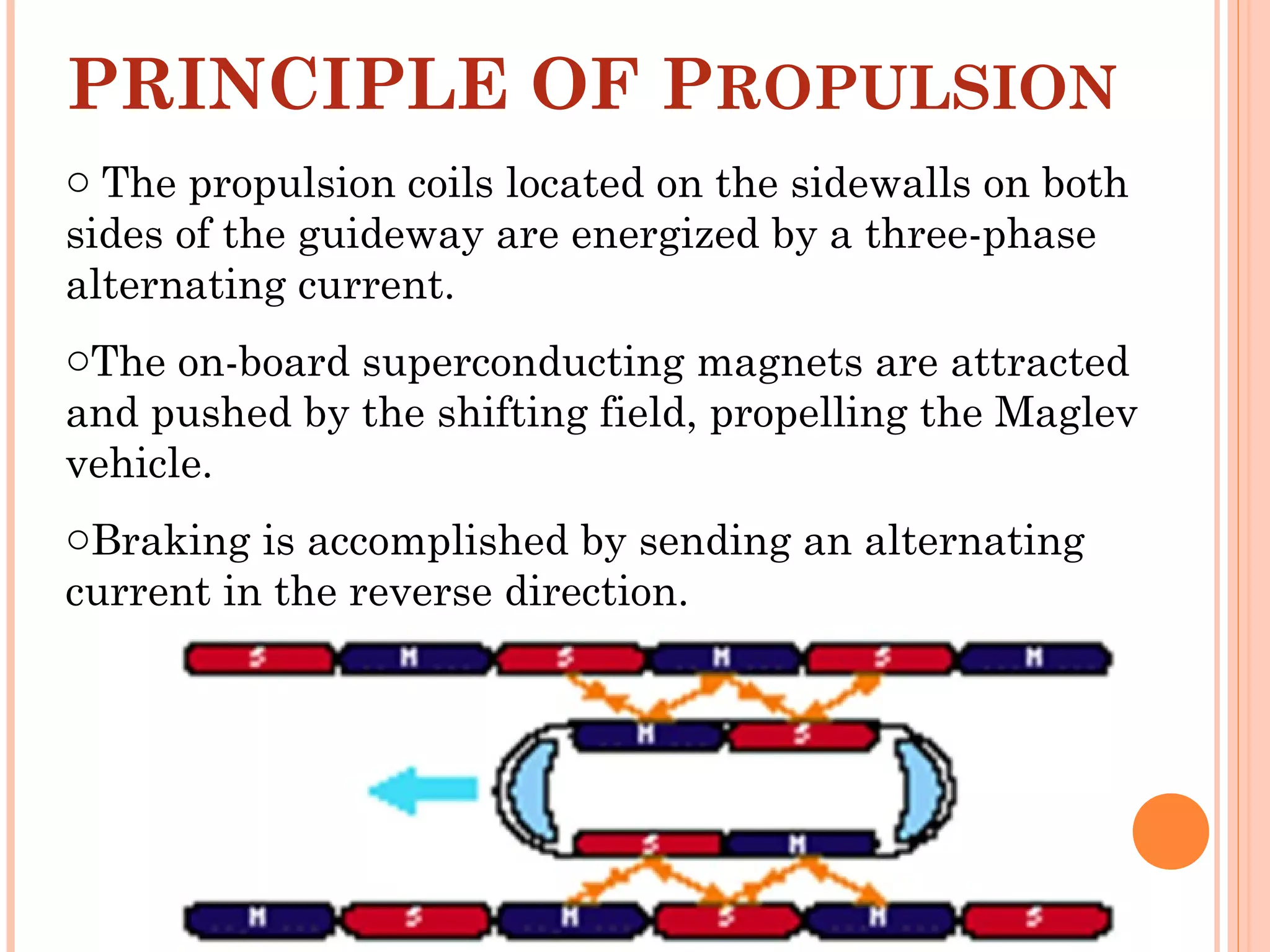
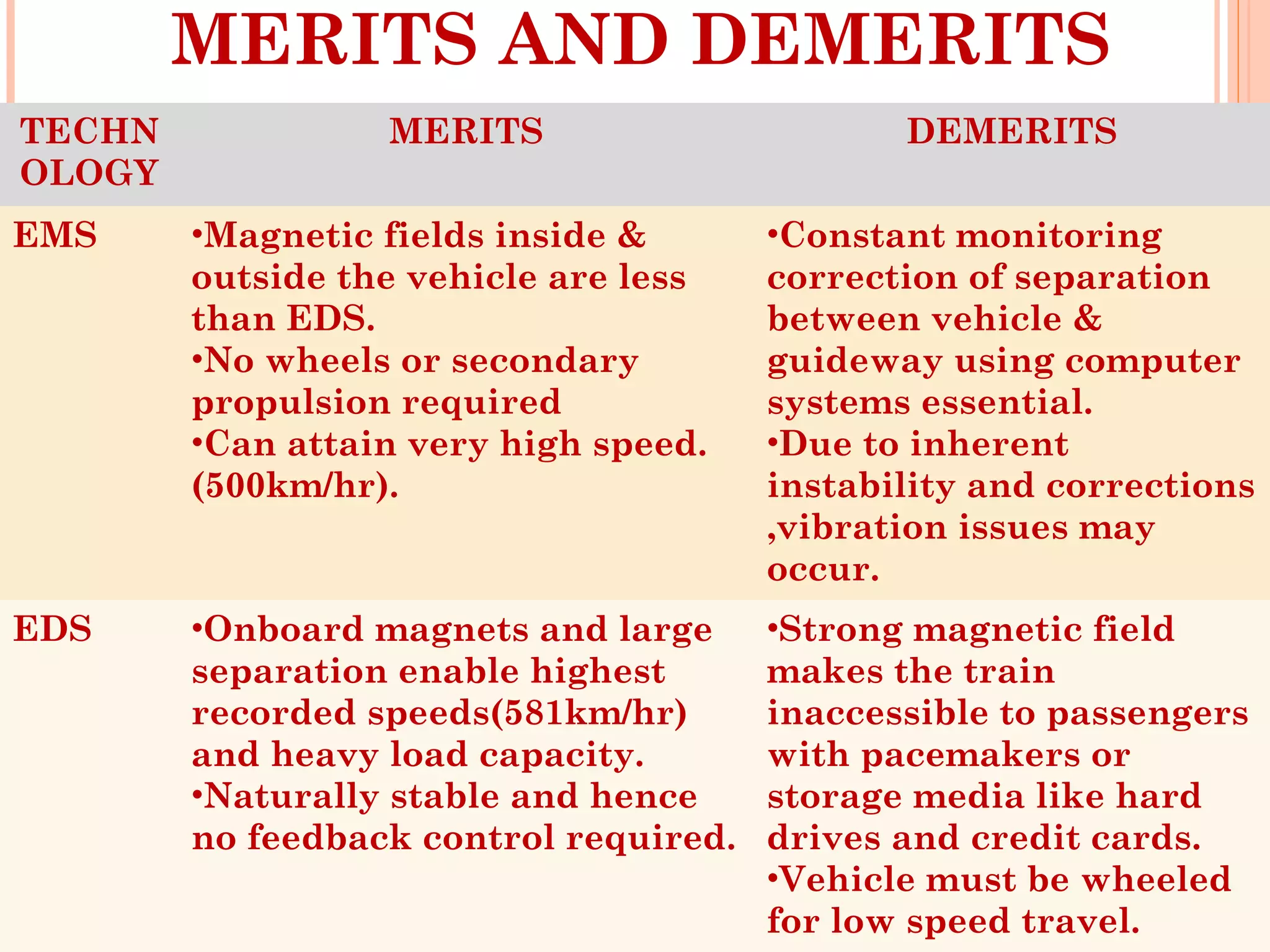
The document discusses Maglev trains, which use magnetic levitation to float above the track without touching it. There are two main types - electromagnetic suspension trains which use electromagnets and electrodynamic suspension trains which use superconductors. Maglev trains have advantages like very high speeds of over 500 km/hr, low noise and friction, and less energy usage compared to conventional trains. However, they also require completely new guideway infrastructure and have high initial construction costs. The document concludes that Maglev trains could provide benefits to countries like India if implemented.