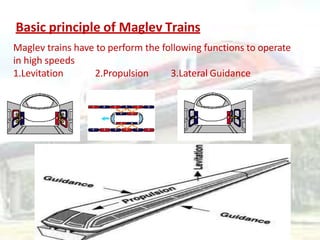
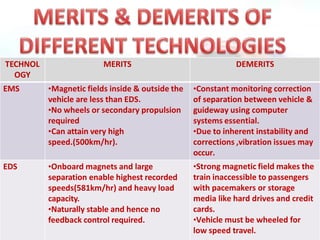
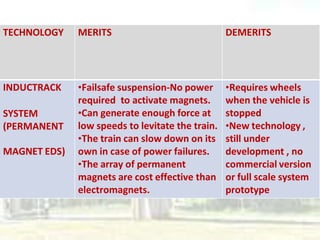
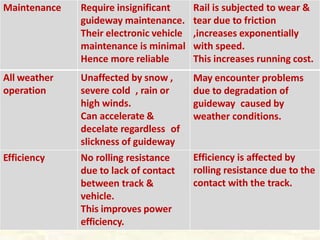
Maglev trains use magnetic levitation to float above the guideway and linear induction motors for propulsion, allowing them to reach very high speeds. There are two main types of maglev technology: electromagnetic suspension (EMS) systems which use electromagnets and electrodynamic suspension (EDS) systems which rely on superconducting magnets. Maglev trains have advantages over conventional trains like higher speeds, less maintenance needs, and better efficiency due to lack of physical contact with the guideway. However, their initial costs are very high. Existing operational maglev systems include the Shanghai Maglev Train in China and various test tracks in Japan, Germany, and South Korea.