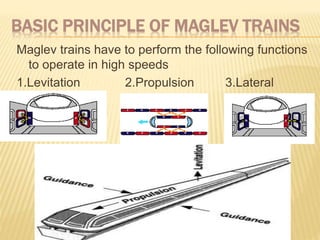
This document discusses magnetic levitation (Maglev) technology. It explains that Maglev trains use electromagnetic or electrodynamic suspension to levitate, propel, and guide the train using magnetic fields. The two main types are electromagnetic suspension (EMS), which uses electromagnets to levitate the train via attraction, and electrodynamic suspension (EDS), which uses superconductors and repulsion. While EDS can reach higher speeds, EMS systems are commercially available and do not require secondary propulsion. The document also briefly mentions the Inductrack design and potential applications of Maglev technology.