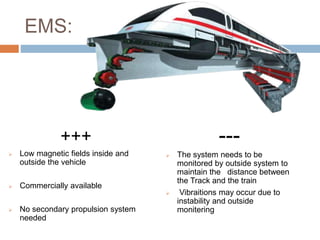
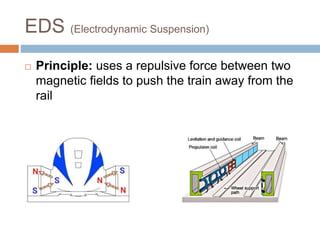
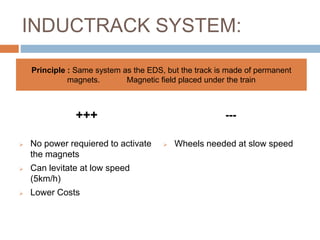
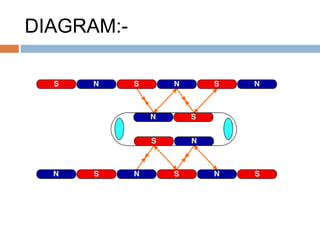
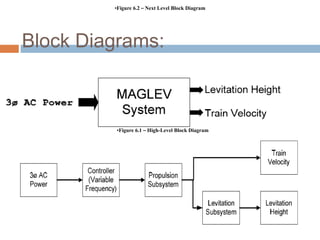
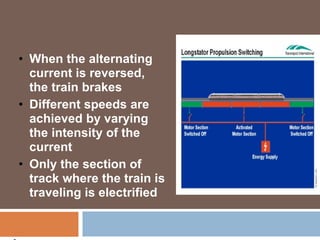
The document discusses Maglev trains, which use magnetic levitation to float above the guideway and propel the train forward. Maglev trains have reached speeds over 500 km/h and have several advantages over conventional trains, such as having no friction, requiring no fuel, and being safer. However, their construction is very expensive. In conclusion, Maglev trains provide efficient high-speed travel but have high initial costs compared to traditional trains.



![HISTORY:
1971: West Germany
(90 kmph)
1972 : Japan (60
kmph)
1975 : West Germany
(401.3 kmph)
1979 : Japan (517
kmph)
•Figure -Trial run of the Transrapid
TR06, near
Lingen, Germany [9]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maglev1-150414121858-conversion-gate01/85/MAGLEV-4-320.jpg)