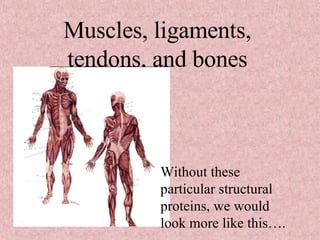
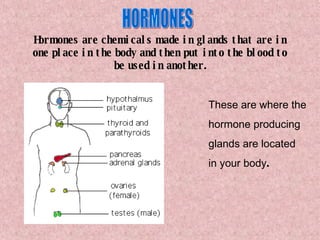
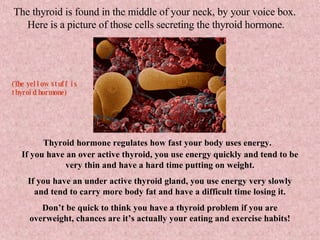
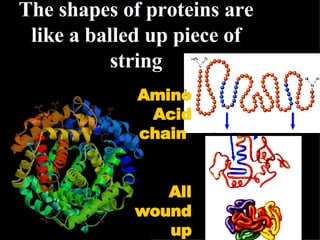
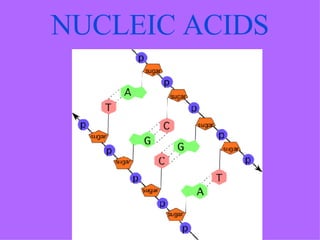
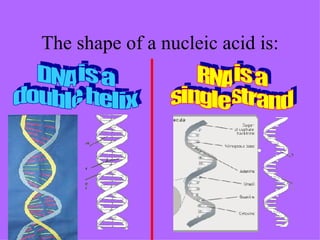
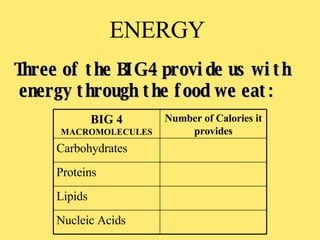
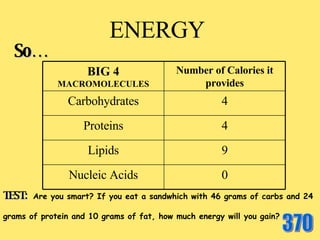
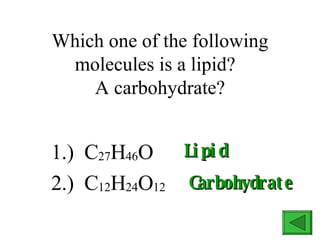The document provides an overview of the four main types of macromolecules - carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. It discusses what each macromolecule is made up of at the molecular level, where they are found, and their main functions in living things. The key points covered include that carbohydrates are polymers of glucose monomers and are an important energy source; lipids are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and function to store energy, insulate, and produce hormones; proteins are polymers of amino acid monomers and compose structures, enzymes, and hormones; nucleic acids include DNA and RNA.