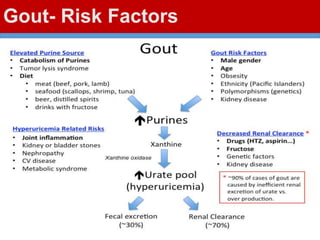
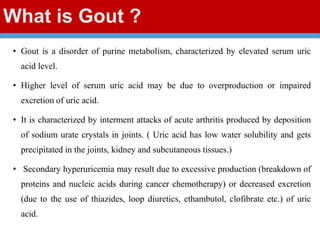
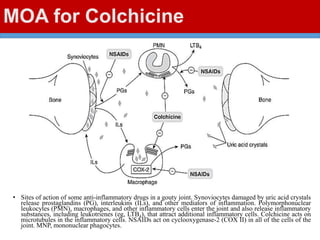
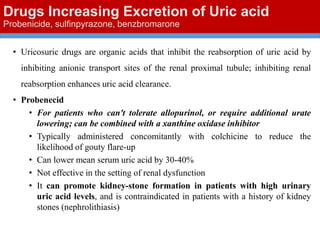
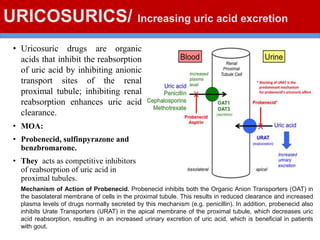
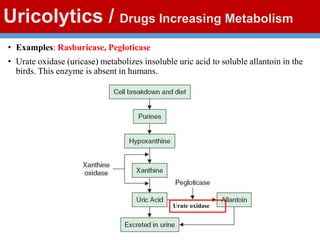
This document discusses gout, a disorder caused by elevated uric acid levels that leads to painful arthritis attacks. It first defines gout and explains its causes as either overproduction or impaired excretion of uric acid. It then discusses the signs and symptoms of acute gout attacks, typically involving hot, swollen, tender joints like the big toe. The document outlines diagnostic criteria and treatment approaches for gout, including using NSAIDs, colchicine, or corticosteroids to relieve acute attack symptoms and allopurinol or probenecid long-term to control uric acid levels and prevent future attacks. It details the mechanisms and considerations for these drug classes.