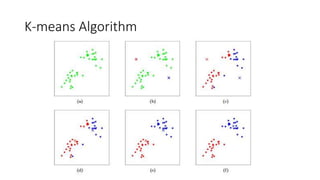
The document presents a comprehensive introduction to machine learning using R, covering key topics such as exploratory data analysis, classification, clustering, and regression. It includes instructions for setting up R and RStudio, various machine learning algorithms, and techniques for performance evaluation and data visualizations. Additionally, it features practical demonstrations and links to resources for further exploration.