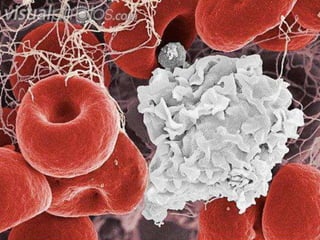
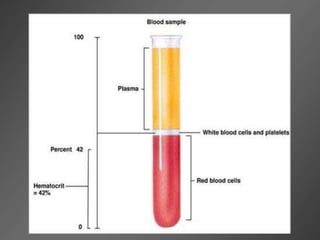
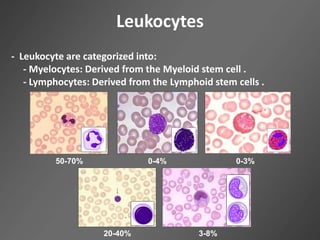
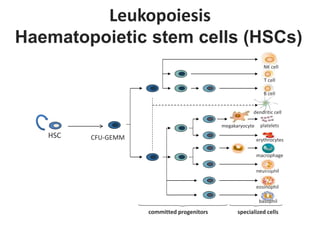
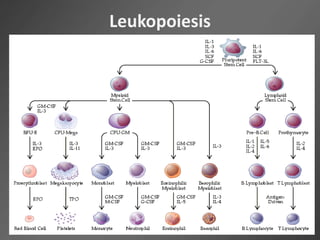
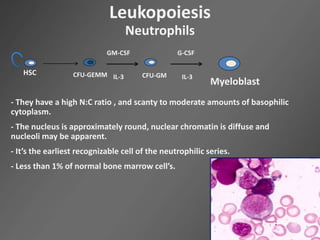
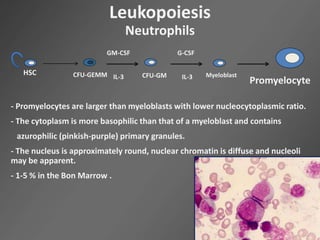
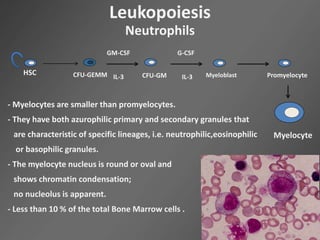
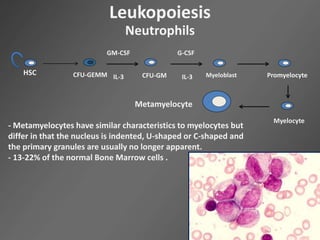
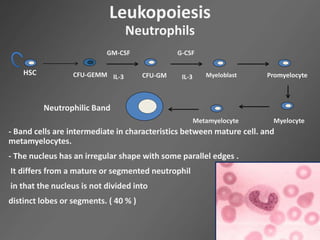
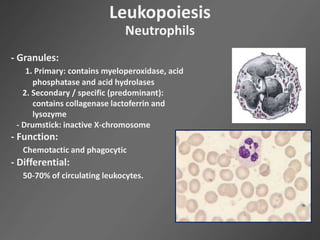
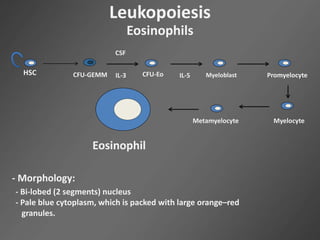
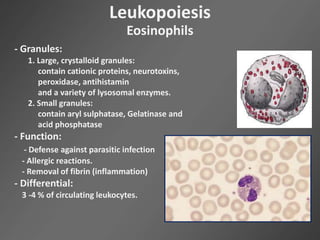
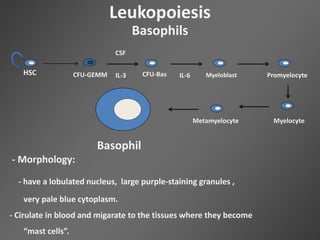
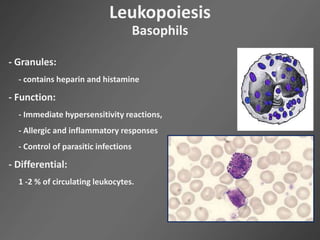
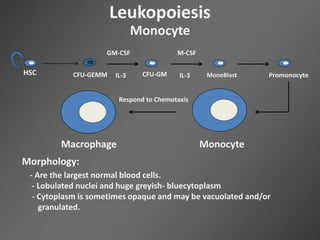
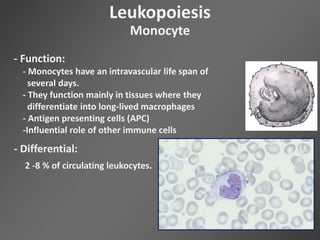
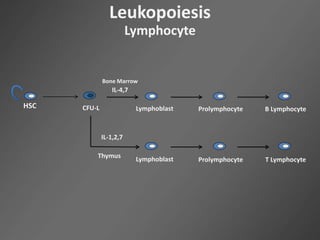
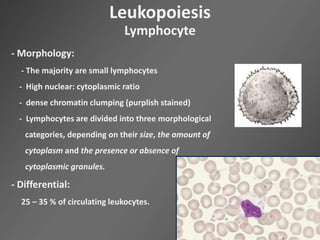
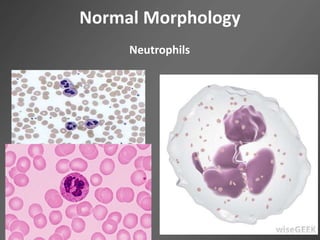
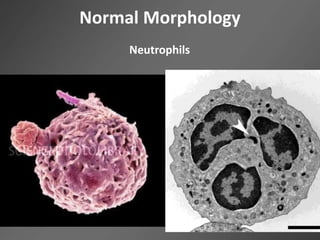
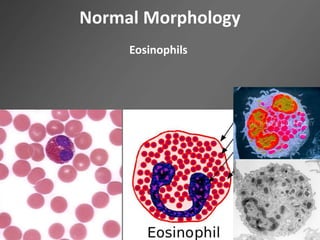
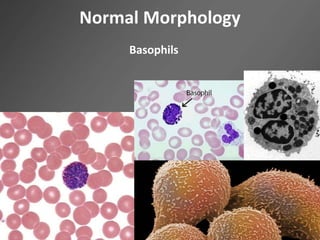
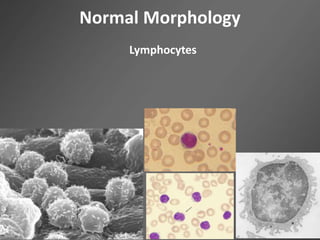
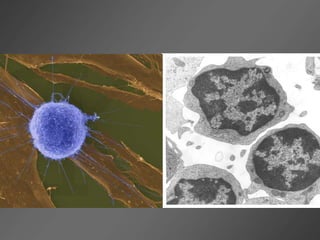
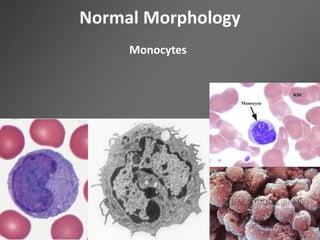
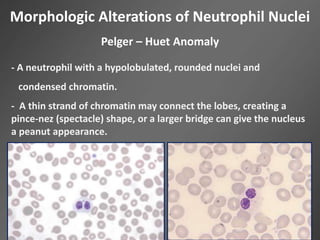
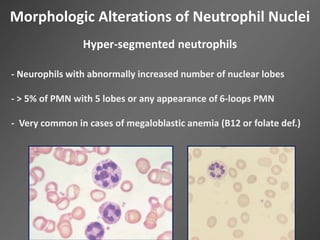
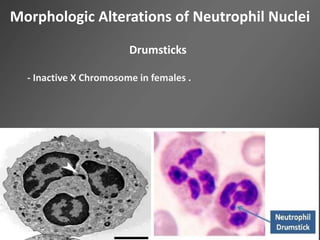
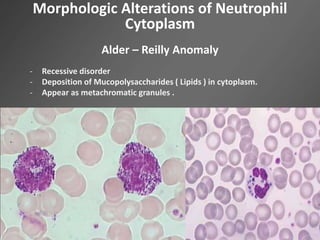
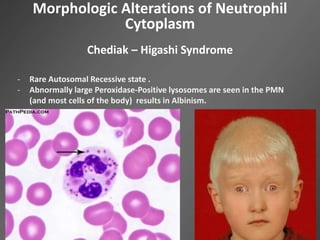
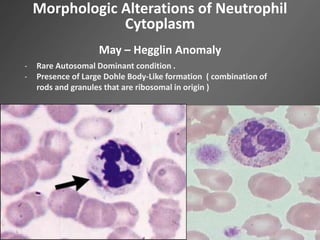
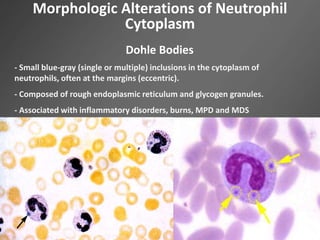
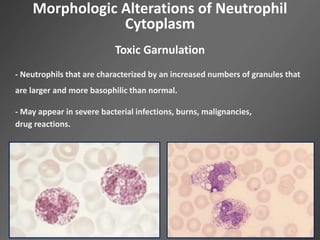
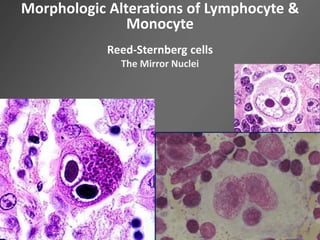
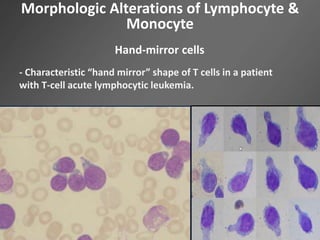
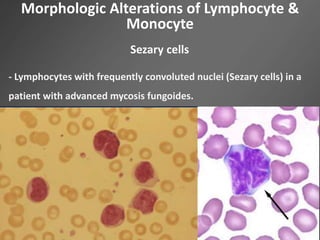
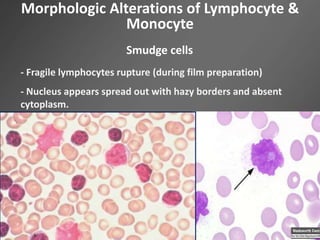
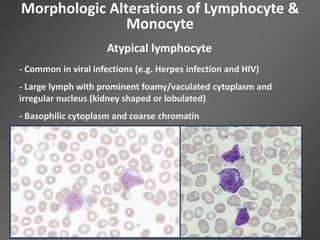
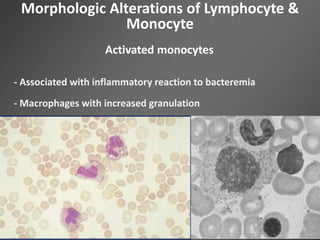
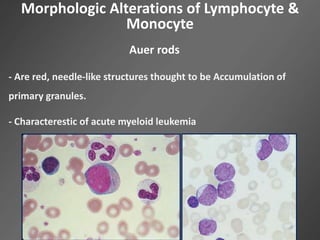
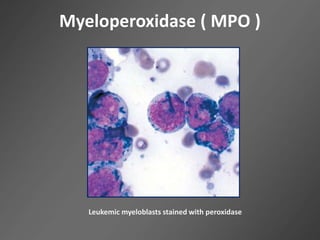
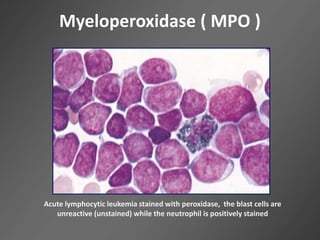
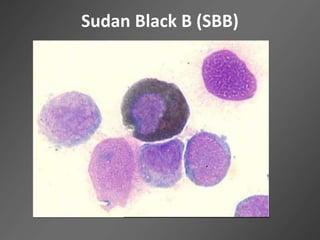
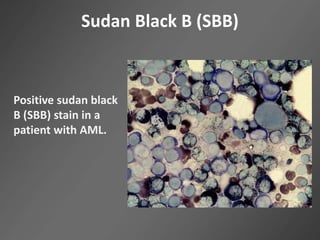
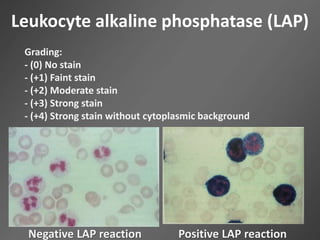
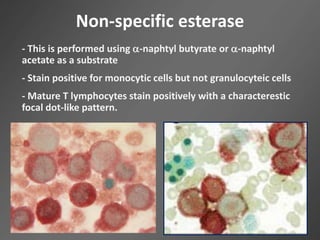
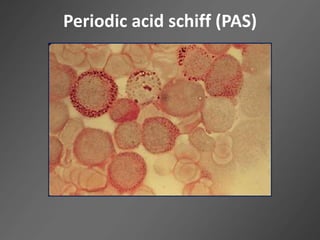
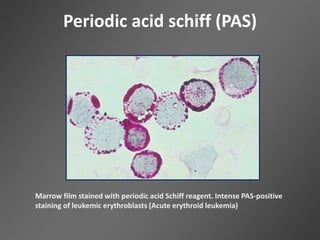
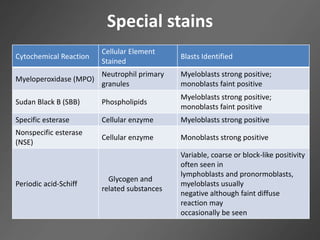
Leukocytes, or white blood cells, are divided into myelocytes and lymphocytes. Myelocytes include granulocytes like neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils, as well as monocytes. Lymphocytes include B and T lymphocytes. Leukopoiesis is the process by which these cells develop from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow. Morphological abnormalities that can occur include alterations in neutrophil nuclei like the Pelger-Huet anomaly and cytoplasmic changes such as May-Hegglin anomaly. Lymphocytes and monocytes can also demonstrate abnormal morphologies like Reed-Sternberg cells.