1. Prussian blue staining is used to identify iron stores in bone marrow samples. It detects ferric iron by forming an insoluble blue compound called Prussian blue when iron reacts with potassium ferrocyanide and hydrochloric acid.
2. Iron is primarily stored in the body bound to the protein ferritin or aggregated as hemosiderin. Prussian blue staining results in hemosiderin appearing blue while nuclei counterstain red.
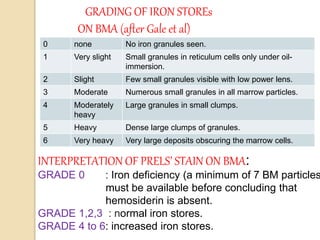
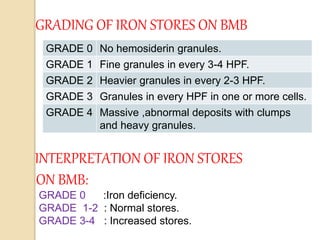
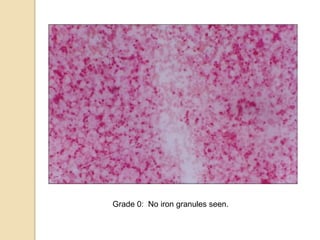
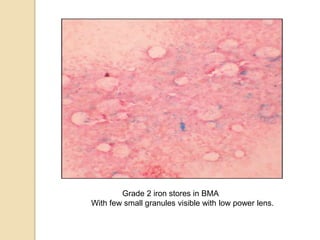
3. The amount of iron stores visualized on bone marrow samples using Prussian blue staining is graded from 0-6, with higher grades indicating increased iron levels and potential iron overload.