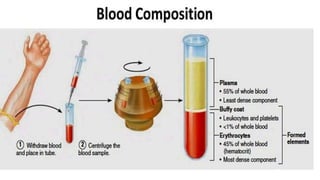
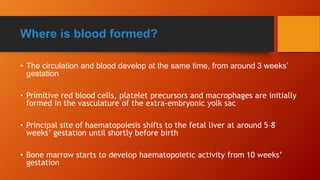
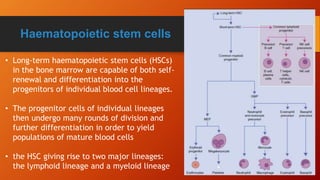
Lymphocytes are mononuclear white blood cells that participate in immunity. They develop from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow and mature in the bone marrow or thymus. There are three main types of lymphocytes - B cells, T cells, and null cells. B cells produce antibodies and mediate humoral immunity. T cells have cell-mediated functions including killing infected and cancer cells. An increased lymphocyte count is called lymphocytosis and can be caused by infections, while a decreased count is lymphopenia which can result from HIV, chemotherapy or steroids.