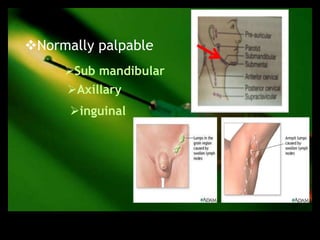
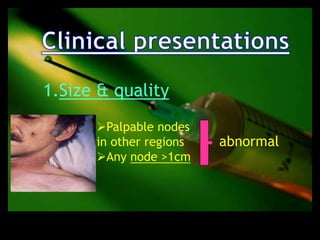
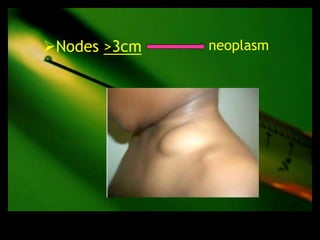
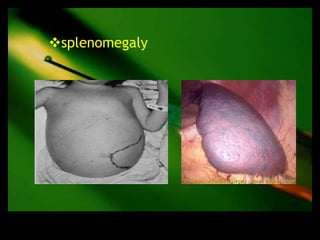
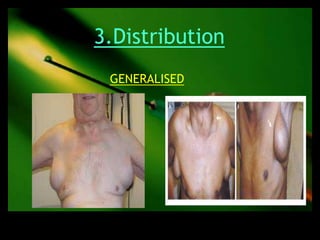
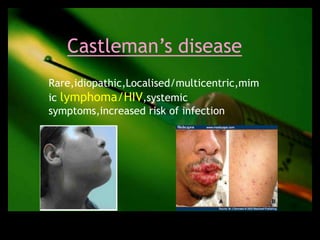
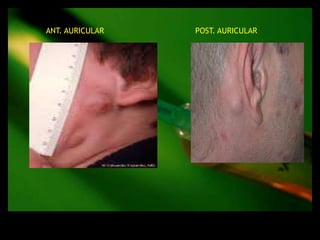
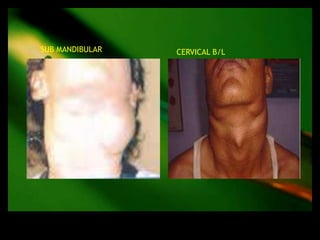
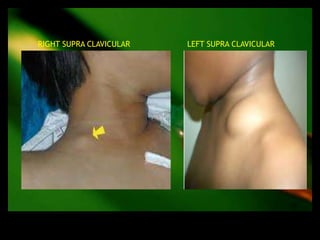
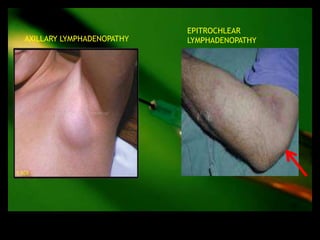
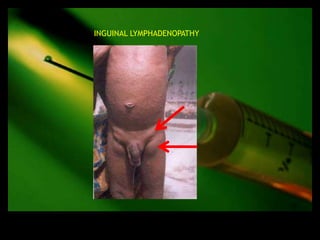
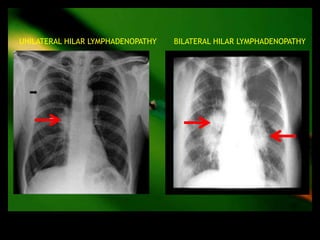
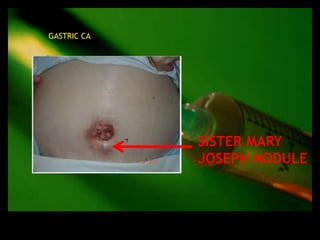
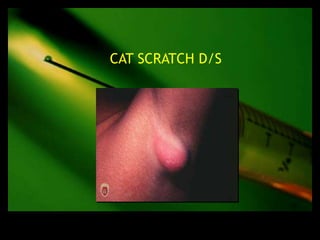
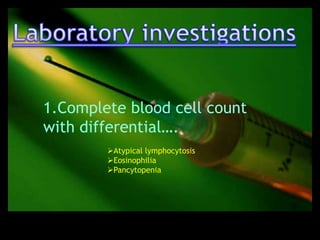
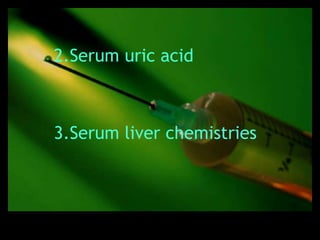
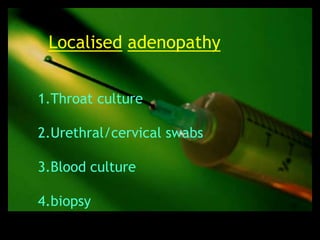
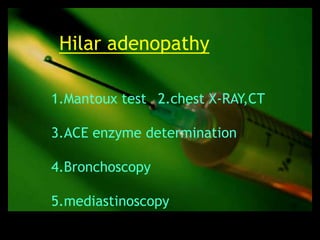
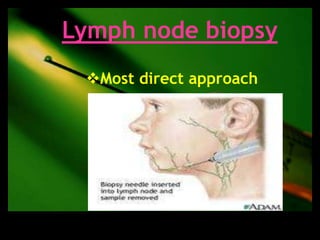
This document discusses the evaluation of lymphadenopathy. It outlines the key steps in evaluation which include determining the size and characteristics of palpable lymph nodes, identifying accompanying symptoms, examining the distribution of enlarged lymph nodes, and considering epidemiological factors. A variety of diagnostic tests are described based on the location and suspected causes of lymphadenopathy including blood tests, imaging studies, biopsies and cultures. The goal of evaluation is to arrive at an accurate diagnosis and guide further treatment.